MAX32665-MAX32668 User Guide
Maxim Integrated Page 430 of 457
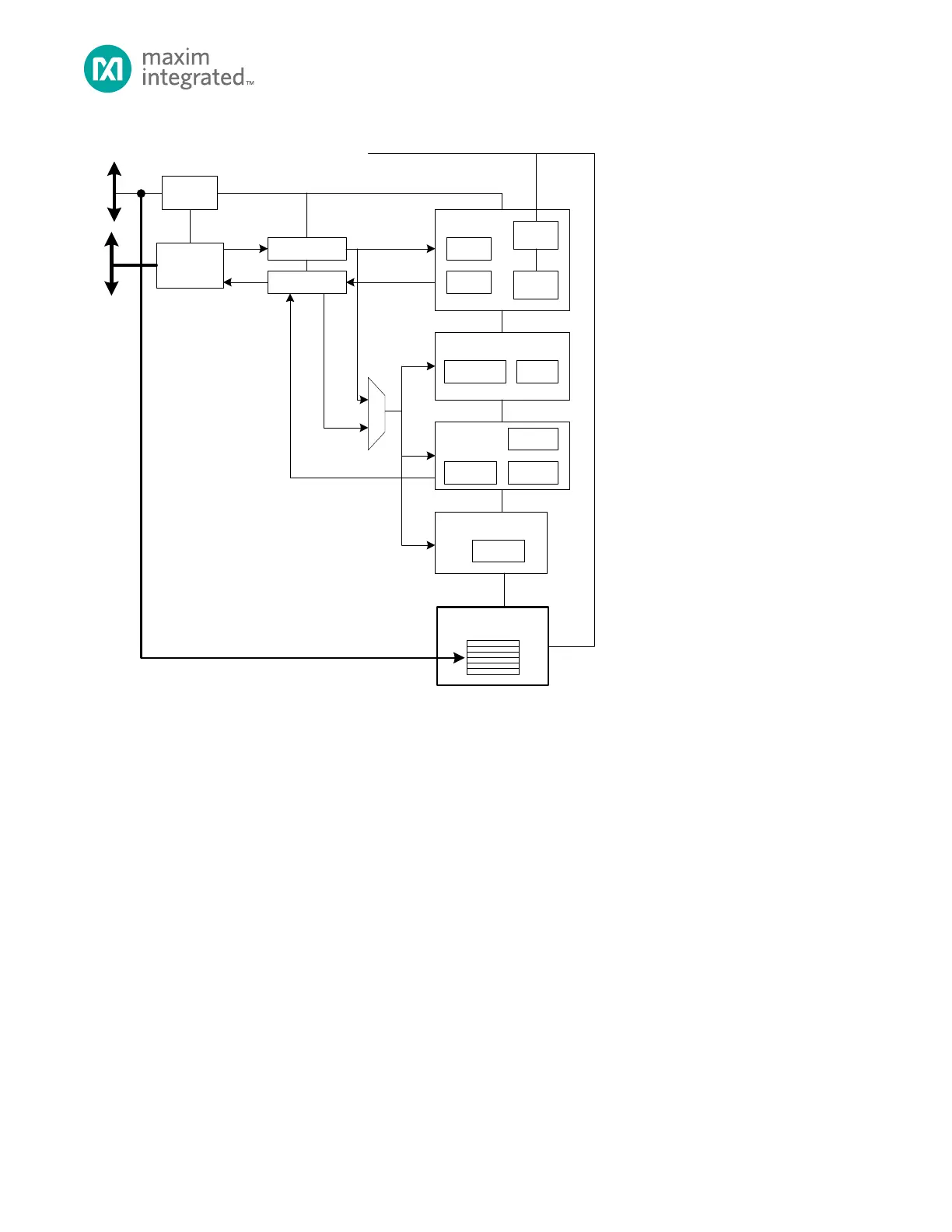
Figure 23-1. Cryptographic Accelerator Block Diagram
23.1 Dedicated Cryptographic DMA Engine (CDMA)
A dedicated DMA engine performs high-speed accesses between the TPU and memory on the AHB bus. This greatly
improves performance during data-intensive operations such as encryption/decryption and hashing. The source,
destination, and count registers are located in the cryptographic accelerator register space. The source and destination of
the DMA engine can point to the same memory location to encrypt or decrypt the data in situ.
While the cryptographic accelerator is busy encrypting or hashing data, the DMA prefetches the data for the next operation
and stores it in the read FIFO. Once the cipher or hash generator is done, the data for the next operation is immediately
available. Data output is buffered in the write FIFO so the next cipher or hash operation can immediately begin calculating
on the next block. This keeps the cipher and hash generator running continuously without having to wait for data to be
written to or read from the bus.
The block cipher can operate in parallel with the hash accelerator as long as only one operation uses the DMA.
 Loading...
Loading...