Chapter 8
Layer 2
RUGGEDCOM ROX II
CLI User Guide
294 GMRP (GARP Multicast Registration Protocol)
Example: Establishing Membership with GMRP
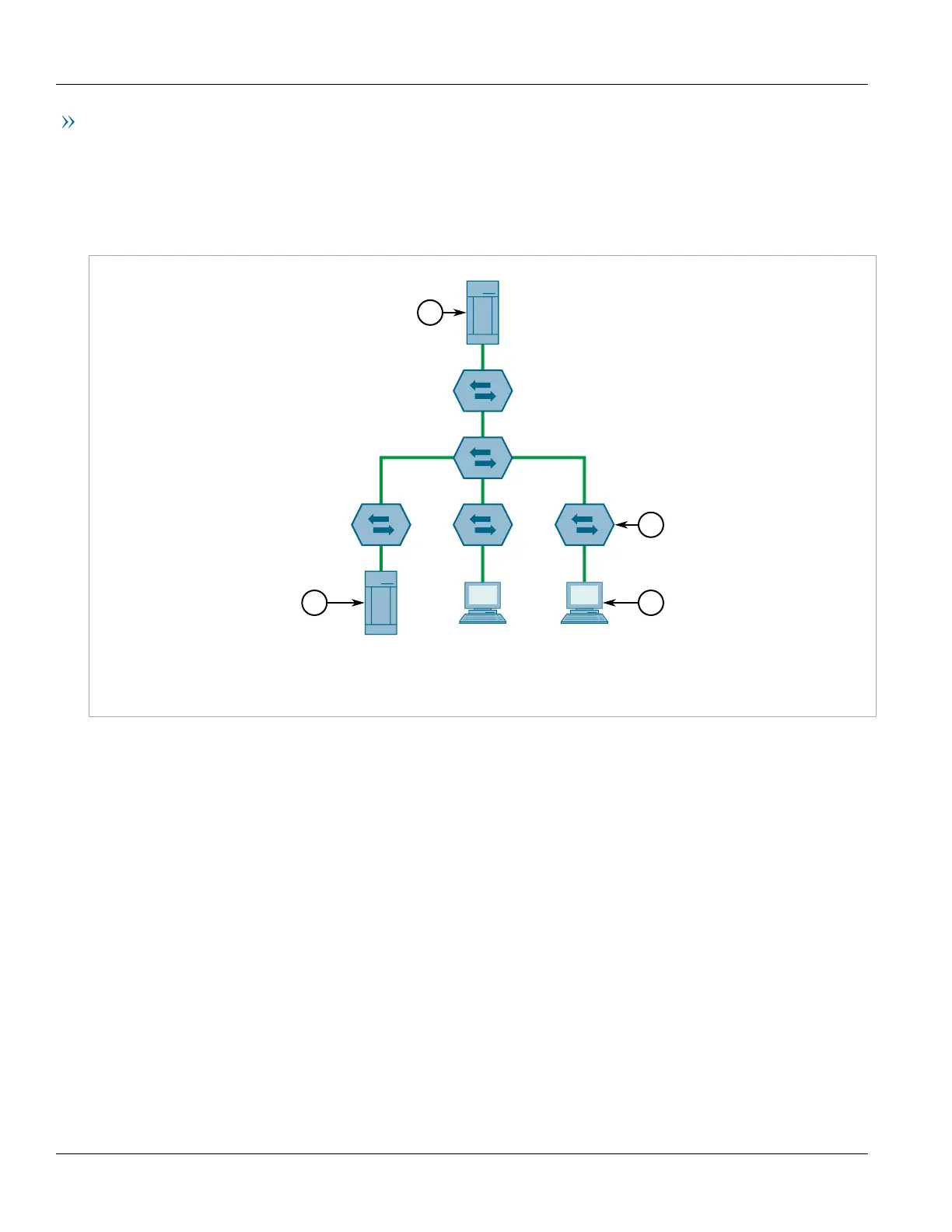
The following example illustrates how a network of hosts and switches can dynamically join two multicast groups
using GMRP.
In this scenario, there are two multicast sources, S1 and S2, multicasting to Multicast Groups 1 and 2, respectively.
A network of five switches, including one core switch (B), connects the sources to two hosts, H1 and H2, which
receive the multicast streams from S1 and S2, respectively.
S1
A
H2H1
S2
CE
B
D
D2
B3
D1
B1
B2
B4
E1
E2
C1
C2
A1
A2
Figure8:Example – Establishing Membership with GMRP
1.Multicast Source 2.Switch 3.Multicast Host
The hosts and switches establish membership with the Multicast Group 1 and 2 as follows:
1. Host H1 is GMRP unaware, but needs to see traffic for Multicast Group 1. Therefore, Port E2 on Switch E is
statically configured to forward traffic for Multicast Group 1.
2. Switch E advertises membership in Multicast Group 1 to the network through Port E1, making Port B4 on
Switch B a member of Multicast Group 1.
3. Switch B propagates the join message, causing Ports A1, C1 and D1 to become members of Multicast Group 1.
4. Host H2 is GMRP-aware and sends a join request for Multicast Group 2 to Port C2, which thereby becomes a
member of Multicast Group 2.
5. Switch C propagates the join message, causing Ports A1, B2, D1 and E1 to become members of Multicast
Group 2.
Once GMRP-based registration has propagated through the network, multicast traffic from S1 and S2 can reach its
destination as follows:
• Source S1 transmits multicast traffic to Port D2 which is forwarded via Port D1, which has previously become a
member of Multicast Group 1.
• Switch B forwards the Group 1 multicast via Port B4 towards Switch E.
• Switch E forwards the Group 1 multicast via Port E2, which has been statically configured for membership in
Multicast Group 1.

 Loading...
Loading...











