RUGGEDCOM ROX II
CLI User Guide
Chapter 13
Unicast and Multicast Routing
Example: Route Reflection in a VRF Instance 513
remote-as 100
route-reflector-client enabled
!
!
Section13.8.11.7
Example: Route Reflection in a VRF Instance
This example demonstrates how to configure BGP route reflection in a VRF instance.
Overview
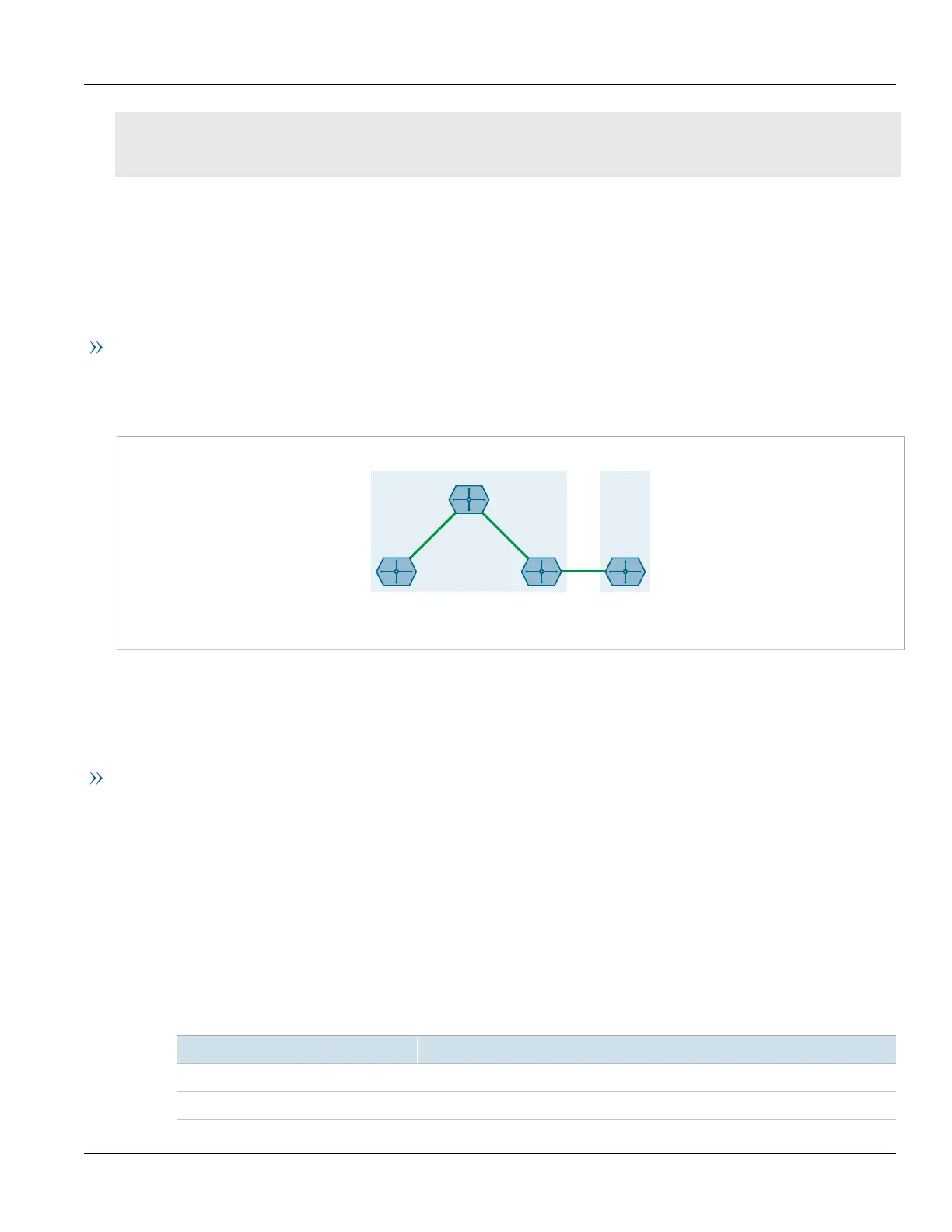
In the following topology, router RR is a BGP route reflector configured with a VRF instance (VRF1). The VRF
instance is configured with a single IPv4 address family consisting of routers R2 and R3. All three routers belong to
the same autonomous system (AS1).
Figure32:Route Reflection in a VRF Instance
RR receives BGP routing information from R2 via its VRF interface, 1.1.2.1. It then readvertises the information to
its client, R1.
R2 receives BGP routing information from R3, an external BGP (eBGP) router.
Configuration
To configure this topology, do the following:
1. Configure RR
a. Configure a VRF definition for VRF1 with a route distinguisher of 100:1. For more information, refer to
Section13.11.5.2, “Adding a VRF Definition”.
b. Define a route target for VRF1 of type both with the export community set to 100:1. For more
information, refer to Section13.11.6.2, “Adding a Route Target”.
c. Make sure interfaces are configured with the IP addresses 1.1.12/24 and 1.1.2.1/24.
d. Assign the interfaces in Step 1.c to forward traffic to VRF1. For more information, refer to
Section13.11.4, “Configuring a VRF Interface”.
e. Enable BGP and configure the following parameters:
Parameter Value
Autonomous System ID 100
Router ID 5.5.5.5

 Loading...
Loading...











