Chapter 13
Unicast and Multicast Routing
RUGGEDCOM ROX II
CLI User Guide
444 Viewing the Status of Neighbors
4. Configure one or more interfaces on which to perform IS-IS routing. For more information, refer to
Section13.6.6, “Managing Interfaces”.
5. Type commit and press Enter to save the changes, or type revert and press Enter to abort.
Example
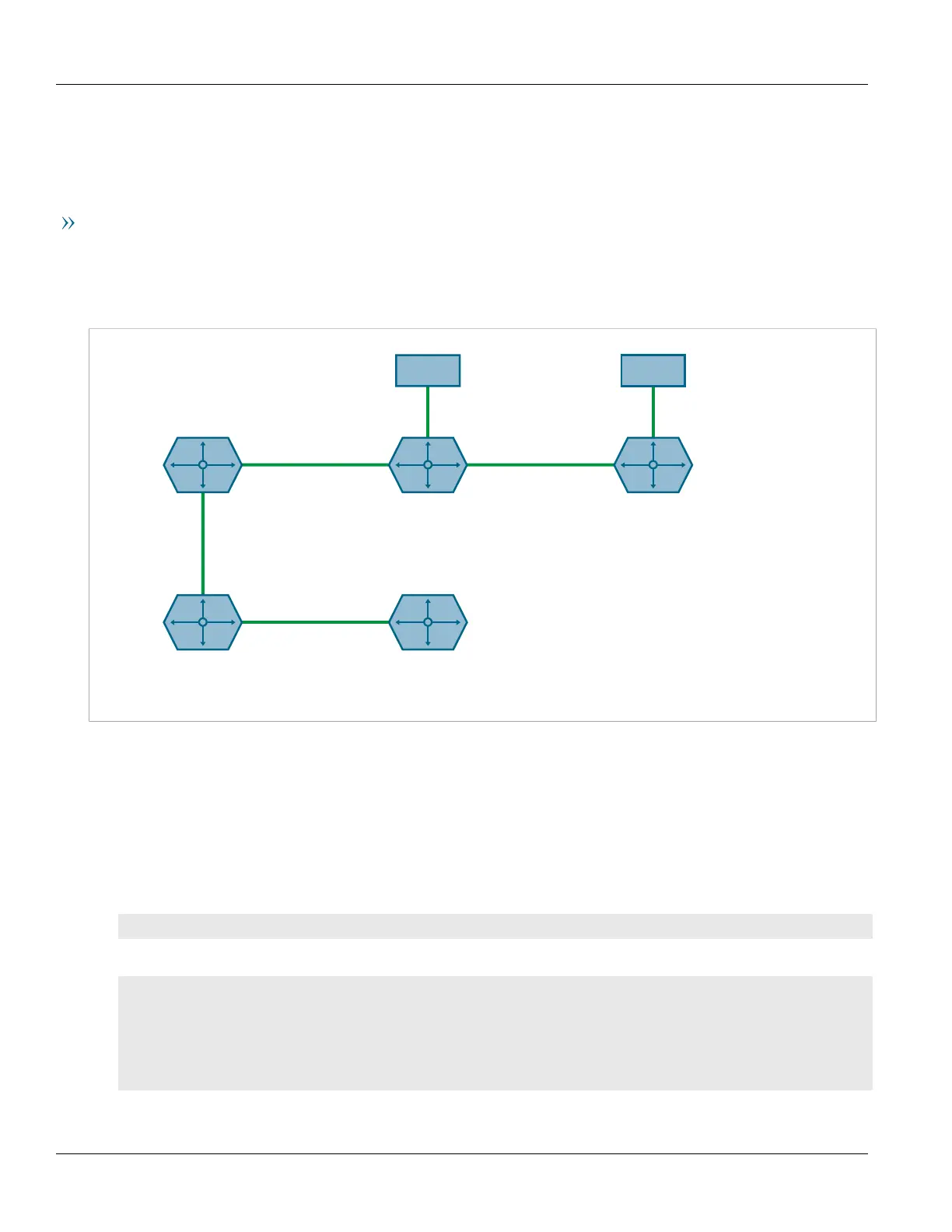
The following illustrates how to configure an IS-IS network that includes all circuit types. In this example, R1 is a
Level-1 router that needs to forward traffic to Level-2 routers. R2 and R3 are configured to be Level-1-2 routers to
facilitate the connection with routers R4 and R5, which are Level-2-only routers. Each router is configured to have
a non-passive interface, use point-to-point network communication, and be in the same area.
192.168.12.0/24 192.168.11.0/24
R4 16.16.16.16 R5 15.15.15.15
R3 18.18.18.18
R1 78.78.78.78 R2 72.72.72.72
eth1
.3
1.3.5.0/32
.3 .2
1.2.6.0/32
.2
eth1 eth1
.1
eth2
.1
eth2
1.9.5.0/32
.2
.2
.3
1.4.5.0/32
.2
Figure22:Multi-Level IS-IS Configuration
Section13.6.3
Viewing the Status of Neighbors
To view the status of neighboring devices on an IS-IS network, do the following:
1. Make sure IS-IS is configured. For more information, refer to Section13.6.2, “Configuring IS-IS”.
2. View the status by typing:
routing status isis isis-neighbors-status
If IS-IS routes have been configured, a table similar to the following example appears:
ruggedcom# routing status isis isis-neighbors-status
isis-neighbors-status
Area area1:
System Id Interface L State Holdtime SNPA
Spirent- switch.0012 3 Up 24 2020.2020.2020
This table displays the following information:
 Loading...
Loading...











