Chapter 13
Unicast and Multicast Routing
RUGGEDCOM ROX II
CLI User Guide
562 Deleting a VRF Definition
Where:
• name is the name for definition. The name must be unique and not exceed 32 characters or contain spaces.
The first character must also not be a special character. Only the following special characters are permitted
in the remainder of the name: hyphen (-), underscore (_), colon (:), and period (.).
3. Configure the following parameter(s) as required:
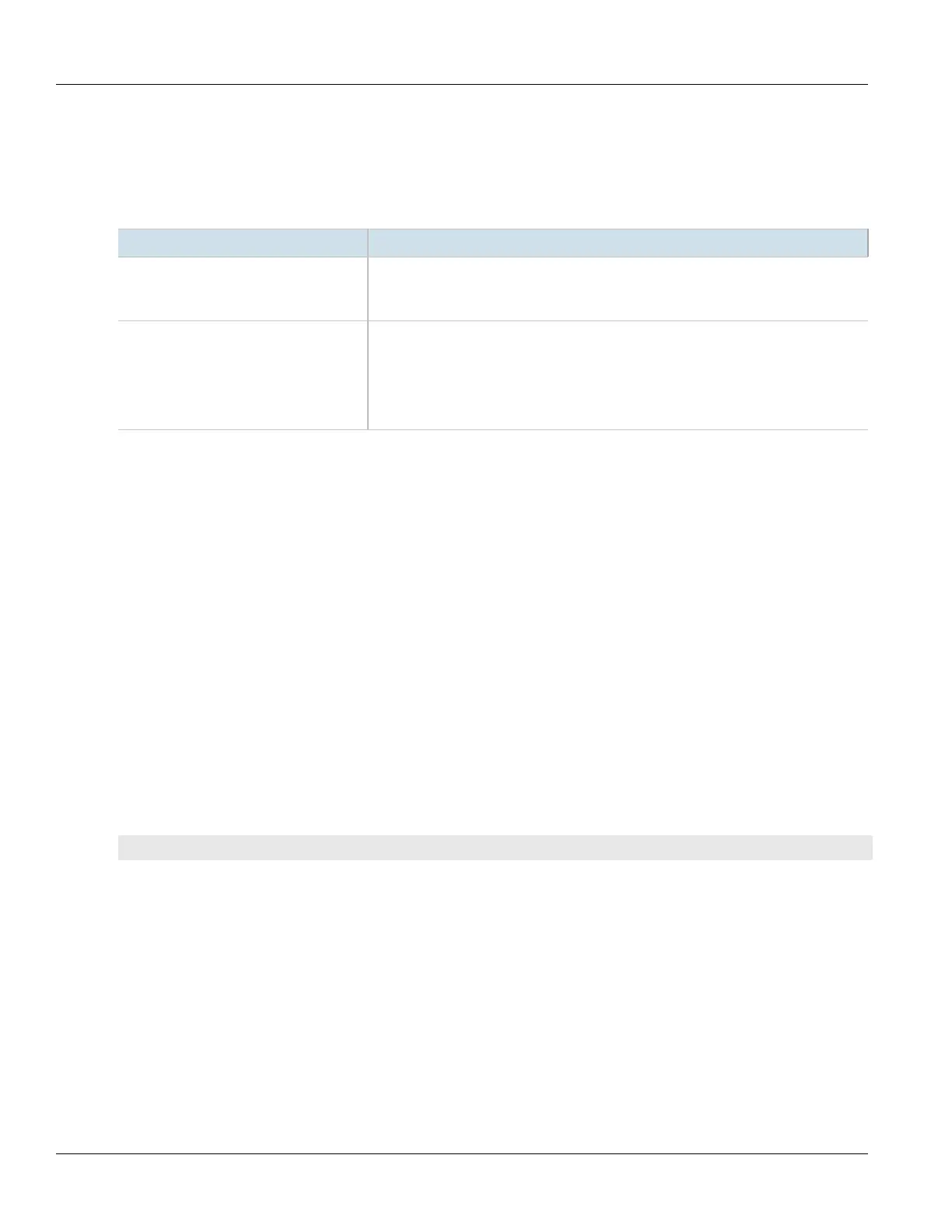
Parameter Description
vrf-description { vrf-description } Synopsis: A string 0 to 256 characters long
A string that can be used to describe the vrf. Maximum length 256 characters, including
blanks.
rd { rd } Synopsis: A string 0 to 32 characters long
The VRF's route distinguisher: 8-byte value, typical format is (as-number:id | ip-
address:id) (e.g. 6500:20). It will be prepended to the IPv4 prefix to create the VPN
IPv4 prefix. Note that changing the route distinguisher will affect the route targets: it is
recommended that you verify that the configured route targets used in your network will
still be correct.
4. Add one or more route targets. For more information, refer to Section13.11.6.2, “Adding a Route Target”.
5. Configure a routable interface for the VRF instance. For more information, refer to Section13.11.4,
“Configuring a VRF Interface”.
6. Type commit and press Enter to save the changes, or type revert and press Enter to abort.
Section13.11.5.3
Deleting a VRF Definition
To delete a VRF definition, do the following:
1. Make sure the CLI is in Configuration mode.
2. Set vrf-forwarding for the associated routable interface to another VRF definition or none at all.
3. Delete the associated VRF instance under OSPF. For more information, refer to Section13.11.7.3, “Deleting a
VRF Instance”.
4. Delete the associated IPv4 address family under BGP. For more information, refer to Section13.11.10.3,
“Deleting an IPv4 Address Family”.
5. Delete the definition key by typing:
no routing vrf definition name
Where:
• name is the name of the definition
6. Type commit and press Enter to save the changes, or type revert and press Enter to abort.
Section13.11.6
Managing Route Targets
Route targets identify those routes to import/export within the Multi-Protocol BGP (MBGP) network. Similar to
the normal global routing instance, the route target sets the route import and export parameters for BGP. This

 Loading...
Loading...











