RUGGEDCOM ROX II
CLI User Guide
Chapter 13
Unicast and Multicast Routing
Understanding Route Reflectors 503
• Section13.8.11.6, “Example: Clusters in Clusters”
• Section13.8.11.7, “Example: Route Reflection in a VRF Instance”
• Section13.8.11.8, “Example: Route Reflection with VPNv4 Clients”
Section13.8.11.1
Understanding Route Reflectors
Route reflectors offer a method for simplifying BGP network topologies and improving scalability.
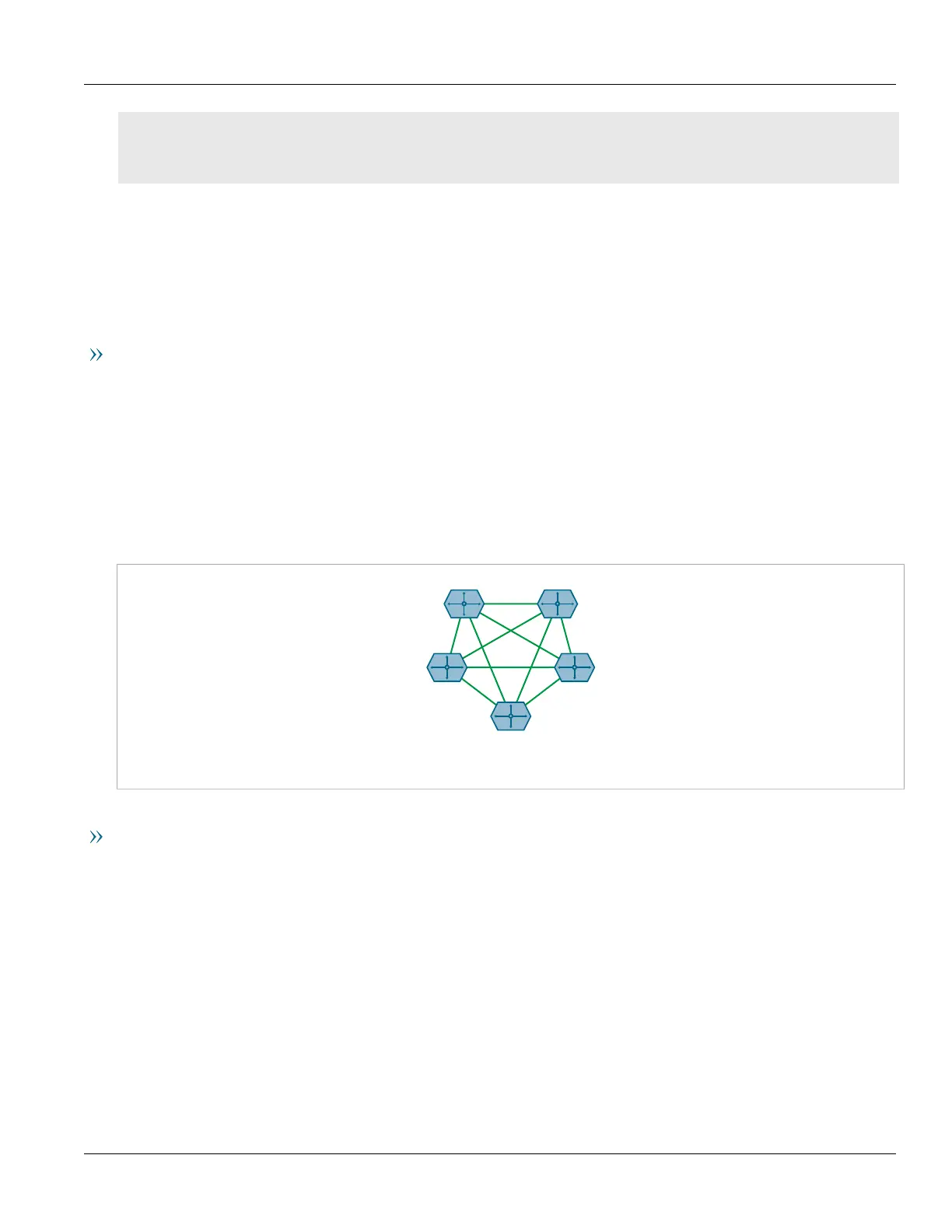
The Full-Mesh Requirement
Due to BGP route advertisement rules, BGP requires a logical full-mesh topology, wherein each router advertises
and forwards its routes to each of its neighbors. This requirement is easily met by external BGP (eBGP) networks,
where connections are established between Autonomous Systems (AS). Routers can easily avoid loops by
dropping any routes that share the same AS numeric identifier. However, in internal BGP (iBGP), each router
shares the same AS numeric identifier, so all routes received by a router would be dropped.
One method for solving this problem is to have each iBGP router establish neighborship with its peers, but that
would result in a significant number of BGP sessions and unnecessary traffic on large networks. The formula for
determining the number of BGP sessions for X number of routers is X*(X-1)/2. Therefore, 20 iBGP routers would
generate 190 BGP sessions (20*[20-1]/2 = 190).
Figure23:A Simple BGP Topology Without a Route Reflector
The Route Reflector Solution
Route reflectors simplify the topology by grouping routers into a cluster. In the cluster, the route reflector
establishes a BGP session with each client (BGP neighbor). The clients are not required to establish BGP sessions
with each other, nor are they required to be fully-meshed. All routes are advertised to the route reflector, who in
turn re-advertises the routes to its clients, thus meeting the logical full-mesh requirement.

 Loading...
Loading...











