RUGGEDCOM ROX II
CLI User Guide
Chapter 12
Tunneling and VPNs
Configuring Dead Peer Detection 413
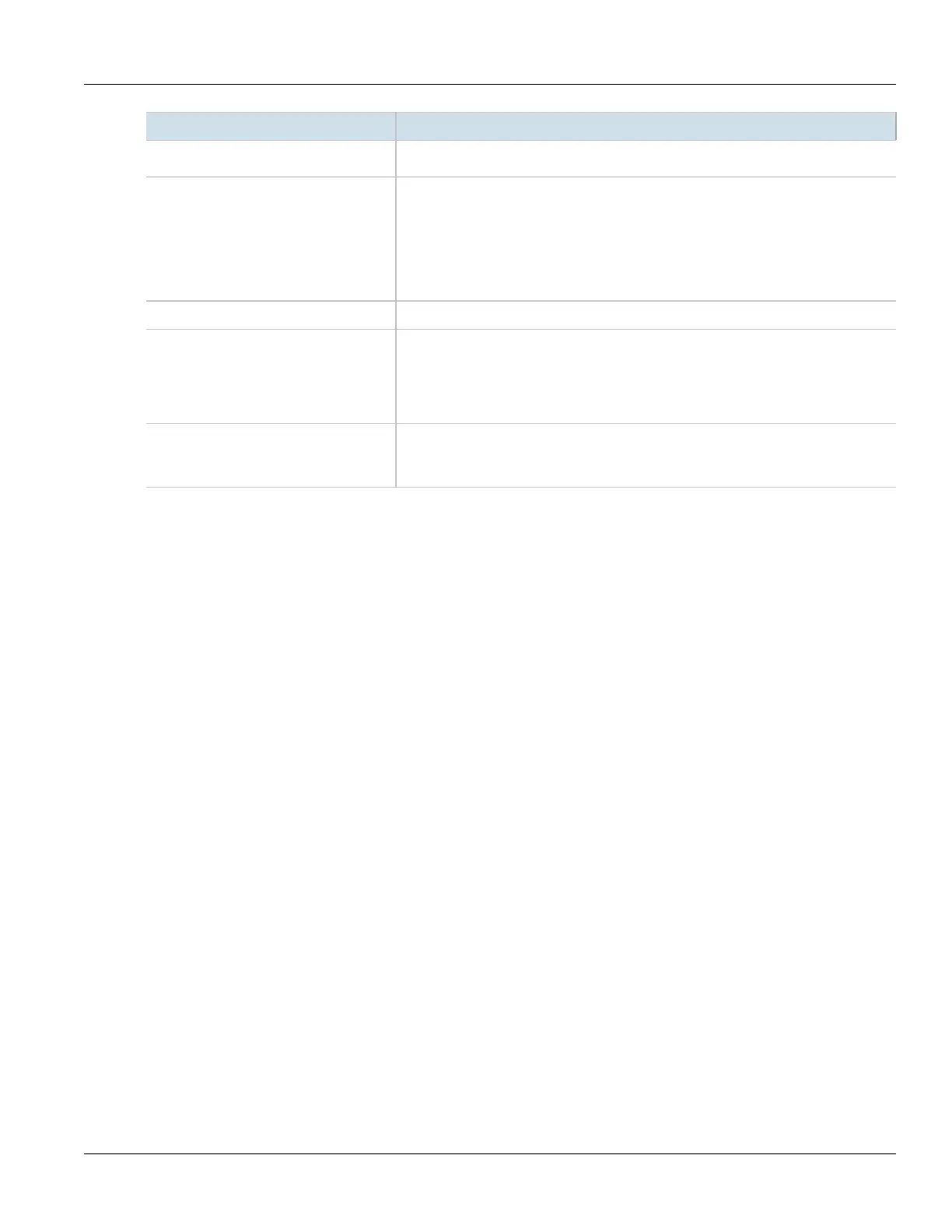
Parameter Description
intervals. However, if peers do not agree, an excess of superseded connections will occur
on the peer that believes the SA lifetime is longer.
ike-lifetime { ike-lifetime } Synopsis: { default } or a 32-bit unsigned integer between 60 and 86400
Default: default
The lifetime in seconds for for the IKE protocol. This determines how long the IKE keying
channel of a connection should last before being renegotiated. The default value is 3600
unless overwritten by the default connection setting. Peers can specify different lifetime
intervals. However, if peers do not agree, an excess of superseded connections will occur
on the peer that believes the IKE lifetime is longer.
l2tp Enables/disables L2TP for this connection.
connection-alarms Synopsis: { true, false }
Default: false
Enables or disables connection up and down alarms. Disabling connection alarms will
prevent alarms from being sent for that connection. Connection alarms may also be
controlled for the whole system under admin > alarm-cfg.
monitor-interface { monitor-interface } Synopsis: A string
The interface to monitor. If the selected interface goes down and then up, this
connection will be restarted.
4. If required, enable and configure dead peer detection. For more information, refer to Section12.8.6.3,
“Configuring Dead Peer Detection”.
5. If required, configure the Internet Key Exchange (IKE) protocol by adding one or more algorithms. For more
information, refer to Section12.8.7.2, “Adding an IKE Algorithm”.
6. If required, configure Encapsulated Security Payload (ESP) encryption for the connection. For more
information, refer to Section12.8.8, “Managing the Encapsulated Security Payload (ESP) Protocol”.
7. If required, configure the left (local router) and right (remote router) ends of the connection. For more
information, refer to Section12.8.9, “Configuring the Connection Ends”.
8. If required, configure L2TP tunnels. For more information, refer to Section12.3.1, “Configuring L2TP
Tunnels”.
9. If certificates and keys are required, make sure they are configured on the device. For more information, refer
to Section12.8.3, “Configuring Certificates and Keys”.
10. Type commit and press Enter to save the changes, or type revert and press Enter to abort.
Section12.8.6.3
Configuring Dead Peer Detection
Dead Peer Detection (DPD), as defined in RFC 3706 [http://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc3706] is used to detect dead
Internet Key Exchange (IKE) peers. In this method, peers exchange DPD Request (ISAKMP R-U-THERE) and DPD
Response (ISAKMP R-U-THERE-ACK) messages. If a DPD Response is not received by a peer after a specified time
and/or number of attempts, the other peer is considered dead. The remaining peer can either hold the connection
until other peer responds, clear the connection, restart the connection and renegotiate the Security Association
(SA), or restart all SA's to the dead peer.
In RUGGEDCOM ROX II, DPD Requests are sent when there is no traffic detected by the peer. How long to wait
before sending a DPD Request and how long to wait for a DPD Response is user configurable.
It is generally recommended that DPD be configured to clear connections with any dead peers.
To configure dead peer detection for an IPsec connection, do the following:
 Loading...
Loading...











