22.3.17 Interrupt Request Register (DMA_INT)
The INT register provides a bit map for the 16 channels signaling the presence of an
interrupt request for each channel. Depending on the appropriate bit setting in the
transfer-control descriptors, the eDMA engine generates an interrupt on data transfer
completion. The outputs of this register are directly routed to the interrupt controller.
During the interrupt-service routine associated with any given channel, it is the
software’s responsibility to clear the appropriate bit, negating the interrupt request.
Typically, a write to the CINT register in the interrupt service routine is used for this
purpose.
The state of any given channel’s interrupt request is directly affected by writes to this
register; it is also affected by writes to the CINT register. On writes to INT, a 1 in any bit
position clears the corresponding channel’s interrupt request. A zero in any bit position
has no affect on the corresponding channel’s current interrupt status. The CINT register is
provided so the interrupt request for a single channel can easily be cleared without the
need to perform a read-modify-write sequence to the INT register.
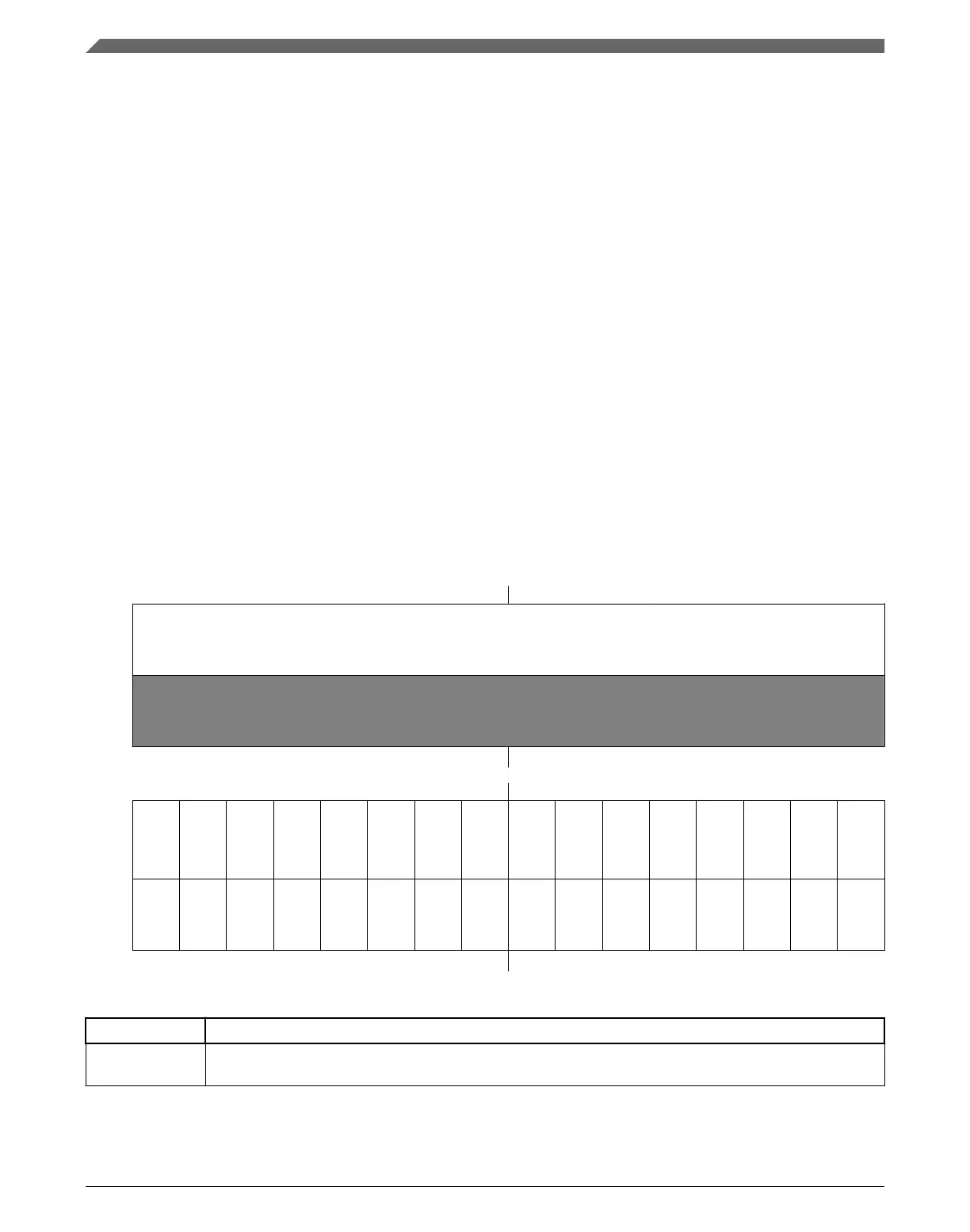
Address:
4000_8000h base + 24h offset = 4000_8024h
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
R
0
W
Reset
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Bit
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
R
INT15
INT14
INT13
INT12
INT11
INT10
INT9
INT8
INT7
INT6
INT5
INT4
INT3
INT2
INT1
INT0
W
w1c w1c w1c w1c w1c w1c
w1c w1c w1c w1c w1c w1c w1c w1c w1c w1c
Reset
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
DMA_INT field descriptions
Field Description
31–16
Reserved
This field is reserved.
This read-only field is reserved and always has the value 0.
Table continues on the next page...
Memory map/register definition
K22F Sub-Family Reference Manual, Rev. 4, 08/2016
458 NXP Semiconductors
 Loading...
Loading...