1
eDMA Engine
Data Path
eDMA
0
Program Model/
64
Control
n-1
To/From Crossbar Switch
2
Channel Arbitration
Address Path
Read Data
Write Data
Address
Read Data
Write Data
Write Address
eDMA Peripheral
Request
eDMA Done
Transfer
Control
Descriptor (TCD)
Internal Peripheral Bus
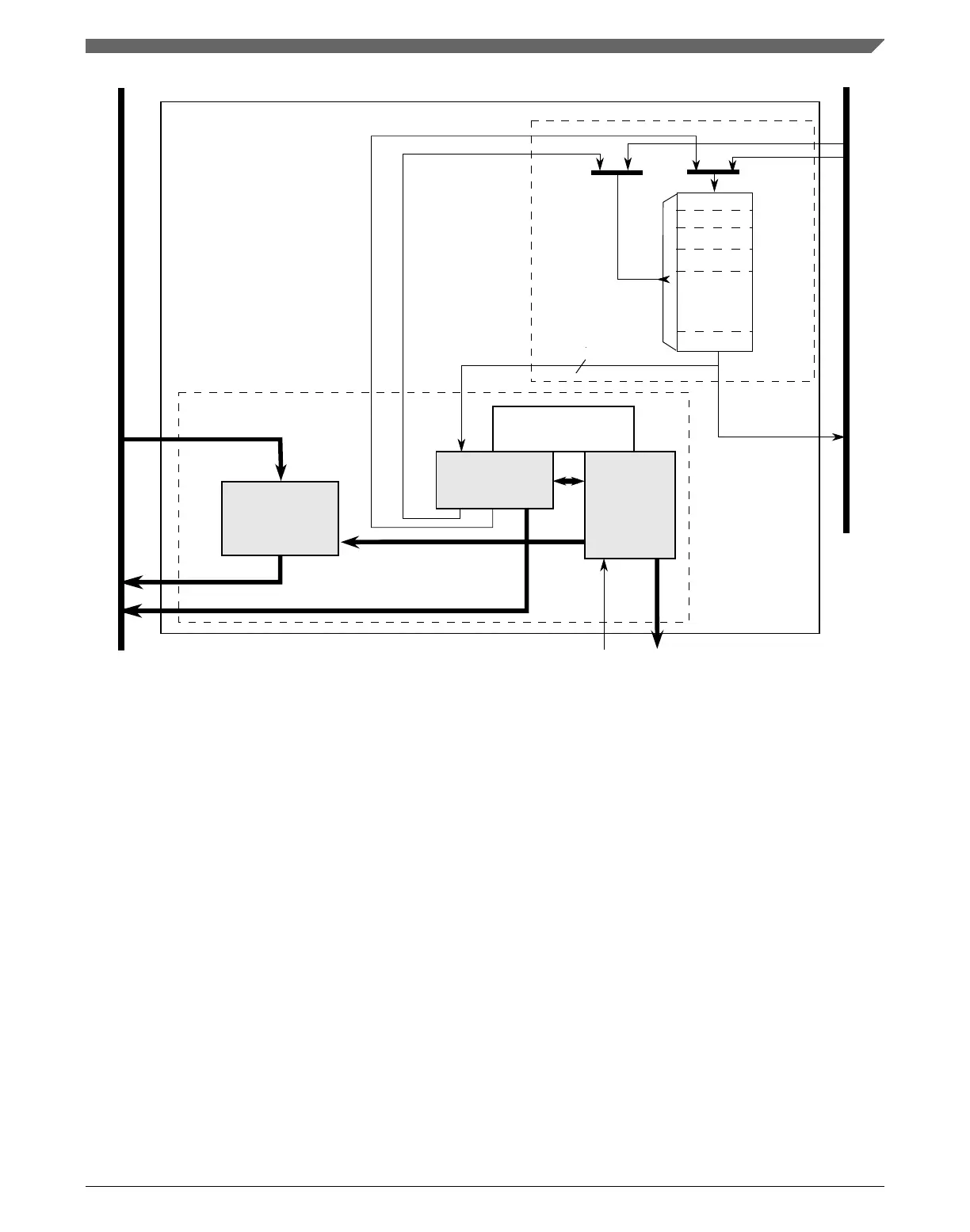
Figure 22-3. eDMA operation, part 2
The modules associated with the data transfer (address path, data path, and control)
sequence through the required source reads and destination writes to perform the actual
data movement. The source reads are initiated and the fetched data is temporarily stored
in the data path block until it is gated onto the internal bus during the destination write.
This source read/destination write processing continues until the minor byte count has
transferred.
After the minor byte count has moved, the final phase of the basic data flow is performed.
In this segment, the address path logic performs the required updates to certain fields in
the appropriate TCD, for example, SADDR, DADDR, CITER. If the major iteration
count is exhausted, additional operations are performed. These include the final address
adjustments and reloading of the BITER field into the CITER. Assertion of an optional
interrupt request also occurs at this time, as does a possible fetch of a new TCD from
memory using the scatter/gather address pointer included in the descriptor (if scatter/
gather is enabled). The updates to the TCD memory and the assertion of an interrupt
request are shown in the following diagram.
Chapter 22 Enhanced Direct Memory Access (eDMA)
K22F Sub-Family Reference Manual, Rev. 4, 08/2016
NXP Semiconductors 485
 Loading...
Loading...