UM10360 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP B.V. 2013. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 3 — 20 December 2013 764 of 841
NXP Semiconductors
UM10360
Chapter 34: Appendix: Cortex-M3 user guide
Remark: Writing 1 to an ICPR bit does not affect the active state of the corresponding
interrupt.
34.4.2.6 Interrupt Active Bit Registers
The IABR0-IABR3 registers indicate which interrupts are active. See:
• the register summary in Table 644 for the register attributes
• Table 645 for which interrupts are controlled by each register.
The bit assignments are shown in Table 650
.
A bit reads as one if the status of the corresponding interrupt is active or active and
pending.
34.4.2.7 Interrupt Priority Registers
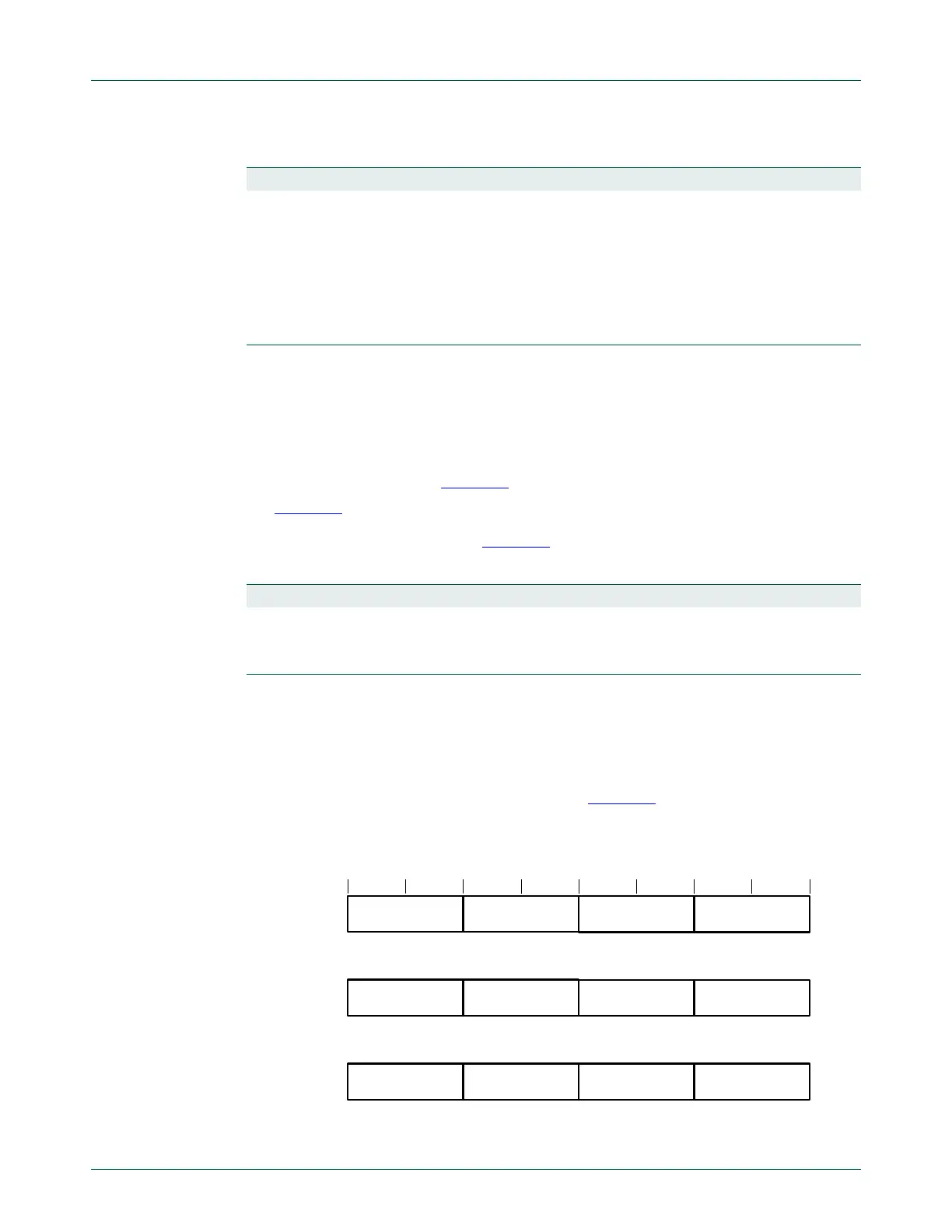
The IPR0-IPR27 registers provide a 5-bit priority field for each interrupt. These registers
are byte-accessible. See the register summary in Table 644
for their attributes. Each
register holds four priority fields, that map to four elements in the CMSIS interrupt priority
array
IP[0]
to
IP[111]
, as shown:
Table 649. ICPR bit assignments
Bits Name Function
[31:0] CLRPEND Interrupt clear-pending bits.
Write:
0 = no effect
1 = removes pending state an interrupt.
Read:
0 = interrupt is not pending
1 = interrupt is pending.
Table 650. IABR bit assignments
Bits Name Function
[31:0] ACTIVE Interrupt active flags:
0 = interrupt not active
1 = interrupt active.
IPR0
IPRm
IPR27
31 24 1623 15 780
.
.
.
IP[111] IP[109] IP[108]IP[110]
IP[4m+3] IP[4m+1] IP[4m]IP[4m+2]
IP[3] IP[1] IP[0]IP[2]
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
 Loading...
Loading...