3.5.1.1 Flash memory types
This device contains the following types of flash memory:
• Program flash memory — non-volatile flash memory that can execute program code
3.5.1.2 Flash Memory Sizes
The devices covered in this document contain:
• 2 blocks of program flash consisting of 2 KB sectors
The amounts of flash memory for the devices covered in this document are:
Device Program flash (KB) Block 0 address range Block 1 address range
MK22FN512VDC12 512 0x0000_0000–0x0003_FFFF 0x0004_0000–0x0007_FFFF
MK22FN512VLL12 512 0x0000_0000–0x0003_FFFF 0x0004_0000–0x0007_FFFF
MK22FN512VLH12 512 0x0000_0000–0x0003_FFFF 0x0004_0000–0x0007_FFFF
MK22FN512VMP12 512 0x0000_0000–0x0003_FFFF 0x0004_0000–0x0007_FFFF
MK22FN512CAP12R 512 0x0000_0000–0x0003_FFFF 0x0004_0000–0x0007_FFFF
MK22FN512CBP12R 512 0x0000_0000–0x0003_FFFF 0x0004_0000–0x0007_FFFF
MK22FN256CAP12R 256 0x0000_0000–0x0003_FFFF
MK22FN512VFX12 512 0x0000_0000–0x0003_FFFF 0x0004_0000–0x0007_FFFF
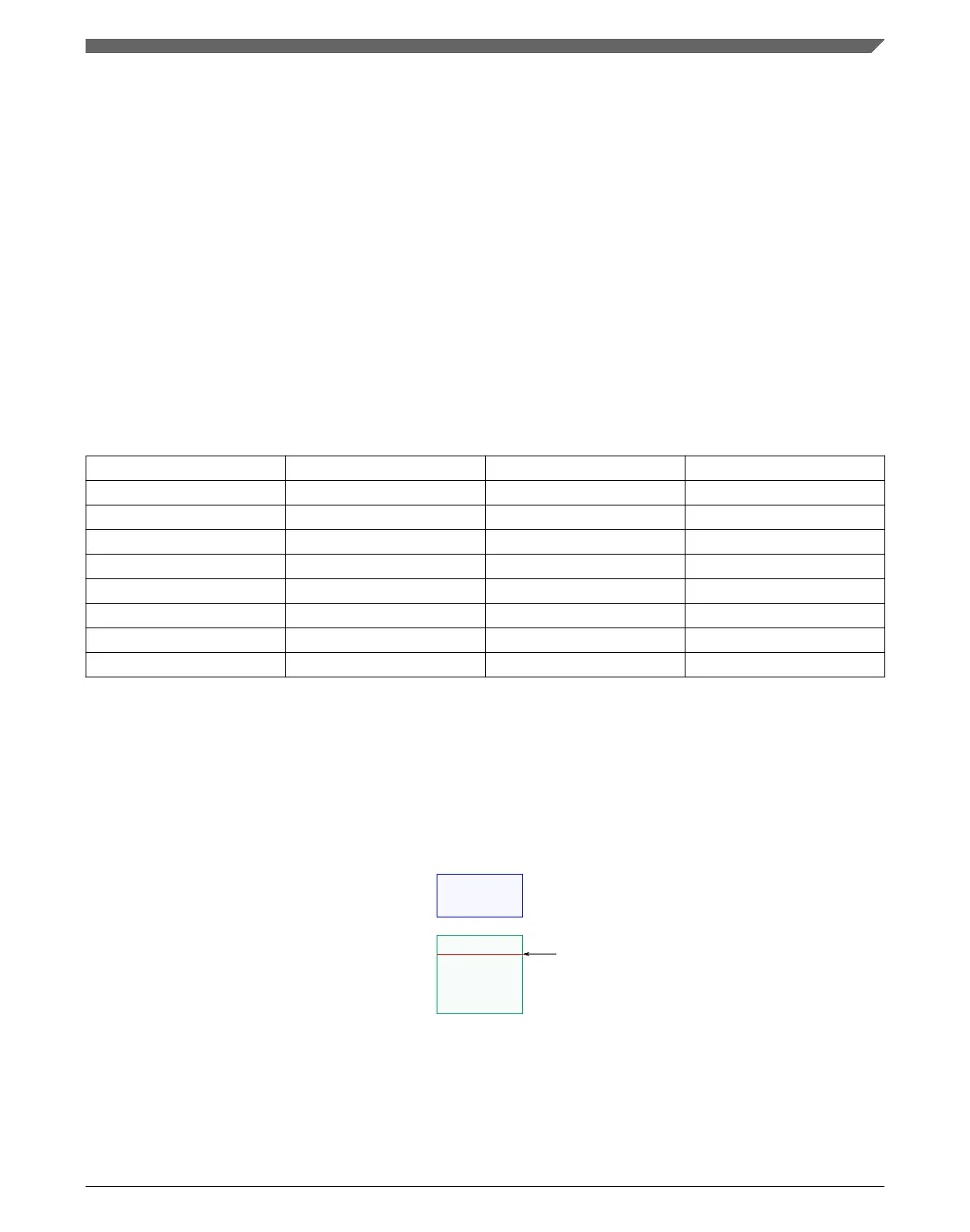
3.5.1.3 Flash Memory Map
The flash memory and the flash registers are located at different base addresses as shown
in the following figure. The base address for each is specified in System memory map.
Program flash
Flash configuration field
Program flash base address
Flash memory base address
Registers
Figure 3-20. Flash memory map
The on-chip Flash is implemented in a portion of the allocated Flash range to form a
contiguous block in the memory map beginning at address 0x0000_0000. See Flash
Memory Sizes for details of supported ranges.
Chapter 3 Chip Configuration
K22F Sub-Family Reference Manual, Rev. 4, 08/2016
NXP Semiconductors 85
 Loading...
Loading...