Random number generator (RNG) RM0351
710/1693 DocID024597 Rev 3
24 Random number generator (RNG)
24.1 Introduction
The RNG processor is a random number generator, based on a continuous analog noise,
that provides a random 32-bit value to the host when read.
The RNG passed the FIPS PUB 140-2 (2001 October 10) tests with a success ratio of 99%.
24.2 RNG main features
• It delivers 32-bit random numbers, produced by an analog generator
• 40 periods of the RNG_CLK clock signal between two consecutive random numbers
• Monitoring of the RNG entropy to flag abnormal behavior (generation of stable values,
or of a stable sequence of values)
• It can be disabled to reduce power consumption
24.3 RNG functional description
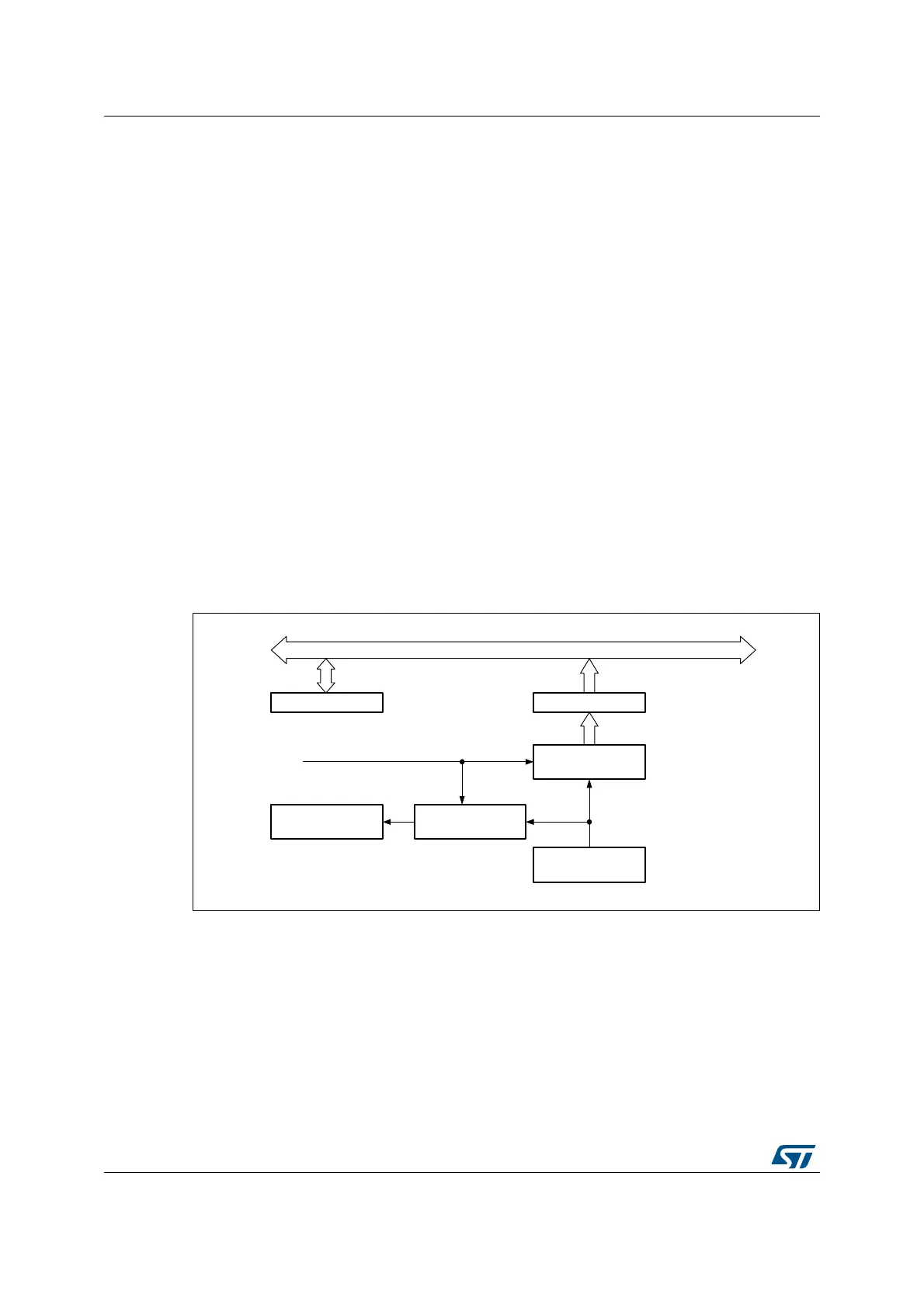
Figure 170 shows the RNG block diagram.
Figure 170. Block diagram
1. For more details about RNG Clock (RNG_CLK) source, please refer to Section 6: Reset and clock control
(RCC).
The random number generator implements an analog circuit. This circuit generates seeds
that feed a linear feedback shift register (RNG_LFSR) in order to produce 32-bit random
numbers.
The analog circuit is made of several ring oscillators whose outputs are XORed to generate
the seeds. The RNG_LFSR is clocked by a dedicated clock (RNG_CLK) at a constant
frequency, so that the quality of the random number is independent of the HCLK frequency.
The contents of the RNG_LFSR are transferred into the data register (RNG_DR) when a
significant number of seeds have been introduced into the RNG_LFSR.
DLE
$QDORJVHHG
ELW$+%EXV
51*B'5
$QDORJVHHG
/)65
)HHGDOLQHDUIHHGEDFN
VKLIWUHJLVWHU
'DWDUHJLVWHU
&ORFNFKHFNHUDQG
IDXOWGHWHFWRU
51*B65
6WDWXVUHJLVWHU
51*B&/.
51*B&5
&RQWUROUHJLVWHU
 Loading...
Loading...