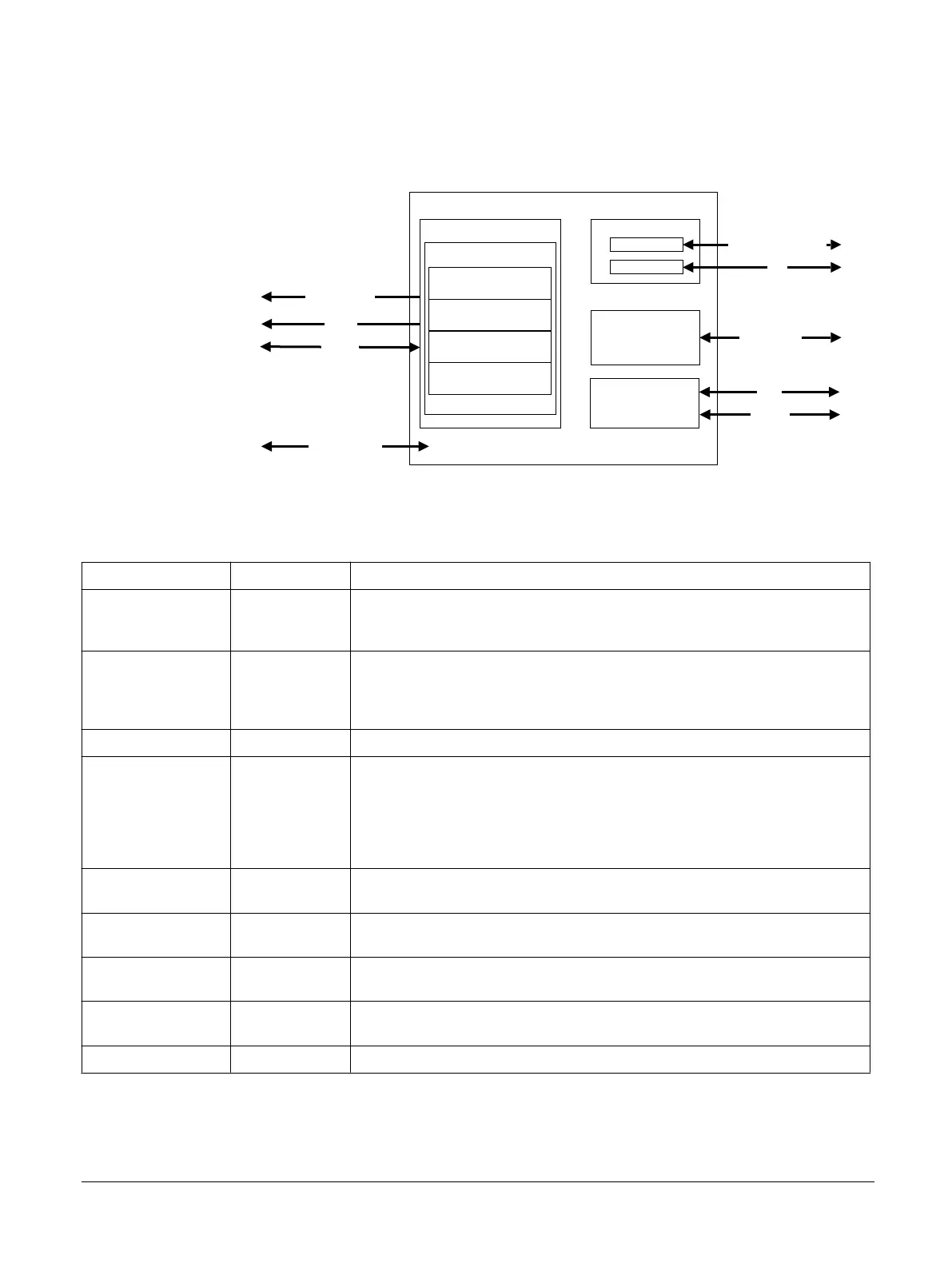
A2.2 Interfaces
The Cortex‑A35 processor has several interfaces to connect it to a SoC.
PMU events
Trace
AXI, ACE, or CHI
DFT
Q-Channel
MBIST
Debug
Processor
SCUCore
L2 cache*
Cross-trigger
AXI
ACP*
Trace
Power
management
Test
Optional*
Main logic
L1 cache
FPU/Neon*
Crypto*
ETM*
Figure A2-2 Interfaces
Table A2-1 Cortex-A35 interfaces
Purpose Technology Notes
PMU events Performance events provide useful information on the operation of the processor that
you can use for debug and code profiling. A subset of available performance events is
exported on the PMU event bus.
Trace ATB
Optional
Outputs trace information for debugging. The ATB interface is compatible with the
CoreSight architecture.
Memory AXI, ACE, or CHI ACE can also be used with AXI peripherals.
ACP AXI
Optional
This slave interface reduces software cache maintenance operations when the cores
share memory regions with other masters and allows other masters to allocate data into
the L2 cache. It allows an external master to make coherent requests to shared memory,
but it does not support cache maintenance, coherency, barrier, or DVM transactions.
Debug APB Allows access to debug registers and resources, for example, to set watchpoints and
breakpoints.
Cross-trigger CTI This external interface is connected to the CoreSight CTI corresponding to each core
through a simplified CTM.
Design for Test (DFT) Allows an industry standard Automatic Test Pattern Generation (ATPG) tool to test
logic.
Memory Built-In Self
Test (MBIST)
Provides support for manufacturing test of the memories embedded in the Cortex‑A35
processor.
Power management Q-channel Enables communication to an external power controller.
Related information
Chapter A9 ACE Master Interface on page A9-113
Chapter A10 CHI Master Interface on page A10-125
Chapter A8 AXI Master Interface on page A8-105
A2 Technical Overview
A2.2 Interfaces
100236_0100_00_en Copyright © 2015–2017, 2019 Arm Limited or its affiliates. All rights
reserved.
A2-44
Non-Confidential
 Loading...
Loading...