A.15 APB interface signals
The debug APB bus supports clock, reset, addressing, and data handling signals when the processor
includes an APB interface to provide access to the debug and performance monitoring registers.
You must balance all APB interface signals with respect to CLKIN and time them relative to
PCLKENDBG.
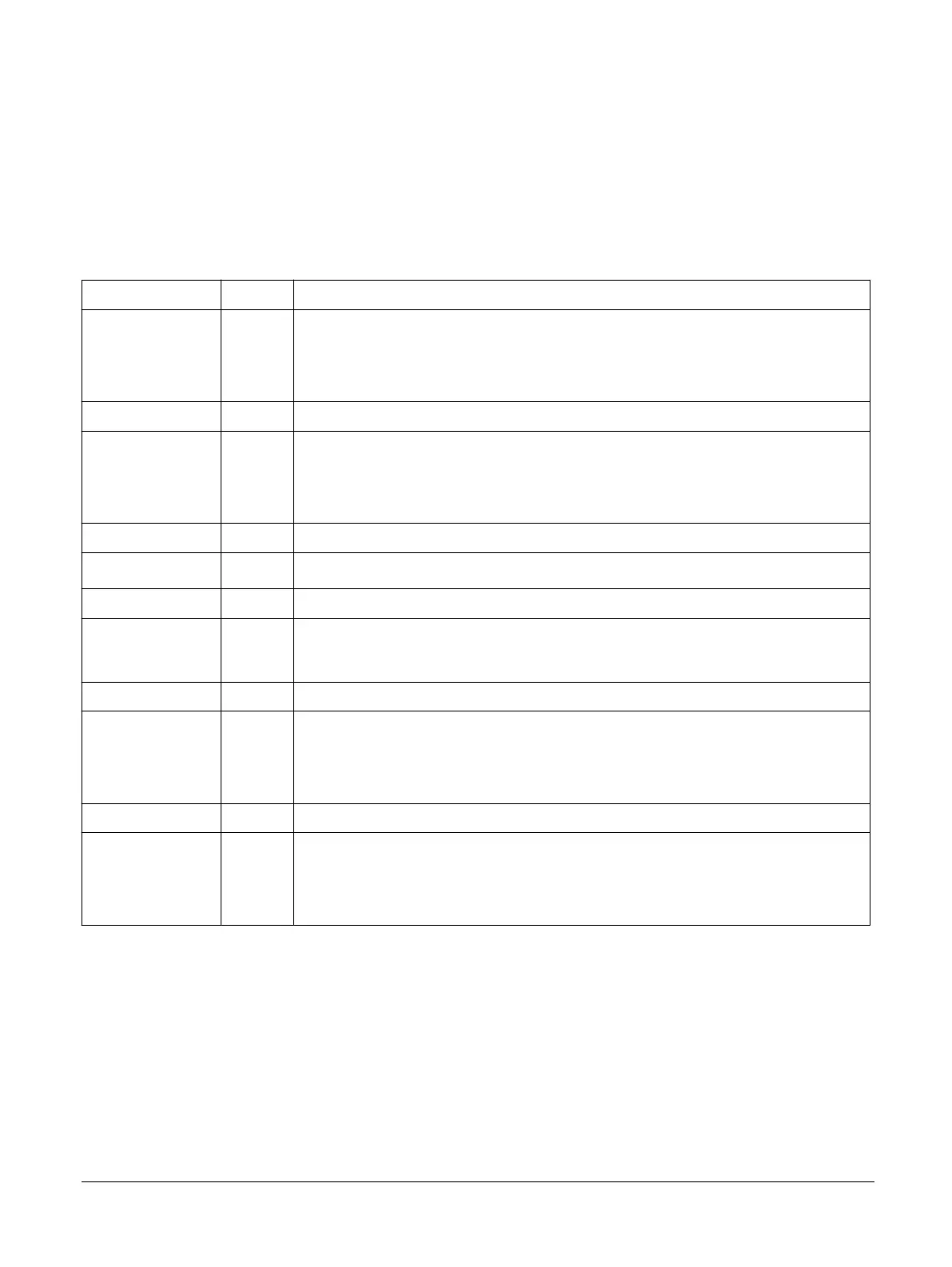
Table A-43 APB interface signals
Signal Direction Description
nPRESETDBG Input
APB reset, active-LOW:
0
Apply reset to APB interface.
1
Do not apply reset to APB interface.
PADDRDBG[21:2] Input APB address bus.
PADDRDBG31 Input
APB address bus bit[31]:
0
Not an external debugger access.
1
External debugger access.
PCLKENDBG Input APB clock enable.
PENABLEDBG Input
Indicates the second and subsequent cycles of an APB transfer.
PRDATADBG[31:0] Output APB read data.
PREADYDBG Output
APB slave ready.
An APB slave can deassert PREADYDBG to extend a transfer by inserting wait states.
PSELDBG Input Debug bus access.
PSLVERRDBG Output
APB slave transfer error:
0
No transfer error.
1
Transfer error.
PWDATADBG[31:0] Input APB write data.
PWRITEDBG Input
APB read or write signal:
0
Reads from APB.
1
Writes to APB.
A Signal Descriptions
A.15 APB interface signals
100236_0100_00_en Copyright © 2015–2017, 2019 Arm Limited or its affiliates. All rights
reserved.
Appx-A-873
Non-Confidential
 Loading...
Loading...