Page A-22
Appendix A — Networking
INTER-TEL
®
AXXESS
®
MANUAL VERSION 11.0 – May 2008
Sample Node Programming
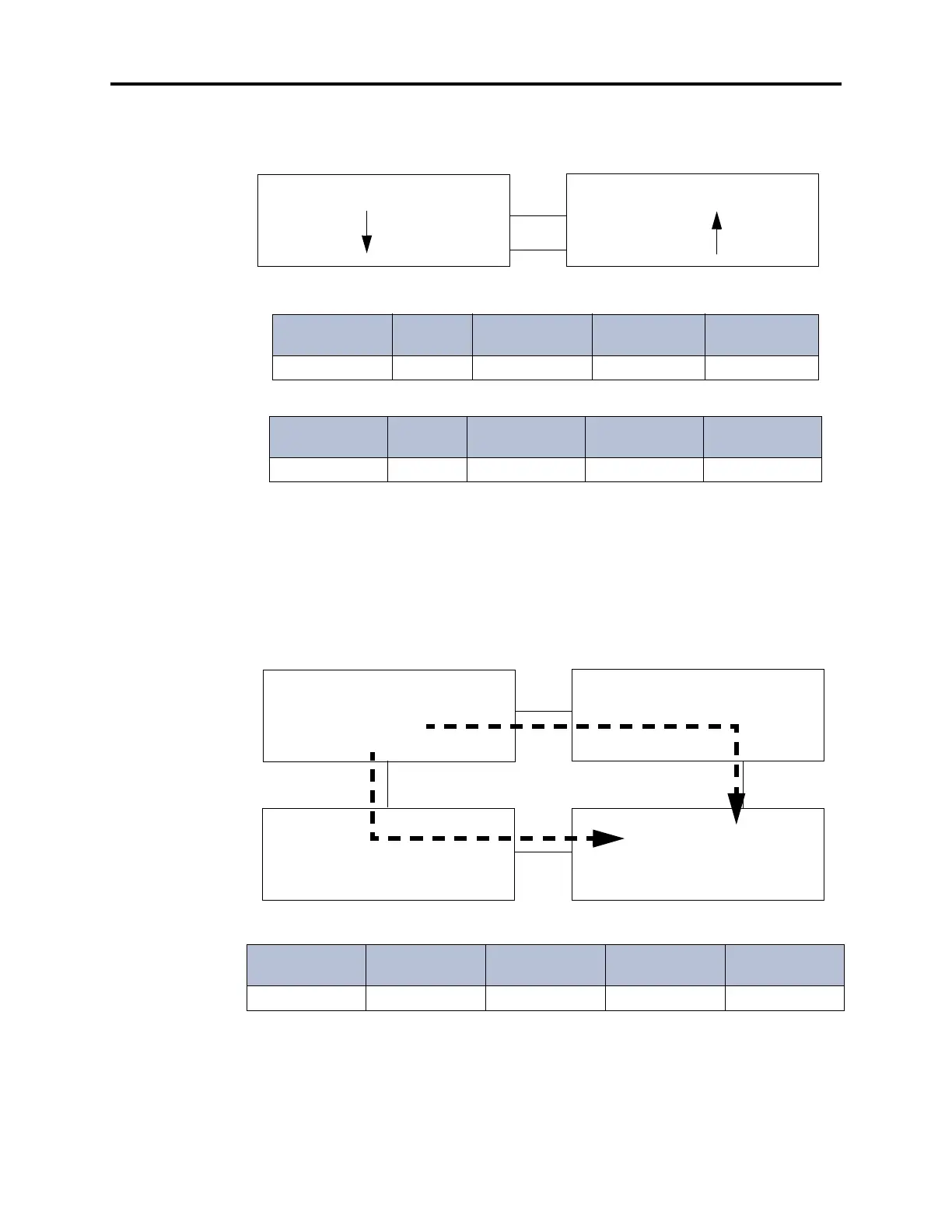
6.11 For example, Linear search type is the preferred method for avoiding glare between
two nodes that have two or more connections. Place the Node Trunk Groups in opposite order
in the Nodes on each side of the connection and use Linear search type, as shown below.
6.12 Programming For Node 1:
6.13 Programming For Node 2:
6.14 In the above example Node 1 uses Linear searches to send calls first through Node
Trunk Group 97501 and then through Node Trunk group 97502. Node 2 reverses the order and
begins searching with Node Trunk Group 97502. With calls beginning at opposite ends of the
trunk lists, it is less likely that both nodes will try to seize the same trunk and cause glare.
6.15 Distributed search type is best for balancing traffic when there are multiple-hop paths
between nodes. In the example shown below, the path to Node 3 from Node 1 has two hops
using either Node Trunk Group. Therefore, the route from Node 1 to Node 3 should be Distrib-
uted to balance the call traffic.
6.16 Programming For Node 1:
Node Route Grp
#
Node # Description
Node Trunk
Grps
Search Type
NRG 02 97002 2 To Node 2 97501, 97502 Linear
Node Route
Grp #
Node # Description
Node Trunk
Grps
Search Type
NRG 01 97001 1 To Node 1 97502, 97501 Linear
Node Route Grp
#
Node # Description
Node Trunk
Grps
Search Type
NRG 03 97003 3 To Node 3 97501, 97502 Distributed
NODE 1
Node Trunk Grp 97501
Node Trunk Grp 97502
NODE 2
Node Trunk Grp 97501
Node Trunk Grp 97502
Linear Order Linear Order
NODE 1
Node Trunk Grp 97501
Node Trunk Grp 97502
NODE 2
Node Trunk Grp 97501
Node Trunk Grp 97502
NODE 4
Node Trunk Grp 97501
Node Trunk Grp 97502
NODE 3
Node Trunk Grp 97502
Node Trunk Grp 97501
 Loading...
Loading...