Page 2-60
Specifications
INTER-TEL
®
AXXESS
®
MANUAL VERSION 11.0 – May 2008
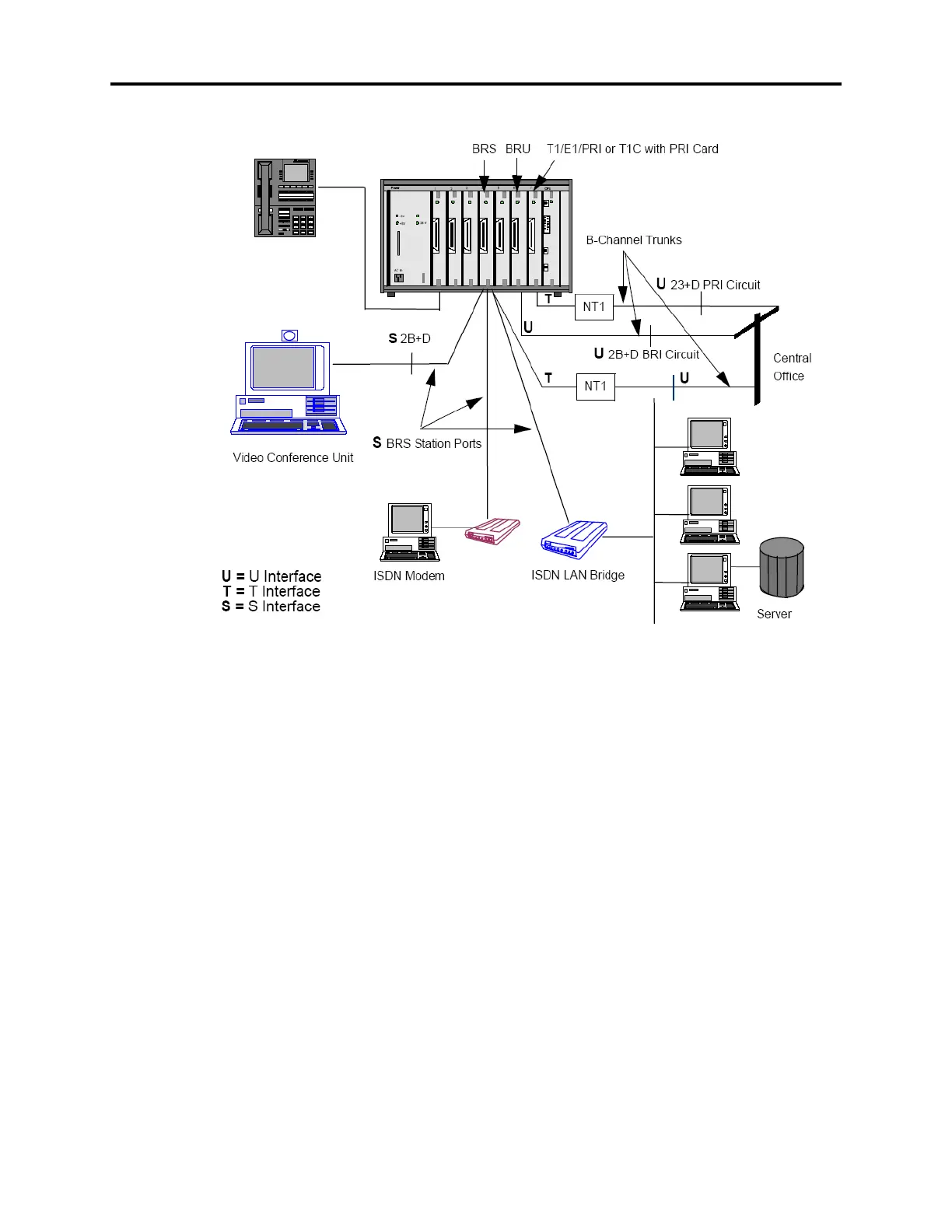
Example of a System Using BRI
Figure 2-4. Example of a System Using BRI
4.209 The drawing above is an example of a system with BRI. It includes the following:
• A video conference unit connected to port 1 of a BRS card in slot 4.
• An ISDN modem connected to port 2 on the same BRS card.
• An ISDN LAN bridge connected to port 3 of the BRS card in slot 4.
• Trunks connected to a BRU card in slot 6 and a T1/E1/PRI or T1C with PRI card in slot
7.
• A Phone in port 1 of the DKSC in slot 1.
4.210 The phone can use the 23 B-channels on the PRI card, 2 B-channels on the BRU card
[30-channels on the European PRI], and the 2 B-channels on the BRS card going to the NT1 to
place outgoing voice calls via ARS, trunk group, or individual trunk access. The phone can
receive incoming voice calls on the same B-channels because all the B-channel trunks are in
the same trunk group that routes calls by trunk number via a call routing table.
4.211 The video conference unit can place an outgoing call on one or both of its B-channels
out any one of the B-channel trunks (either BRI or PRI). The video conference unit can receive
an incoming call on one or both of its B-channels via a call routing table used by the trunk
group that contains the B-channels. Note that the video conference unit could place an IC call
to another video conference unit in the same system by dialing the extension or extensions of
the B-channel station of the other video conference unit.
4.212 The ISDN modem and ISDN LAN Bridge function the same way as the video confer-
ence unit for incoming and outgoing calls.
4.213 Basic Rate Interface terminology and the two different types of BRI cards are described
in the following pages.
 Loading...
Loading...