Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
54-3
Cisco MDS 9000 Family Fabric Manager Configuration Guide
OL-17256-03, Cisco MDS NX-OS Release 4.x
Chapter 54 Configuring IPv6 for Gigabit Ethernet Interfaces
About IPv6
IPv6 Address Prefix Format
An IPv6 address prefix, in the format ipv6-prefix/prefix-length, can be used to represent bit-wise
contiguous blocks of the entire address space. The ipv6-prefix is specified in hexadecimal using 16-bit
values between the colons. The prefix-length is a decimal value that indicates how many of the
high-order contiguous bits of the address comprise the prefix (the network portion of the address). For
example, 2001:0DB8:8086:6502::/32 is a valid IPv6 prefix.
IPv6 Address Type: Unicast
An IPv6 unicast address is an identifier for a single interface on a single node. A packet that is sent to a
unicast address is delivered to the interface identified by that address. The Cisco MDS NX-OS supports
the following IPv6 unicast address types:
• Global addresses
• Link-local addresses
Global Addresses
Global IPv6 addresses are defined by a global routing prefix, a subnet ID, and an interface ID.
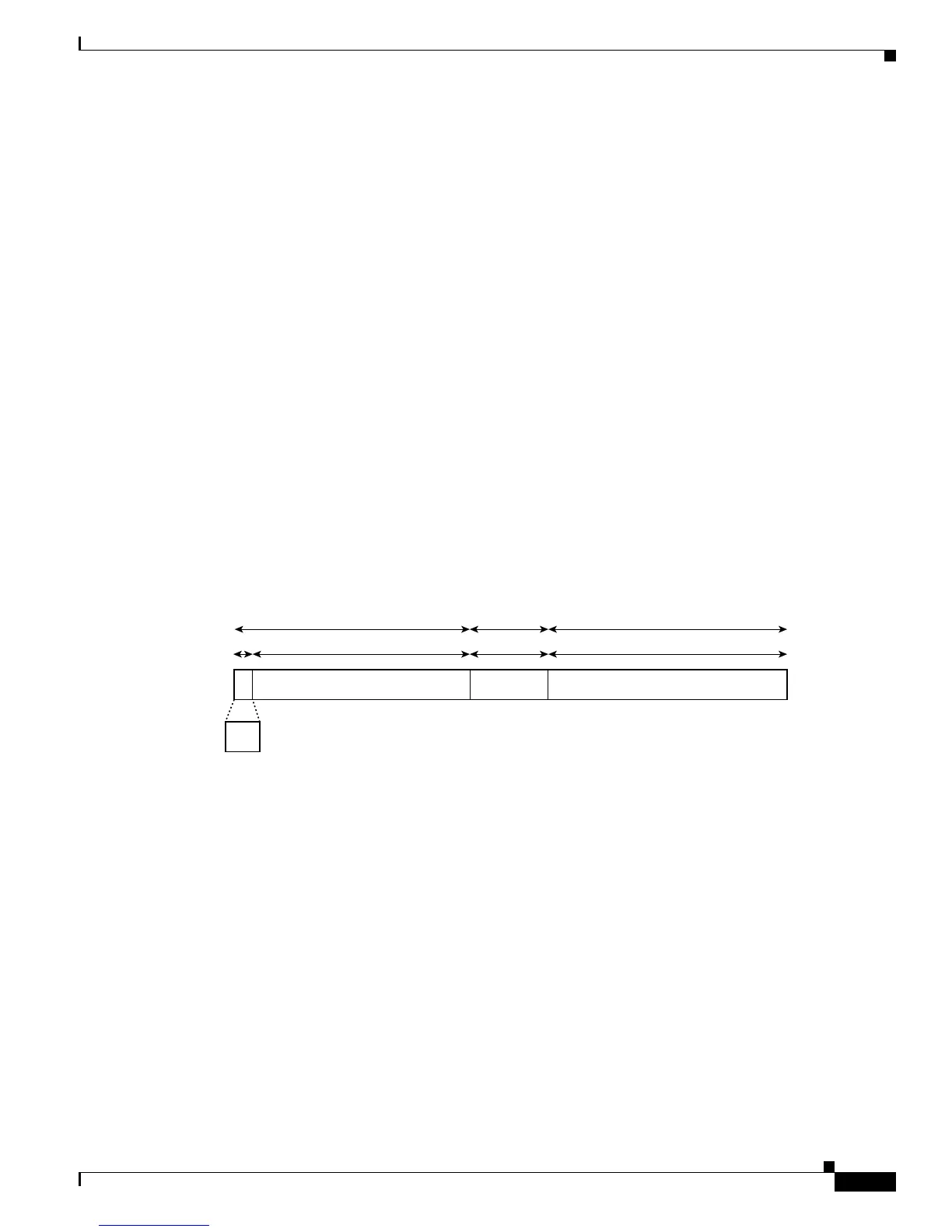
Figure 54-1 shows the structure of a global address.
Figure 54-1 Global Address Format
Addresses with a prefix of 2000::/3 (001) through E000::/3 (111) are required to have 64-bit interface
identifiers in the extended universal identifier (EUI)-64 format. The Internet Assigned Numbers
Authority (IANA) allocates the IPv6 address space in the range of 2000::/16 to regional registries.
The aggregatable global address typically consists of a 48-bit global routing prefix and a 16-bit subnet
ID or Site-Level Aggregator (SLA). In the IPv6 aggregatable global unicast address format document
(RFC 2374), the global routing prefix included two other hierarchically structured fields named
Top-Level Aggregator (TLA) and Next-Level Aggregator (NLA).The IETF decided to remove the TLS
and NLA fields from the RFCs because these fields are policy-based. Some existing IPv6 networks
deployed before the change might still be using networks based on the older architecture.
A 16-bit subnet field called the subnet ID could be used by individual organizations to create their own
local addressing hierarchy and to identify subnets. A subnet ID is similar to a subnet in IPv4, except that
an organization with an IPv6 subnet ID can support up to 65,535 individual subnets.
An interface ID is used to identify interfaces on a link. The interface ID must be unique to the link. They
may also be unique over a broader scope. In many cases, an interface ID will be the same as, or based
on, the link-layer address of an interface, which results in a globally unique interface ID. Interface IDs
used in aggregatable global unicast and other IPv6 address types must be 64 bits long and constructed
in the modified EUI-64 format.
147996
Interface IDGlobal routing prefix SLA
45 bits
001
16 bits 64 bits3
Provider Site Host

 Loading...
Loading...