Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
29-6
Cisco MDS 9000 Family Fabric Manager Configuration Guide
OL-17256-03, Cisco MDS NX-OS Release 4.x
Chapter 29 Configuring Inter-VSAN Routing
Inter-VSAN Routing
If you have a message that is not recognized by IVR NAT and contains the destination ID in the payload,
you cannot use IVR with NAT in your topology. You can still use IVR with unique domain IDs.
IVR VSAN Topology
IVR uses a configured IVR VSAN topology to determine how to route traffic between the initiator and
the target across the fabric. You can configure this IVR VSAN topology manually on an IVR-enabled
switch and distribute the configuration using CFS in Cisco MDS SAN-OS Release 2.0(1b) or later.
Alternately, in Cisco MDS SAN-OS Release 2.1(1a) or later, you can configure IVR topology in auto
mode. Prior to Cisco MDS SAN-OS Release 2.0(1b), you need to manually copy the IVR VSAN
topology to each switch in the fabric.
Auto mode automatically builds the IVR VSAN topology and maintains the topology database when
fabric reconfigurations occur. Auto mode distributes the IVR VSAN topology to IVR-enabled switches
using CFS.
Using auto mode, you no longer need to manually update the IVR VSAN topology when
reconfigurations occur in your fabric. If a manually configured IVR topology database exists, auto mode
initially uses that topology information. This reduces disruption in the network by gradually migrating
from the user-specified topology database to the automatically learned topology database. User
configured topology entries that are not part of the network are aged out in about three minutes. New
entries that are not part of the user configured database are added as they are discovered in the network.
When auto IVR topology is turned on it starts with the previously active, if any, manual IVR topology.
Auto topology then commences its discovery process, and may come up with new, alternate or better
paths. If the traffic is switched to an alternate or better path, there may be temporary traffic disruptions
that are normally associated with switching paths.
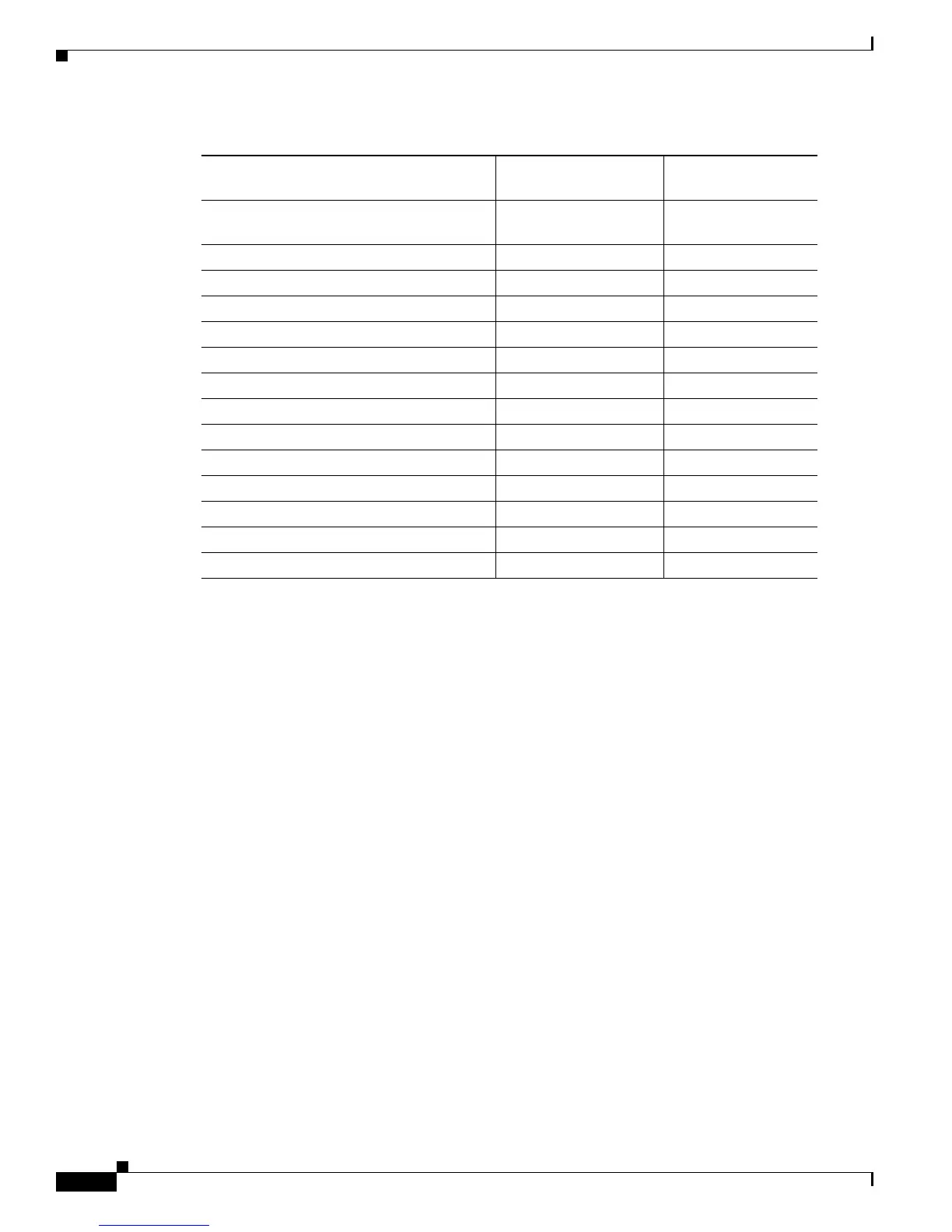
Fibre Channel Address Resolution Protocol
Request
0x54 00 00 00 FARP-REQ
Logout 0x05 00 00 00 LOGO
Port Login 0x30 00 00 00 PLOGI
Read Exchange Concise 0x13 00 00 00 REC
Read Exchange Concise Accept 0x02 00 00 00 REC ACC
Read Exchange Status Block 0x08 00 00 00 RES
Read Exchange Status Block Accept 0x02 00 00 00 RES ACC
Read Link Error Status Block 0x0F 00 00 00 RLS
Read Sequence Status Block 0x09 00 00 00 RSS
Reinstate Recovery Qualifier 0x12 00 00 00 RRQ
Request Sequence Initiative 0x0A 00 00 00 RSI
Scan Remote Loop 0x7B 00 00 00 RSL
Third Party Process Logout 0x24 00 00 00 TPRLO
Third Party Process Logout Accept 0x02 00 00 00 TPRLO ACC
Table 29-2 Extended Link Service Messages Supported by IVR NAT (continued)
Extended Link Service Messages
Link Service Command
(LS_COMMAND) Mnemonic

 Loading...
Loading...