Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
48-26
Cisco MDS 9000 Family Fabric Manager Configuration Guide
OL-17256-03, Cisco MDS NX-OS Release 4.x
Chapter 48 Configuring FCIP
Using the FCIP Wizard
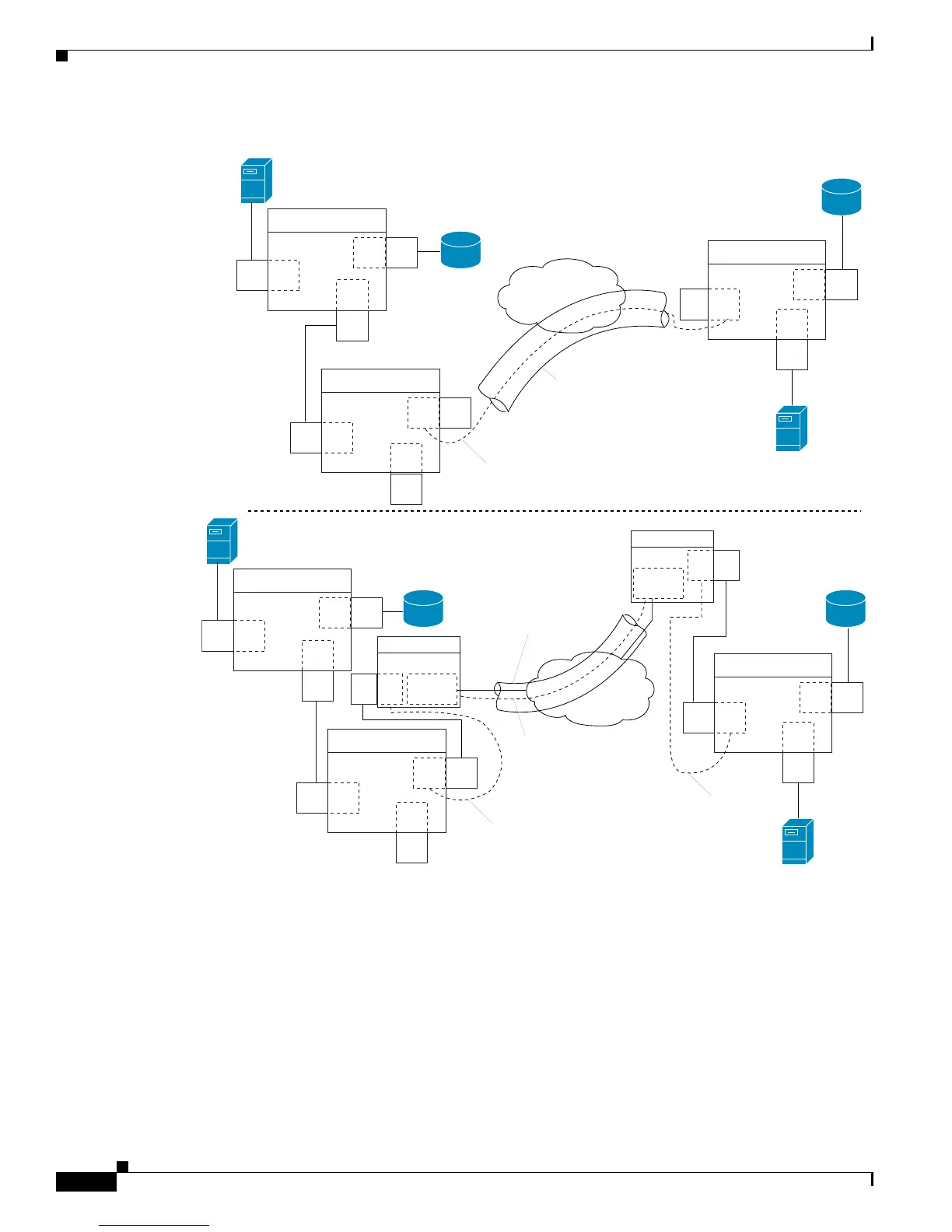
Figure 48-20 FCIP B Port and Fibre Channel E Port
B ports bridge Fibre Channel traffic from a local E port to a remote E port without participating in
fabric-related activities such as principal switch election, domain ID assignment, and Fibre Channel
fabric shortest path first (FSPF) routing. For example, Class F traffic entering a SAN extender does not
interact with the B port. The traffic is transparently propagated (bridged) over a WAN interface before
exiting the remote B port. This bridge results in both E ports exchanging Class F information that
ultimately leads to normal ISL behavior such as fabric merging and routing.
FCIP links between B port SAN extenders do not exchange the same information as FCIP links between
E ports, and are therefore incompatible. This is reflected by the terminology used in FC-BB-2: while VE
ports establish a virtual ISL over an FCIP link, B ports use a B access ISL.
FC
FC
FC
F
F
F
Switch A
GE
FC
FC
VE
F
E
Switch C
FC
GE
FC
E
VE
F
Switch B
FCIP link
Virtual ISL
IP
91559
IP
FC
FC
FC
F
F
FC
FC
B
B
B
access
B
access
E
Switch A
FC bridge
FC
FC
FC
E
F
E
Switch C
FC bridge
FC
FC
FC
E
E
F
Switch B
B access ISL
FCIP link
ISL
ISL
E port
B port

 Loading...
Loading...