Frequency Modulated Phase Locked Loop and System Clocks (FMPLL)
MPC5566 Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor 11-25
Table 11-9 shows the clock-out to clock-in frequency relationships for the possible clock modes.
When programming the FMPLL, do not violate the maximum system clocks frequency, or maximum and
minimum ICO frequency specifications. For determining the MFD value, use a value of zero for the RFD
(translates to divide-by-one). This ensures that the FMPLL does not try to synthesize a frequency out of
its range. Refer to the device Data Sheet for more information.
11.4.3.1 Programming System Clock Frequency Without Frequency Modulation
The following steps are required to accommodate the frequency overshoot that can occur when the
PREDIV or MFD bits are changed. If frequency modulation is going to be enabled, the maximum
allowable frequency must be reduced by the programmed ΔF
m
.
NOTE
Following these steps produces immediate changes in supply current,
therefore make sure the power supply is decoupled with low ESR
capacitors.
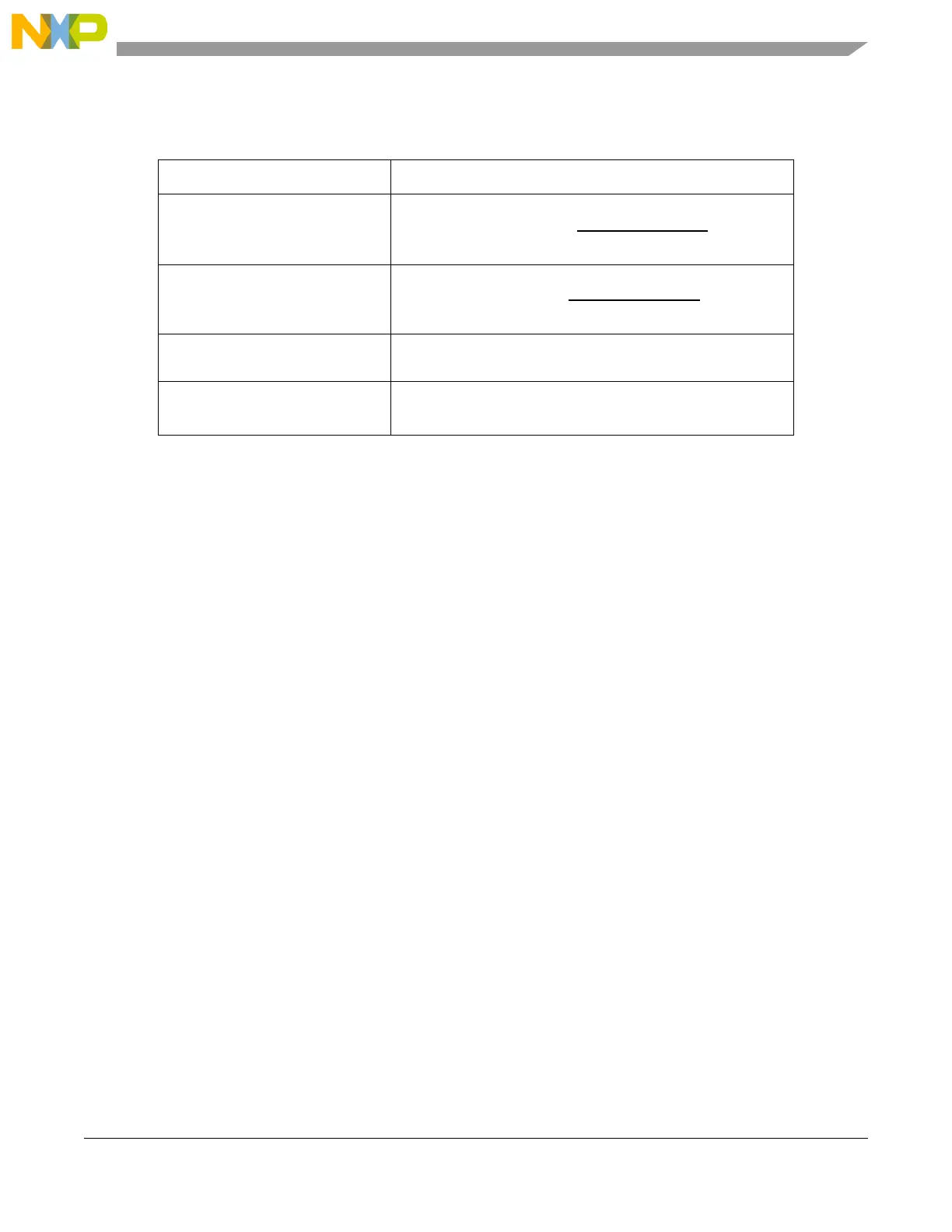
Table 11-9. Clock-out vs. Clock-in Relationships
Clock Mode PLL Option
Crystal Reference Mode
External Reference Mode
Dual Controller (1:1) Mode
Bypass Mode
NOTES:
F
sys
= system frequency
F
prediv
= clock frequency after PREDIV.
F
ref_crystal
and F
ref_ext
= clock frequencies at the EXTAL_EXTCLK signal. (Refer to Figure 11-1).
MFD ranges from 0 to 31.
RFD ranges from 0 to 7.
PREDIV normal reset value is 0. Caution: Programming a PREDIV value such that the ICO operates
outside its specified range causes unpredictable results and the FMPLL does not lock. Refer to the
device Data Sheet for details on the ICO range.
F
sys
= F
ref_crystal
×
(MFD + 4)
[(PREDIV + 1)
×
2
RFD
]
F
sys
= F
ref_ext
×
(MFD + 4)
[(PREDIV + 1)
×
2
RFD
]
 Loading...
Loading...