TC1796
System Units (Vol. 1 of 2)
On-Chip System Buses and Bus Bridges
User’s Manual 6-5 V2.0, 2007-07
Buses, V2.0
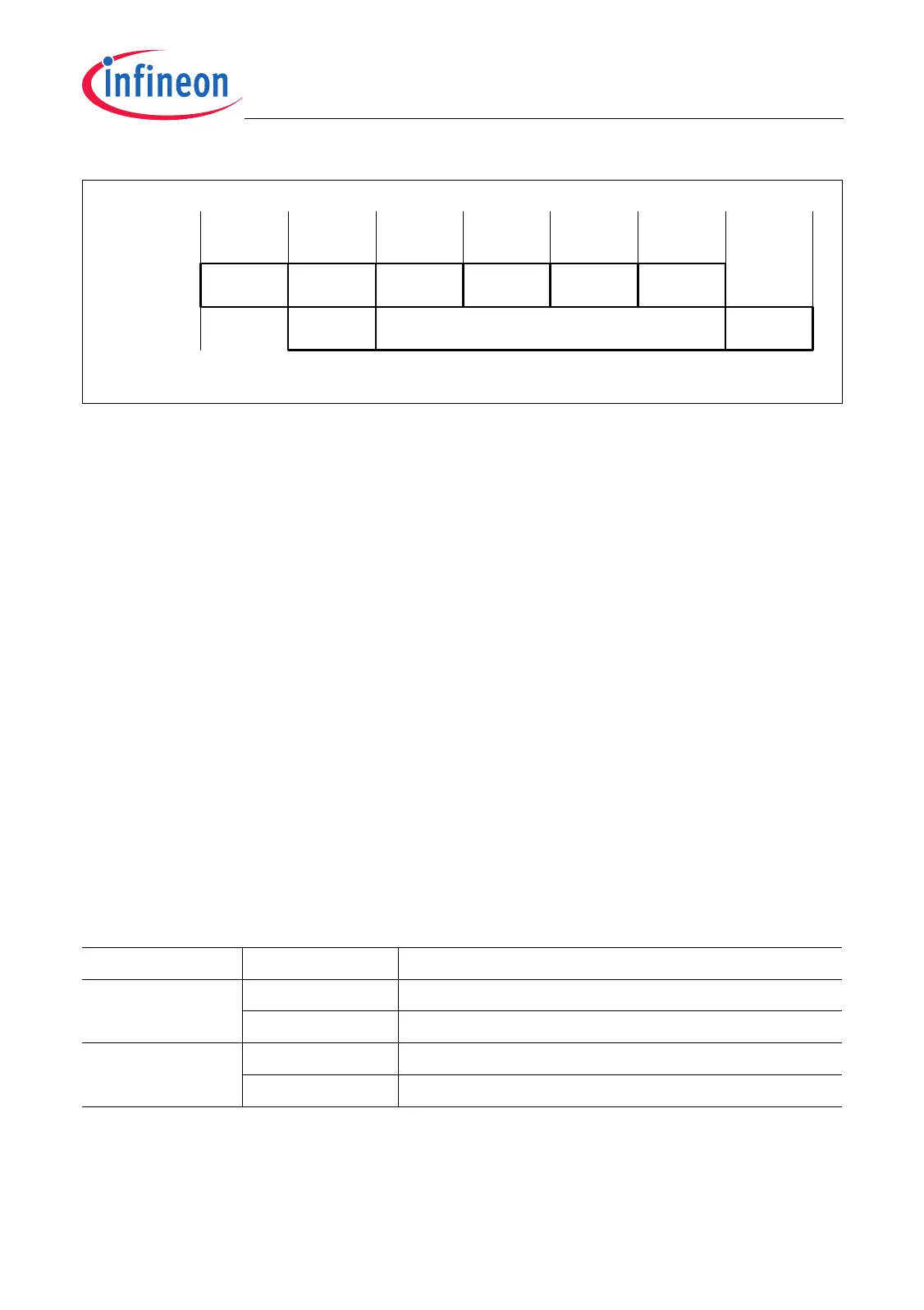
Figure 6-3 LMB Block Transactions
6.2 Local Memory Bus Controller Units
Each of the two LMBs in the TC1796 have a LMB Bus Control Unit (LBCU), one for the
DLMB (DBCU) and one for the PLMB (PBCU). Where the description in this section
refers to LBCU, the related topic is also valid for DBCU and PBCU.
6.2.1 Basic Operation
The LBCU handles the cycle sequences of the transfers that have been requested by
the LMB master devices. The LBCU is also able to detect bus protocol violations and
addressing of un-implemented addresses. In case of a bus error, the LBCU captures all
relevant data such as bus address, bus data and bus status information in register where
the information can be analyzed by software.
6.2.2 LMB Bus Arbitration
All LMB master devices requesting the LMB will participate in an arbitration round.
Arbitration rounds are performed in each cycle that preceeds a possible address cycle.
Each LMB master device has a fixed priority as shown in Table 6-2.
For all the masters requesting an LMB (PLMB or DLMB) during any one cycle, the
master that is granted the LMB is the one with the highest priority.
Table 6-2 Priority of Master PLMB Agents
LMB Bus Priority LMB Bus Master
PLMB Low priority DMU
High priority PMI (Default Master)
DLMB Low priority LFI
High priority DMI (Default Master)
Request/
Grant
Data
Cycle
Address
Cycle
Bus Cycle 1 2 3 4
Request/
Grant
Address Cycle
5
MCA05629
Transfer 1
Transfer 2
6
Data
Cycle
7
Data
Cycle
Data
Cycle
Data
Cycle

 Loading...
Loading...