TC1796
System Units (Vol. 1 of 2)
Interrupt System
User’s Manual 14-26 V2.0, 2007-07
Interrupt, V2.0
14.10.4 SRAM Parity Error NMI
If an SRAM parity error is detected in an SRAM memory block that is enabled for parity
error detection (corresponding enable bit SCU_PETCR.PENx is set), the NMIPER flag
in register NMISR is set together with related parity error flag SCU_PETSR.PFLx. In
contrast to the other NMI flags, the NMIPER flag remains set when reading register
NMISR. NMIPER is cleared only with an NMISR read operation when no error flag PFLx
is set during the NMISR read operation. This parity error flag mechanism has some
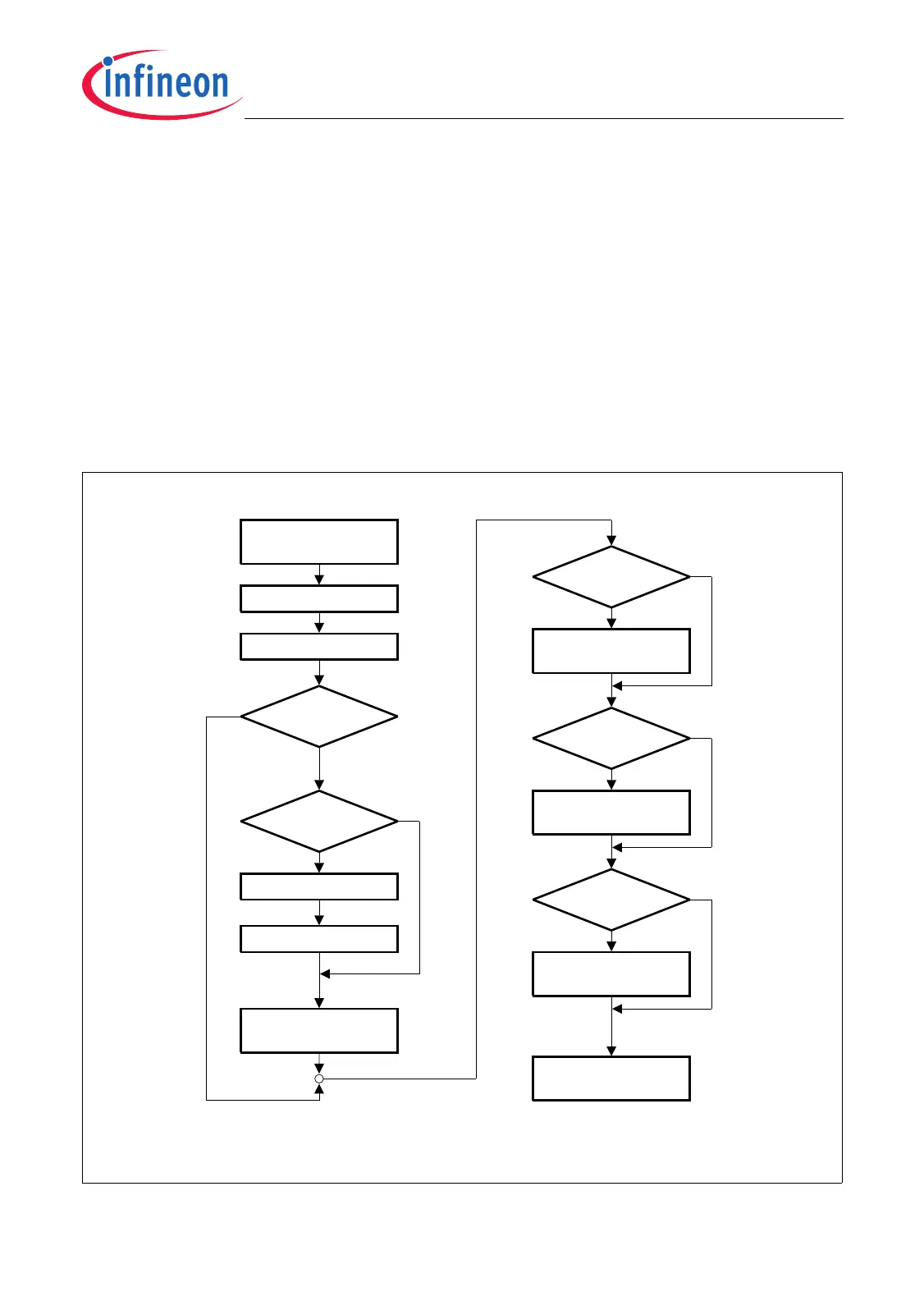
effects on na NMI trap handling routine. Figure 14-5 shows a trap handler flow diagram
that especially handles a typical SRAM parity error NMI trap recognition.
Additional details about SRAM parity error control are described in section “SRAM
Parity Control” on Page 5-37.
Figure 14-5 NMI Trap Handler Routine for Parity Error Handling
MCA06449a
V1 := SCU_PETSR
V2.NMIPER = 1?
no
yes
V2 := NMISR
V2.NMIEXT set?
Execute External
NMI Req. Handler
V2.NMIPLL set?
Execute NMI PLL
Request Handler
V2.NMIWDT set?
Execute Watchdog
NMI Req. Handler
yes
yes
Execute Parity Error
NMI Req. Handler
Entry in Trap
Handler Routine
V1 = 0?
1)
V1 := SCU_PETSR
yes
no
Exit Trap Handler
Routine
no
no
yes
no
V2 := NMISR
1)
This test is for the case that a parity error
occurs after the first read of SCU_PETSR.
 Loading...
Loading...