PWM
t
T
PWM
T
SYSCLK
PWMresolution(%)=F /F x100%
PWM SYSCLKOUT
PWMresolution(bits)=Log (T /T )
2 PWM SYSCLKOUT
www.ti.com
Introduction
327
SPRUI07–March 2020
Submit Documentation Feedback
Copyright © 2020, Texas Instruments Incorporated
High-Resolution Pulse Width Modulator (HRPWM)
4.1 Introduction
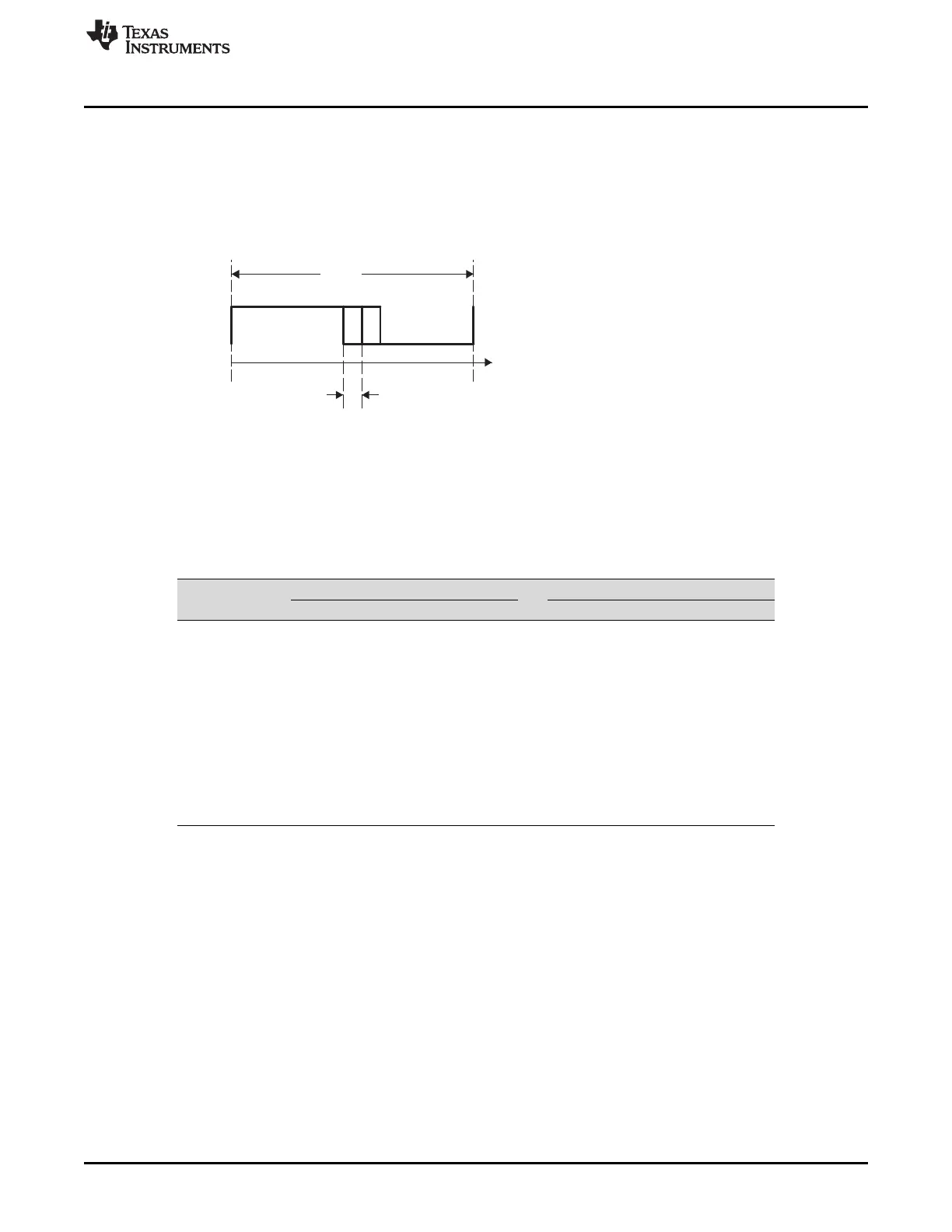
The ePWM peripheral is used to perform a function that is mathematically equivalent to a digital-to-analog
converter (DAC). As shown in Figure 4-1, where T
SYSCLKOUT
= 10 ns (that is, 100 MHz clock), the effective
resolution for conventionally generated PWM is a function of PWM frequency (or period) and system clock
frequency.
Figure 4-1. Resolution Calculations for Conventionally Generated PWM
If the required PWM operating frequency does not offer sufficient resolution in PWM mode, you may want
to consider HRPWM. As an example of improved performance offered by HRPWM, Table 4-1 shows
resolution in bits for various PWM frequencies. These values assume a 100 MHz SYSCLK frequency and
a MEP step size of 180 ps. See the device-specific datasheet for typical and maximum performance
specifications for the MEP.
Table 4-1. Resolution for PWM and HRPWM
PWM Freq
(kHz)
Regular Resolution (PWM) High Resolution (HRPWM)
Bits % Bits %
20 12.3 0.0 18.1 0.000
50 11.0 0.0 16.8 0.001
100 10.0 0.1 15.8 0.002
150 9.4 0.2 15.2 0.003
200 9.0 0.2 14.8 0.004
250 8.6 0.3 14.4 0.005
500 7.6 0.5 13.8 0.007
1000 6.6 1.0 12.4 0.018
1500 6.1 1.5 11.9 0.027
2000 5.6 2.0 11.4 0.036
Although each application may differ, typical low frequency PWM operation (below 250 kHz) may not
require HRPWM. HRPWM capability is most useful for high frequency PWM requirements of power
conversion topologies such as:
• Single-phase buck, boost, and flyback
• Multi-phase buck, boost, and flyback
• Phase-shifted full bridge
• Direct modulation of D-Class power amplifiers

 Loading...
Loading...