Yes
No
Yes
No
running.
Transmit stays
ignore frame pulse.
With frame ignore
Case 1:
transfer.
Restart current
Set XSYNCERR.
abort transfer.
Without frame ignore
Case 3:
Start new transmit.
Normal transmission.
Case 2:
pulse occurs.
Transmit frame-sync
?
XFIG=1
?
pulse
frame-sync
Unexpected
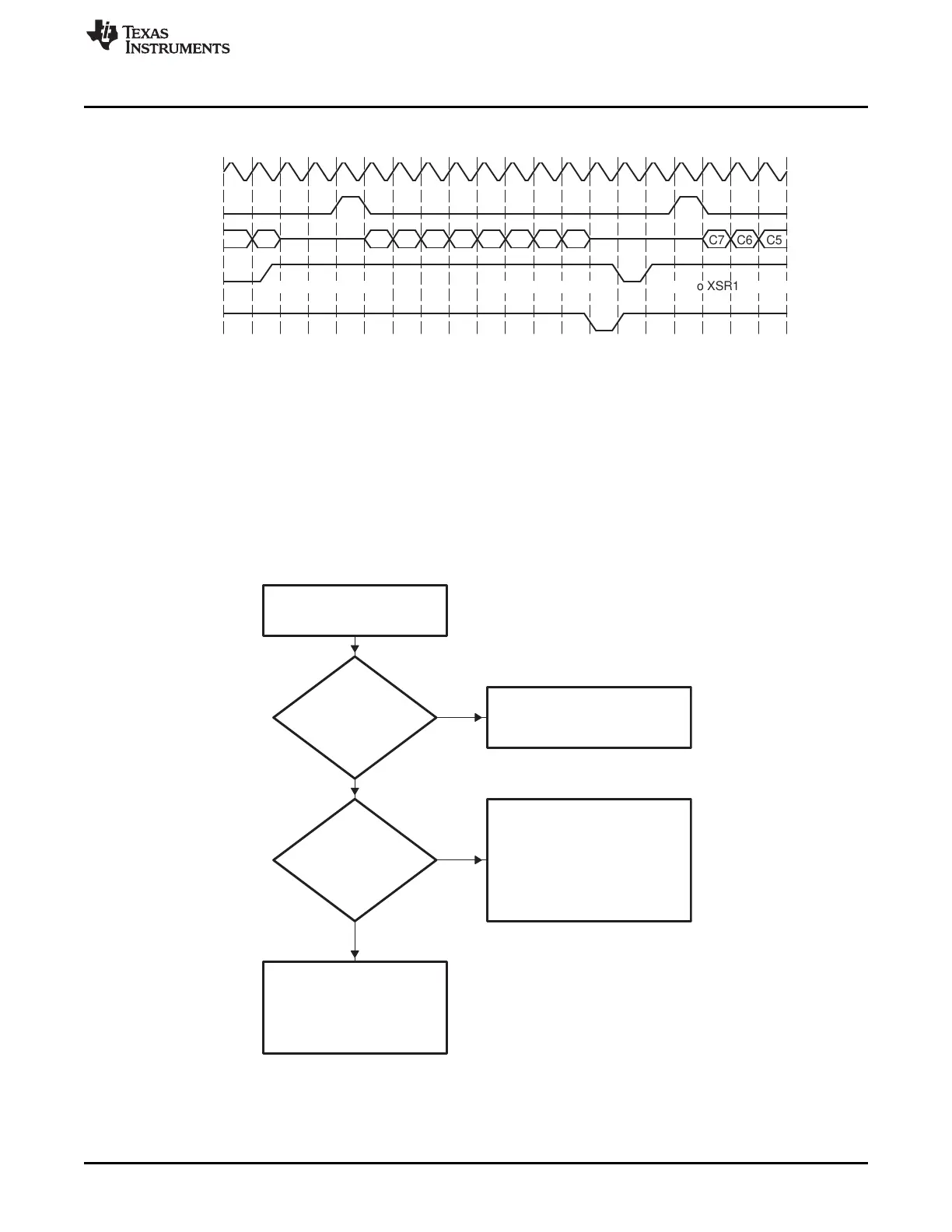
C5C6C7B0B1B2B3B4B5B6B7A0A1
XRDY
DX
FSX
CLKX
DXR1 to XSR1 copy(C)Write to DXR1(C)DXR1 to XSR1 copy
www.ti.com
McBSP Exception/Error Conditions
683
SPRUI07–March 2020
Submit Documentation Feedback
Copyright © 2020, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Multichannel Buffered Serial Port (McBSP)
Figure 12-28. Underflow Prevented in the McBSP Transmitter
12.5.6 Unexpected Transmit Frame-Synchronization Pulse
Section 12.5.6.1 shows how the McBSP responds to any transmit frame-synchronization pulses, including
an unexpected pulse. Section 12.5.6.2 and Section 12.5.6.3 show examples of a frame-synchronization
error and an example of how to prevent such an error, respectively.
12.5.6.1 Possible Responses to Transmit Frame-Synchronization Pulses
Figure 12-29 shows the decision tree that the transmitter uses to handle all incoming frame-
synchronization pulses. The figure assumes that the transmitter has been started (XRST = 1 in SPCR2).
Case 3 shows where an error occurs.
Figure 12-29. Possible Responses to Transmit Frame-Synchronization Pulses
Any one of three cases can occur:
• Case 1: Unexpected internal FSX pulses with XFIG = 1 in XCR2. Transmit frame-synchronization
pulses are ignored, and the transmission continues.
• Case 2: Normal serial port transmission. Transmission continues normally because the frame-

 Loading...
Loading...