Write to DXR1(E)DXR1 to XSR1 Copy(D)Write to DXR1(C)
D5D6D7B0B1B2B3B4B5B6B7A0A1
XRDY
DX
FSX
CLKX
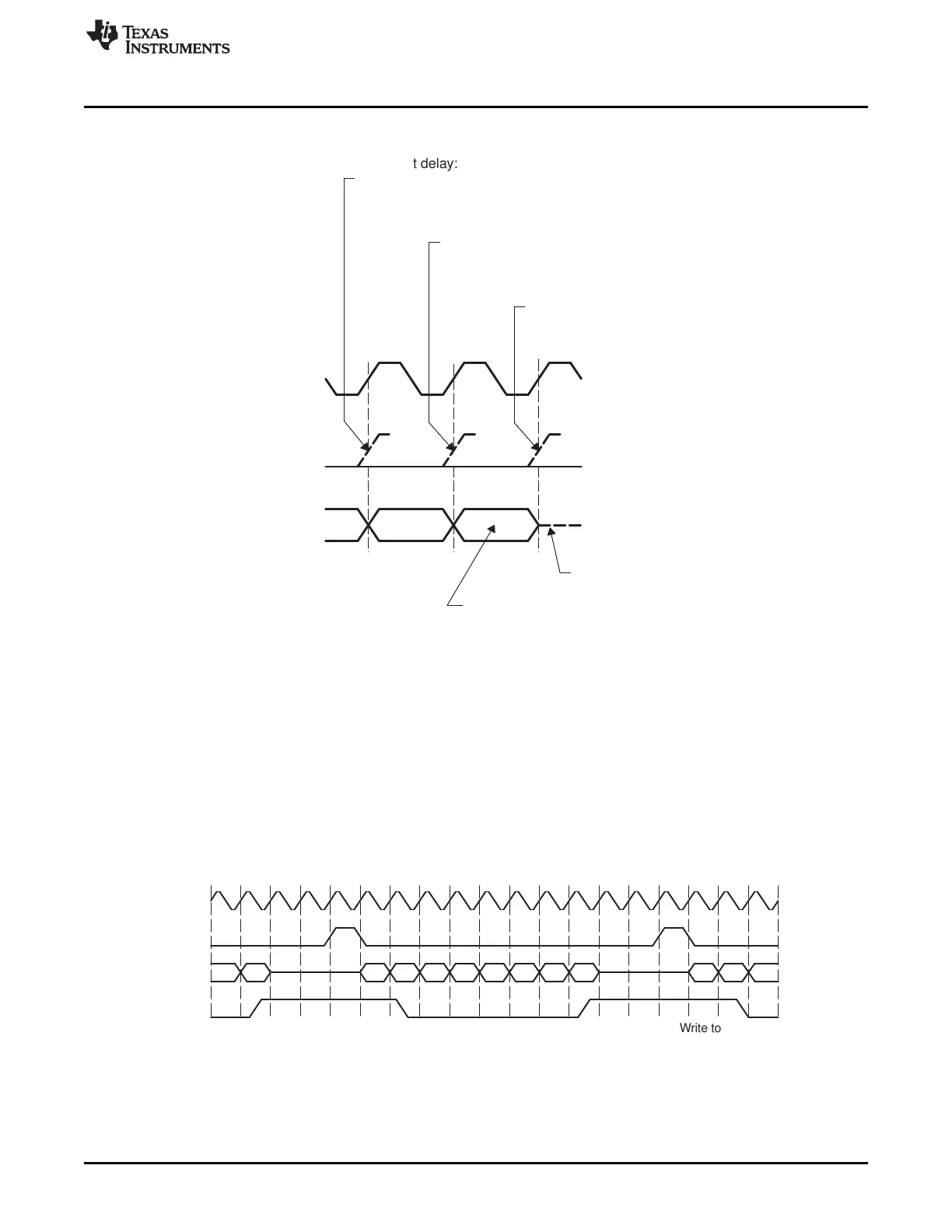
For 2-bit delay:
Next frame-synchronization
pulse here or later is OK.
For 1-bit delay:
Next frame-synchronization
pulse here or later is OK.
For 0-bit delay:
Next frame-synchronization
pulse here or later is OK.
CLKR/CLKX
FSR/FSX
DR/DX
Last bit of
current frame
Earliest possible
time to begin transfer
of next frame
www.ti.com
McBSP Exception/Error Conditions
681
SPRUI07–March 2020
Submit Documentation Feedback
Copyright © 2020, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Multichannel Buffered Serial Port (McBSP)
Figure 12-25. Proper Positioning of Frame-Synchronization Pulses
12.5.4 Overwrite in the Transmitter
As described in Section 12.3.6), the transmitter must copy the data previously written to the DXR(s) by the
CPU or DMA controller into the XSR(s) and then shift each bit from the XSR(s) to the DX pin. If new data
is written to the DXR(s) before the previous data is copied to the XSR(s), the previous data in the DXR(s)
is overwritten and thus lost.
12.5.4.1 Example of Overwrite Condition
Figure 12-26 shows what happens if the data in DXR1 is overwritten before being transmitted. Initially,
DXR1 is loaded with data C. A subsequent write to DXR1 overwrites C with D before C is copied to XSR1.
Thus, C is never transmitted on DX.
Figure 12-26. Data in the McBSP Transmitter Overwritten and Thus Not Transmitted
12.5.4.2 Preventing Overwrites
You can prevent CPU overwrites by making the CPU:
• Poll for XRDY = 1 in SPCR2 before writing to the DXR(s). XRDY is set when data is copied from DXR1
to XSR1 and is cleared when new data is written to DXR1.

 Loading...
Loading...