Cortex-M3 Processor (Reference Material)
UG0331 User Guide Revision 15.0 108
3.7.2.7 Configuration and Control Register
The CCR controls entry to Thread mode and enables:
• the handlers for NMI, HardFault and faults escalated by FAULTMASK to ignore BusFaults
• trapping of divide by zero and unaligned accesses
• access to the STIR by unprivileged software, see "Software Trigger Interrupt Register" on page 93.
See the register summary in Ta ble 50 , page 102 for the CCR attributes.
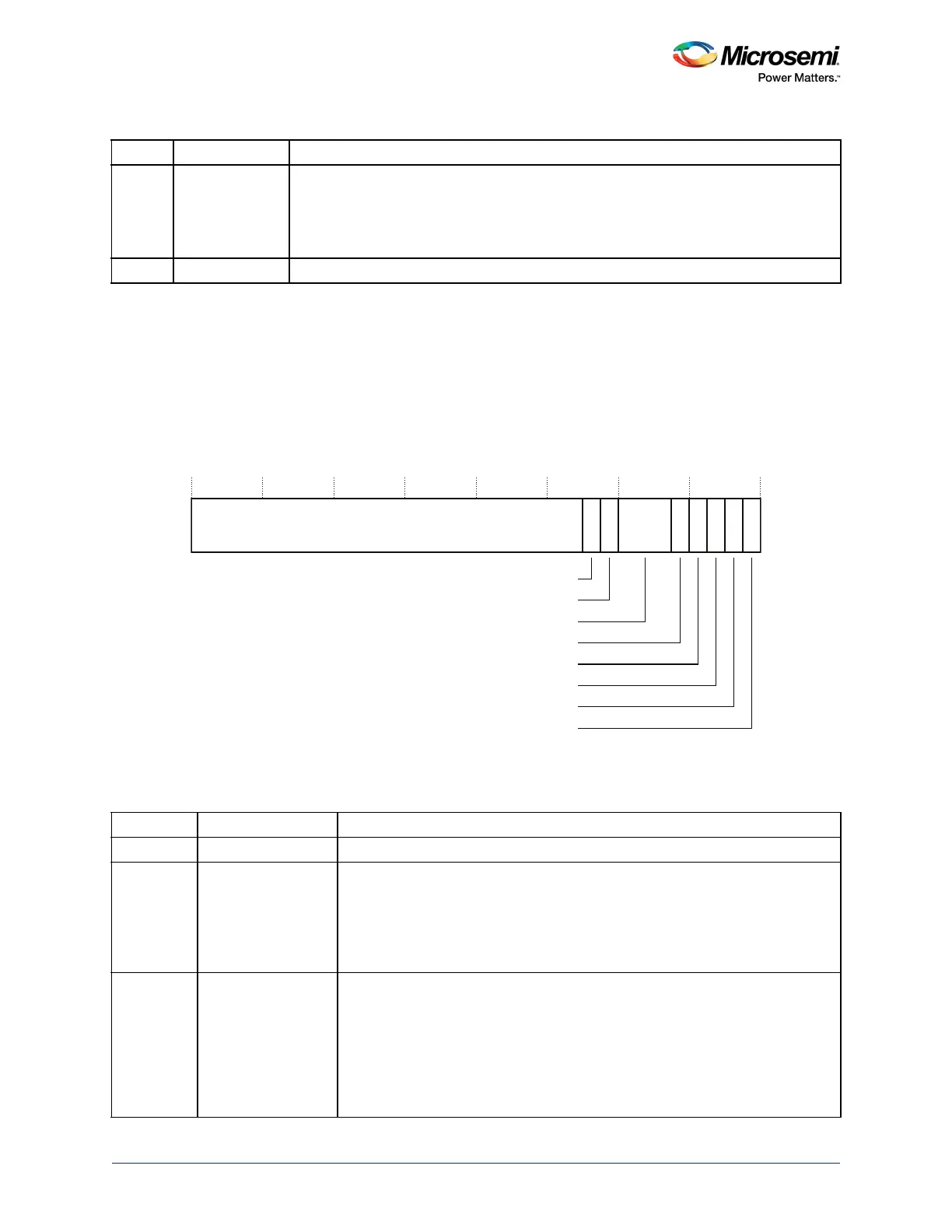
The bit assignments are:
Figure 36 • CCR Bit Assignments
[1] SLEEPONEXIT Indicates sleep-on-exit when returning from Handler mode to Thread mode:
0: do not sleep when returning to Thread mode.
1: enter sleep, or deep sleep, on return from an ISR.
Setting this bit to 1 enables an interrupt driven application to avoid returning to an empty
main application.
[0] Reserved.
Table 58 • CCR Bit Assignments
Bits Name Function
[31:10] Reserved.
[9] STKALIGN Indicates stack alignment on exception entry:
0: 4-byte aligned
1: 8-byte aligned.
On exception entry, the processor uses bit[9] of the stacked PSR to indicate the
stack alignment. On return from the exception it uses this stacked bit to restore
the correct stack alignment.
[8] BFHFNMIGN Enables handlers with priority -1 or -2 to ignore data BusFaults caused by load
and store instructions. This applies to the HardFault, NMI, and FAULTMASK
escalated handlers:
0: data BusFaults caused by load and store instructions cause a lock-up
1: data BusFaults caused by load and store instructions are ignored.
Set this bit to 1 only when the handler and its data are in absolutely safe memory.
The normal use of this bit is to probe system devices and bridges to detect
problems.
Table 57 • SCR Bit Assignments (continued)
Bits Name Function
DIV_0_TRP
Reserved
UNALIGN_TRP
NONBASETHRDENA
USERSETMPEND
BFHFNMIGN
STKALIGN
Reserved
31 10987 543210
Reserved

 Loading...
Loading...




