Cortex-M3 Processor (Reference Material)
UG0331 User Guide Revision 15.0 56
number of branch instructions in code. The table also shows the relationship between condition code
suffixes and the N, Z, C, and V flags.
The following example shows the use of a conditional instruction to find the absolute value of a number.
R0
=
abs
(
R1
).
Example 1
Absolute value
MOVS R0, R1 ; R0 = R1, setting flags
IT MI ; skipping next instruction if value 0 or positive
RSBMI R0, R0, #0 ; If negative, R0 = -R0
The following example shows the use of conditional instructions to update the value of
R4
if the signed
values
R0
is greater than
R1
and
R2
is greater than
R3
.
Example 2
Compare and update value
CMP R0, R1 ; Compare R0 and R1, setting flags
ITT GT ; Skip next two instructions unless GT condition holds
CMPGT R2, R3 ; If 'greater than', compare R2 and R3, setting flags
MOVGT R4, R5 ; If still 'greater than', do R4 = R5
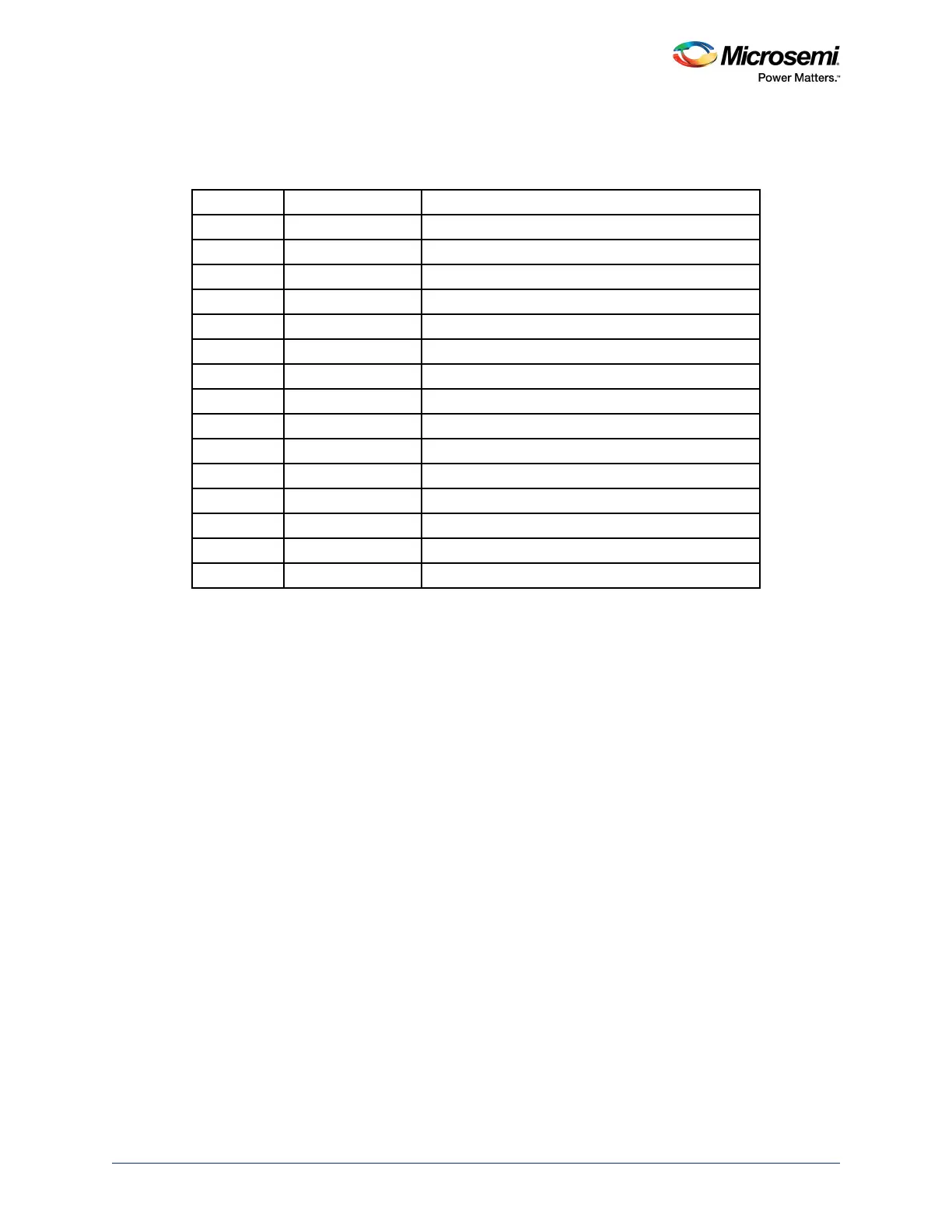
Table 29 • Condition Code Suffixes
Suffix Flags Meaning
EQ Z = 1 Equal
NE Z = 0 Not equal
CS or HS C = 1 Higher or same, unsigned
CC or LO C = 0 Lower, unsigned
MI N = 1 Negative
PL N = 0 Positive or zero
VS V = 1 Overflow
VC V = 0 No overflow
HI C = 1 and Z = 0 Higher, unsigned
LS C = 0 or Z = 1 Lower or same, unsigned
GE N = V Greater than or equal, signed
LT N != V Less than, signed
GT Z = 0 and N = V Greater than, signed
LE Z = 1 and N != V Less than or equal, signed
AL Can have any value Always. This is the default when no suffix is specified.
 Loading...
Loading...




