Cortex-M3 Processor (Reference Material)
UG0331 User Guide Revision 15.0 112
If you disable a system handler and the corresponding fault occurs, the processor treats the fault as a
HardFault.
You can write to this register to change the pending or active status of system exceptions. An OS kernel
can write to the active bits to perform a context switch that changes the current exception type.
• Software that changes the value of an active bit in this register without correct adjustment to the
stacked content can cause the processor to generate a fault exception. Ensure software that writes
to this register retains and subsequently restores the current active status.
• After you have enabled the system handlers, if you have to change the value of a bit in this register
you must use a read-modify-write procedure to ensure that you change only the required bit.
3.7.2.10 Configurable Fault Status Register
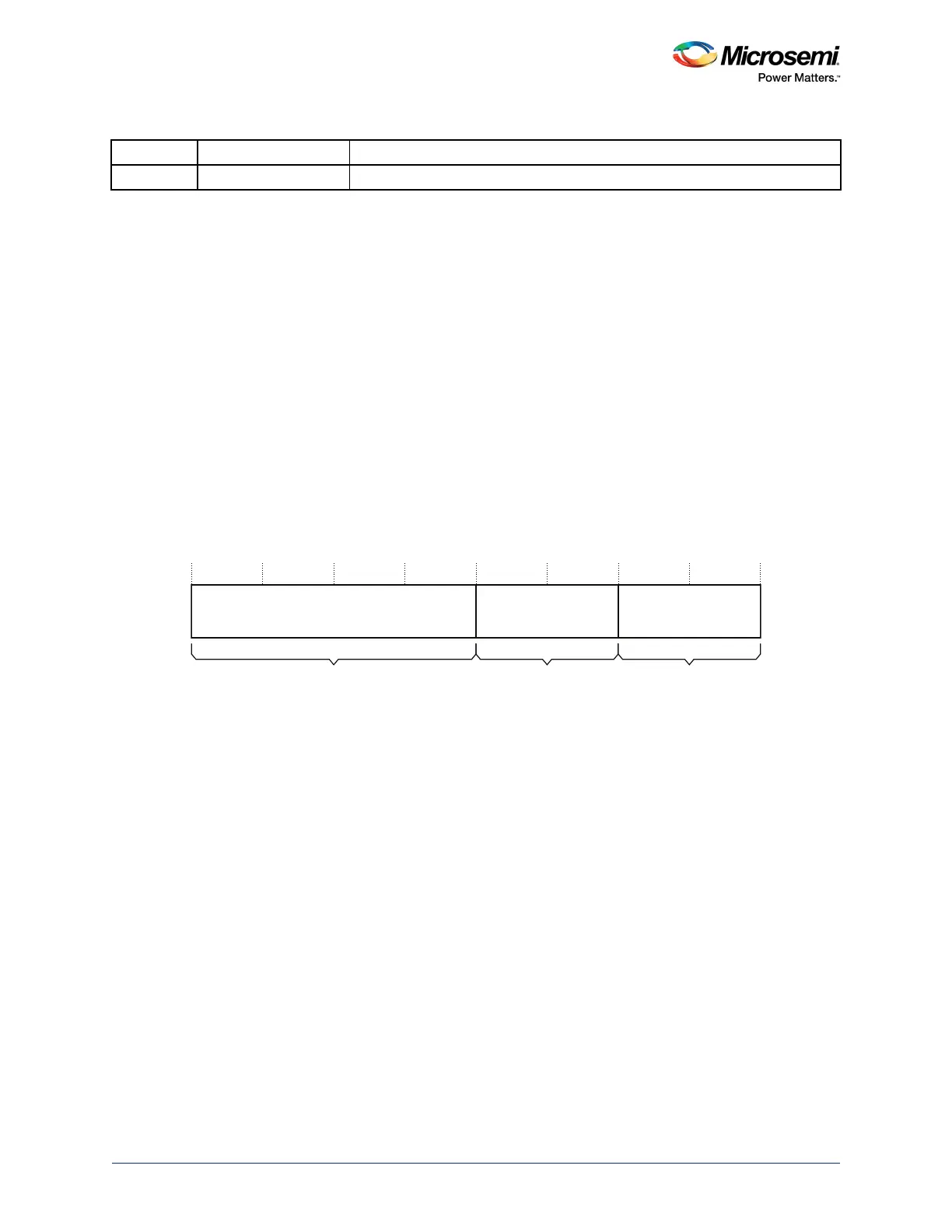
The CFSR indicates the cause of a MemManage fault, BusFault, or UsageFault. See the register
summary in Ta b le 50 , page 102 for its attributes. The bit assignments are:
Figure 41 • CFSR Bit Assignments
The following subsections describe the sub-registers that make up the CFSR:
The CFSR is byte accessible. You can access the CFSR or its sub-registers as follows:
• access the complete CFSR with a word access to 0xE000ED28
• access the MMFSR with a byte access to 0xE000ED28
• access the MMFSR and BFSR with a halfword access to 0xE000ED28
• access the BFSR with a byte access to 0xE000ED29
• access the UFSR with a halfword access to 0xE000ED2A
[0] MEMFAULTACT MemManage exception active bit, reads as 1 if exception is active
1. Enable bits, set to 1 to enable the exception, or set to 0 to disable the exception.
2. Pending bits, read as 1 if the exception is pending, or as 0 if it is not pending. You can write to these bits to change the pending
status of the exceptions.
3. Active bits, read as 1 if the exception is active, or as 0 if it is not active. You can write to these bits to change the active status of
the exceptions, but see the Caution in this section.
Table 63 • SHCSR Bit Assignments (continued)
Bits Name Function
Memory Management
Fault Status Register
31 16 15 8 7 0
Usage Fault Status Register
Bus Fault Status
Register
UFSR BFSR MMFSR
 Loading...
Loading...




