Cortex-M3 Processor (Reference Material)
UG0331 User Guide Revision 15.0 44
even though the stack push for the handler failed. The fault handler operates but the stack contents are
corrupted.
Only Reset and NMI can preempt the fixed priority HardFault. A HardFault can preempt any exception
other than Reset, NMI, or another HardFault.
3.5.4.3 Fault Status Registers and Fault Address Registers
The fault status registers indicate the cause of a fault. For BusFaults and MemManage faults, the fault
address register indicates the address accessed by the operation that caused the fault, as detailed in the
following table.
3.5.4.4 Lockup
The processor enters a lockup state if a fault occurs when executing the NMI or HardFault handlers.
When the processor is in lockup state it does not execute any instructions. The processor remains in
lockup state until either:
• It is reset
• An NMI occurs
• It is halted by the debugger.
Note: If lockup state occurs from the NMI handler a subsequent NMI does not cause the processor to leave
lockup state.
3.5.5 Power Management
The Cortex-M3 processor sleep modes reduce power consumption:
• Sleep mode stops the processor clock.
• Deep sleep mode stops the system clock and switches off the PLL and flash memory.
The SLEEPDEEP bit of the SCR selects which Sleep mode is used, refer to System Control Register,
page 108.
This section describes the mechanisms for entering Sleep mode, and the conditions for waking up from
Sleep mode.
3.5.5.1 Entering Sleep Mode
This section describes the mechanisms software can use to put the processor into Sleep mode.
The system can generate spurious wakeup events, for example a debug operation wakes up the
processor. Therefore software must be able to put the processor back into Sleep mode after such an
event. A program might have an idle loop to put the processor back to Sleep mode.
3.5.5.1.1 Wait for Interrupt
The wait for interrupt instruction,
WFI
, causes immediate entry to sleep mode unless the wake-up
condition is true, see Wakeup from WFI or sleep-on-exit, page 46. When the processor executes a
WFI
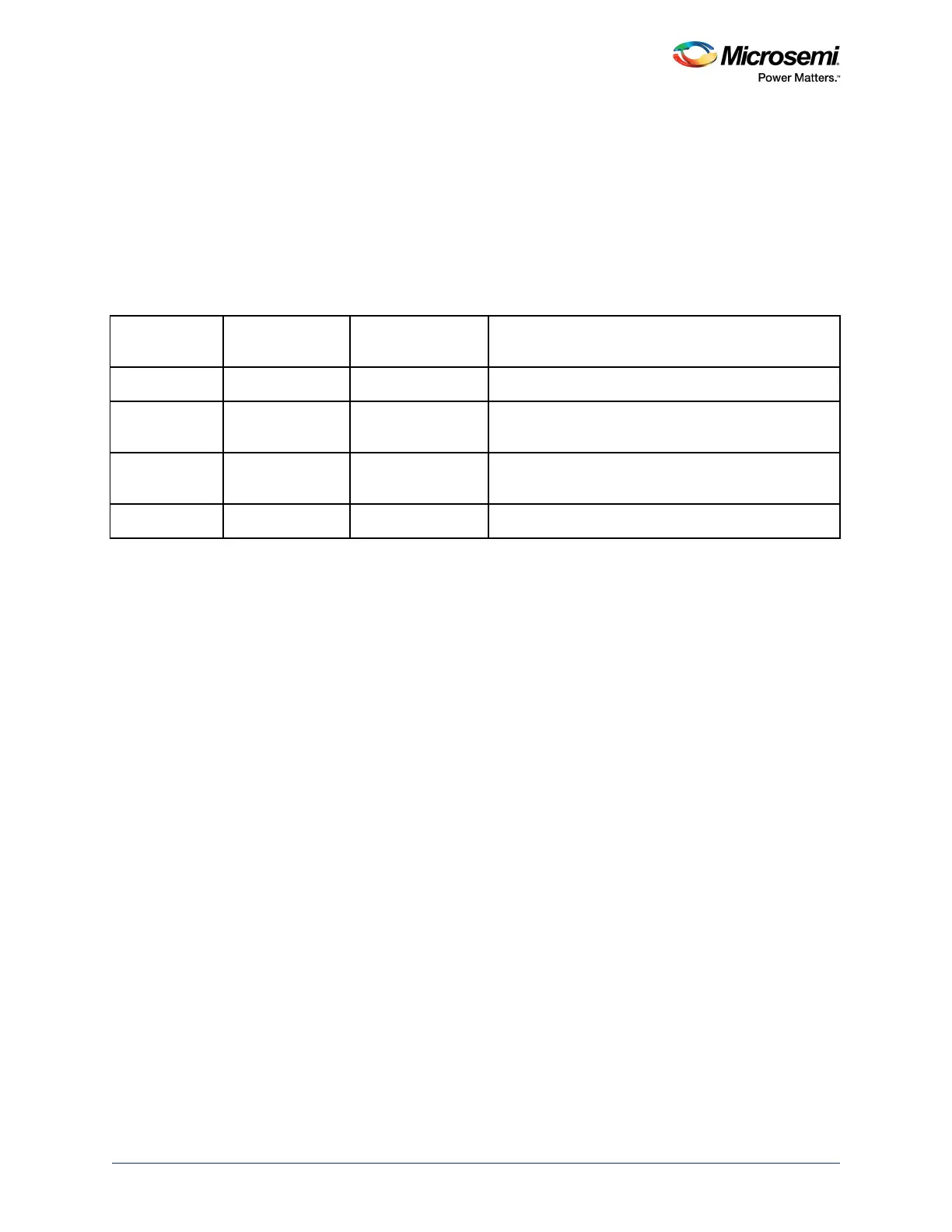
Table 25 • Fault Status and Fault Address Registers
Handler
Status Register
Name
Address Register
Name Register Description
HardFault HFSR HardFault Status Register
MemManage MMFSR MMFAR MemManage Fault Status Register
MemManage Fault Address Register
BusFault BFSR BFAR BusFault Status Register
BusFault Address Register
UsageFault UFSR UsageFault Status Register

 Loading...
Loading...




