Peripheral DMA
UG0331 User Guide Revision 15.0 264
9 Peripheral DMA
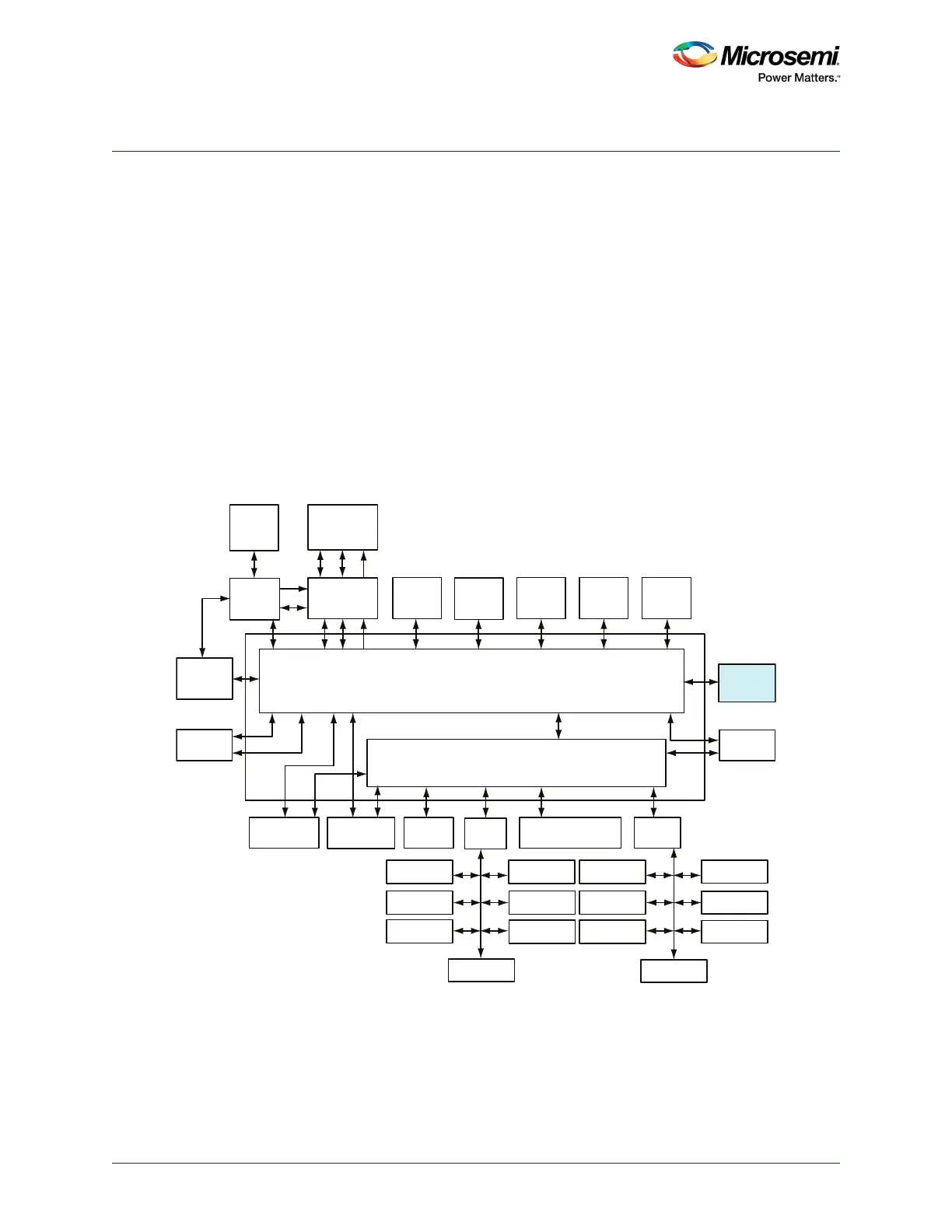
The peripheral direct memory access (PDMA) is an AHB master associated with the AHB bus matrix, as
shown in the following figure. The PDMA allows data transfers from various MSS peripherals to memory,
memory to various peripherals, and memory to memory. The peripheral can be MSS peripheral
(MMUART, CAN, SPI, and COMM_BLK) or fabric peripheral (FIC_0 and FIC_1). The memory can be
MSS memory (eNVM_0, eNVM_1, eSRAM_0, and eSRAM_1) or fabric internal memory (LSRAM and
uSRAM) or external memory connected to fabric.
The PDMA is typically used for off loading byte-intensive operations and involving peripherals from the
Cortex-M3 processor. For example, the firmware could direct the PDMA to transfer the next 1,000
characters received on one of the MMUARTs to eSRAM and notify the processor when ready.
9.1 Features
• Up to 8 DMA channels
• Ping-pong mode support
• Channels priority designations
• Memory to memory DMA capable
• Interrupt capability
Figure 129 • PDMA Interfacing with AHB Bus Matrix
AHB Bus Matrix
eSRAM_0
System
Controller
Cache
Controller
SD IC
ARM Cortex-M3
Processor
SDI
MSS DDR
Bridge
PDMA
MS6
MM3
AHB To AHB Bridge with Address Decoder
USB OTG
HPDMA
MDDR
APB_0
SYSREG
Triple Speed
Ethernet MAC
FIC_0
MM4 MS4
MS2 MS3 MS0
MS5
MS1
MM5 MM6
MM7
MM8
MM2 MM1 MM0 MM9
IDC
D/S
eNVM_0 eNVM_1 eSRAM_1
FIC_2 (Peripheral
Initialization)
APB_1
MMUART_0
SPI_0
I2C_0
PDMA
Configuration
WATCHDOG
FIIC
TIMERx2
MMUART_1
SPI_1
I2C_1
GPIO
CAN
RTC
COMM_BLK
FIC_1
MSS_FIC
MS6_USB
MS5_MAC MS5_SR MS5_APB0 MS5_FIC2 MS5_APB1

 Loading...
Loading...




