Asynchronous Memory Interface
3-20 ADSP-21368 SHARC Processor Hardware Reference
Asynchronous Memory Interface
Both the processor core and the I/O processor have access to external
memory using the AMI. Table 3-9 describes the processor pins used for
interfacing to external memory.
The processor’s memory control signals also permit direct connection to
fast static RAM devices. Memory-mapped peripherals and slower memo-
ries can also connect to the processor using a user-defined combination of
programmable waitstates and hardware acknowledge signals.
External memory can hold data and packed instructions (the ADSP-2136x
cannot execute from external memory). Data packing of 16 to 32 bits or 8
to 32 bits is supported for transfers directly from 32-bit, 16-bit, or 8-bit
wide external memories to and from internal memory.
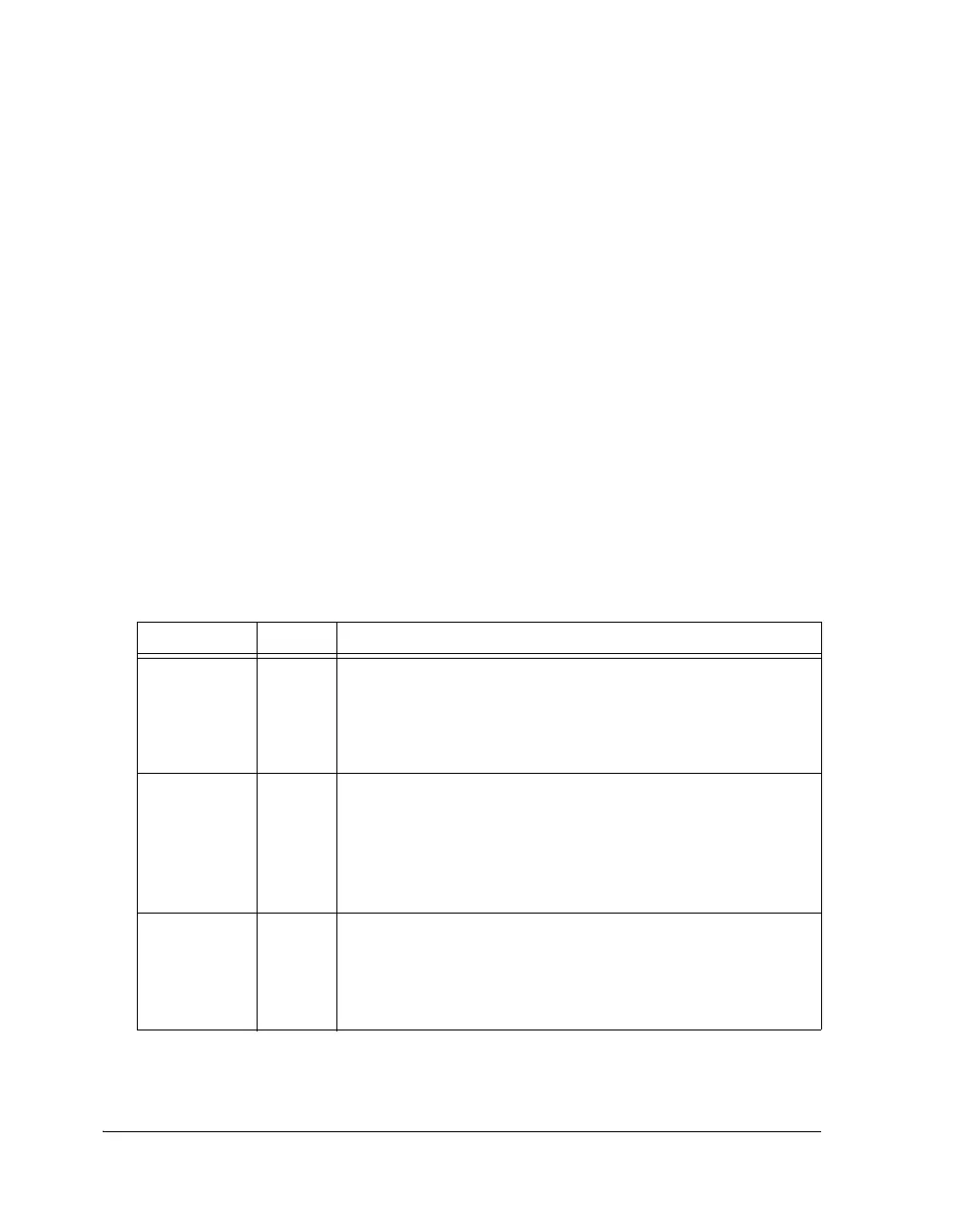
Table 3-9. Asynchronous Memory Interface Signals
Pin Type Description
ACK I Memory Acknowledge. External devices can deassert ACK (low) to
hold off an external memory access. ACK is used by I/O devices,
memory controllers, or other peripherals to hold off completion of
an external memory access. ACK has a 22.5 kΩ internal pull-up
resistor that is enabled during reset.
ADDR23-0 O External Bus Address. The processor outputs addresses for external
memory and peripherals on these pins. A pull-up enabled on the
processor’s ADDR23-0 pins maintains the input at the level it was
last driven. This pull-up is only enabled on the processor with
ID2-0=01x in shared memory system during reset. Note that only
the ADSP-21368 processor has shared memory capability.
DATA31–0 I/O External Bus Data. The processor inputs and outputs data on these
pins. Pull-up resistors on unused data pins are not necessary. A
pull-up on the processor’s DATA31-0 pins maintains the input at
the level it was last driven. This pull-up is only enabled on the pro-
cessors with ID2-0=01x in shared memory system during reset.
 Loading...
Loading...