Programming Examples
12-16 ADSP-21368 SHARC Processor Hardware Reference
2. Program the
TXTWI8 or TXTWI16 register. These are the initial data
values to be transmitted in the event the slave is addressed as a
transmitter. This is an optional step. If no data is written and the
slave is addressed and a transmit is required, the serial clock (SCL) is
stretched and an interrupt is generated.
3. Program the TWIFIFOCTL register. Indicate if transmit (or receive)
FIFO buffer interrupts should occur with each byte transmitted
(received) or with each 2 bytes transmitted (received).
4. Program the TWIIMASK register. Enable bits associated with the
desired interrupt sources. As an example, programming the value
0x000F results in an interrupt output to the processor when a valid
address match is detected, a valid slave transfer completes, a slave
transfer has an error, or a subsequent transfer has begun but the
previous transfer has not been serviced.
5. Program the TWISCTL register. This prepares and enables slave
mode operation. As an example, programming the value 0x0005
enables slave mode operation, requires 7-bit addressing, and indi-
cates that data in the transmit FIFO buffer is intended for slave
mode transmission.
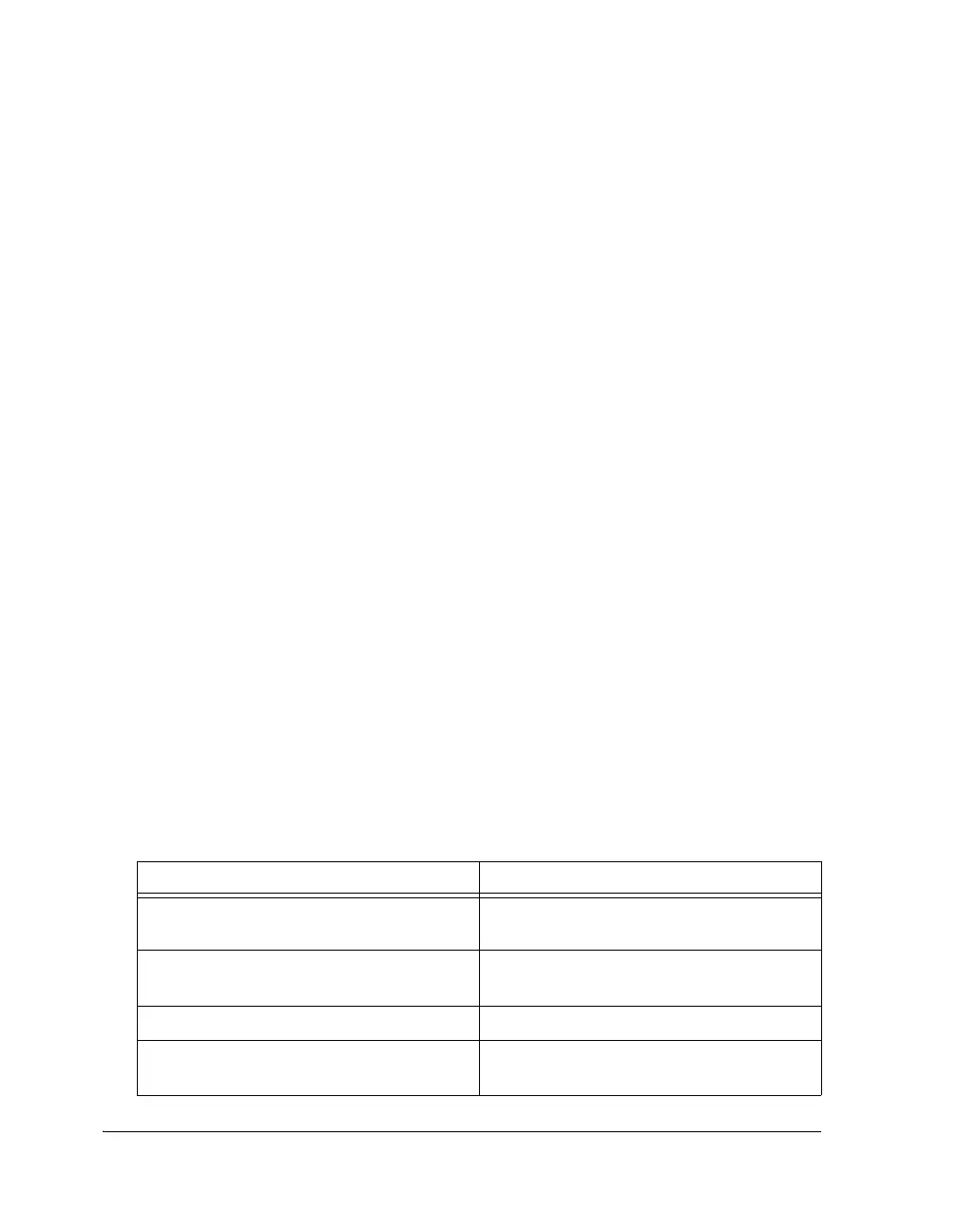
Table 12-2 shows what the interaction between the TWI controller and
the processor might look like when the slave is addressed as a receiver.
Table 12-2. Slave Mode Setup Interaction (Slave Addressed as Receiver)
TWI Controller Master Processor
Interrupt: TWISINIT – Slave transfer has been
initiated.
Acknowledge: Clear interrupt source bits.
Interrupt: TWIRXS – Receive buffer has 1 or 2
bytes (according to TWIRXINT).
Read receive FIFO buffer.
Acknowledge: Clear interrupt source bits.
... ...
Interrupt: TWISCOMP – Slave transfer com-
plete.
Read receive FIFO buffer.
Acknowledge: Clear interrupt source bits.

 Loading...
Loading...