SPI Data Transfer Operations
6-18 ADSP-21368 SHARC Processor Hardware Reference
Master Transfer Preparation
When the processor is enabled as a master, the initiation of a transfer is
defined by the two bit fields (bits 1–0) of
TIMOD in the SPICTLx registers.
Based on these two bits and the status of the interface, a new transfer is
started upon either a read of the RXSPIx registers or a write to the TXSPIx
registers. This is summarized in Table 6-1.
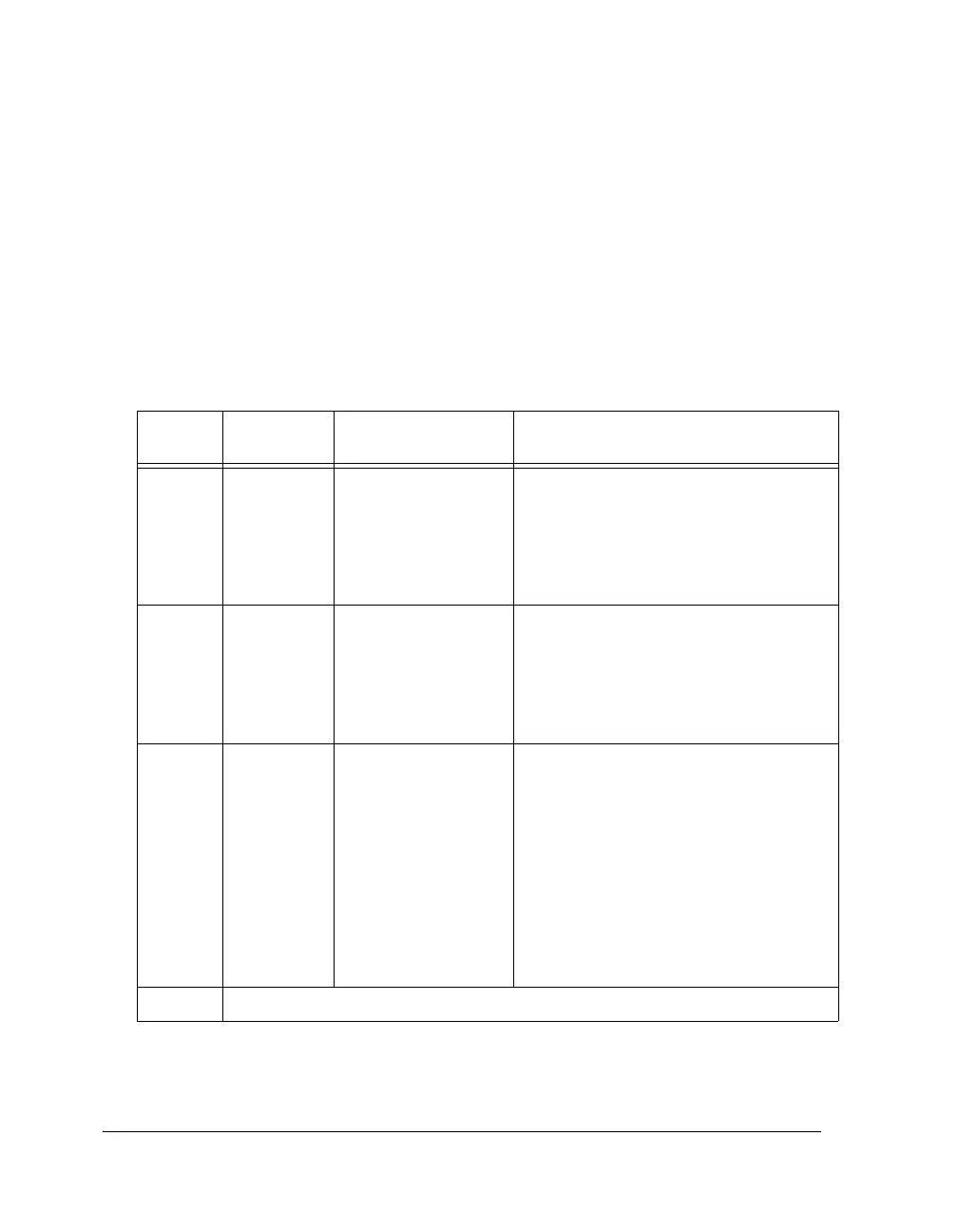
Table 6-1. Transfer Initiation
TIMOD Function Transfer Initiated
Upon
Action, Interrupt
00 Transmit and
Receive
Initiate new single
word transfer upon
read of RXSPI and pre-
vious transfer
completed.
The SPI interrupt is latched in every core
clock cycle in which the RXSPI buffer has a
word in it.
Emptying the RXSPI buffer or disabling the
SPI port at the same time (SPIEN = 0) stops
the interrupt latch.
01 Transmit and
Receive
Initiate new single
word transfer upon
write to TXSPI and
previous transfer
completed.
The SPI interrupt is latched in every core
clock cycle in which the TXSPI buffer is
empty.
Writing to the TXSPI buffer or disabling the
SPI port at the same time (SPIEN = 0) stops
the interrupt latch.
10 Transmit or
Receive with
DMA
Initiate new multiword
transfer upon write to
DMA enable bit. Indi-
vidual word transfers
begin with either a
DMA write to TXSPI
or a DMA read of
RXSPI depending on
the direction of the
transfer as specified by
the SPIRCV bit.
If chaining is disabled, the SPI interrupt is
latched in the cycle when the DMA count
decrements from 1 to 0.
If chaining is enabled, interrupt function is
based on the CPI bit in the CP register. If
CPI = 0, the SPI interrupt is latched at the
end of the DMA sequence. If CPI = 1, then
the SPI interrupt is latched after each DMA
in the sequence. For more information, see
“DMA Transfer Direction” on page 2-24.
11 Reserved

 Loading...
Loading...