R01UH0823EJ0100 Rev.1.00 Page 384 of 1823
Jul 31, 2019
RX23W Group 19. Data Transfer Controller (DTCa)
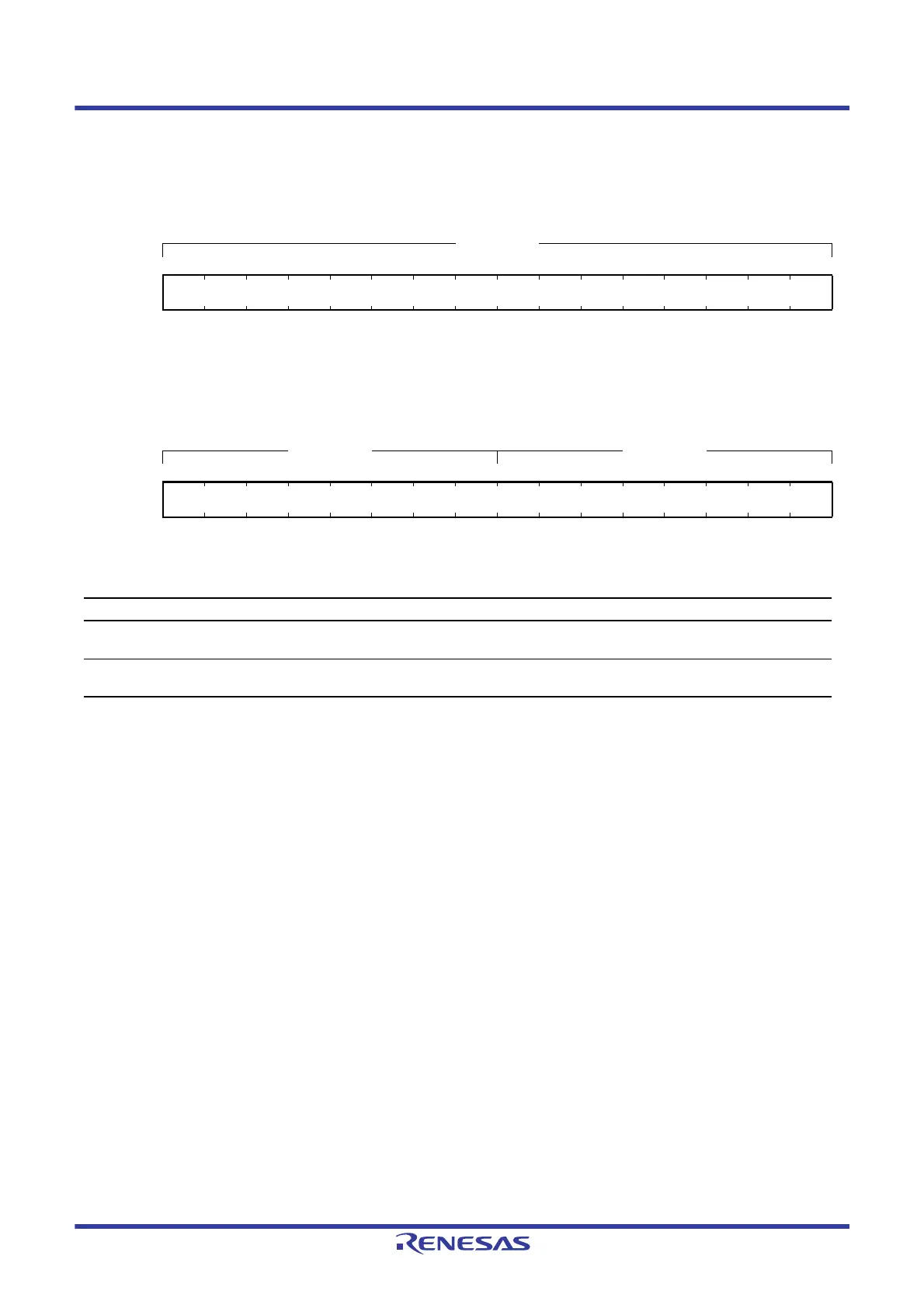
19.2.5 DTC Transfer Count Register A (CRA)
Normal transfer mode
Repeat transfer mode/block transfer mode
Note: The function depends on transfer mode.
Note: Set CRAH and CRAL to the same value in repeat transfer mode and block transfer mode.
This register is for counting the number of transfers and cannot be accessed directly from the CPU.
(1) Normal transfer mode (MRA.MD[1:0] bits = 00b)
CRA register functions as a 16-bit transfer counter in normal transfer mode.
The transfer count is 1, 65535, and 65536 when the set value is 0001h, FFFFh, and 0000h, respectively.
The CRA value is decremented (–1) at each data transfer.
(2) Repeat transfer mode (MRA.MD[1:0] bits = 01b)
The CRAH register retains the transfer count and the CRAL register functions as an 8-bit transfer counter.
The transfer count is 1, 255, and 256 when the set value is 01h, FFh, and 00h, respectively.
The CRAL value is decremented (–1) at each data transfer. When it reaches 00h, the CRAH value is reloaded to the
CRAL register.
(3) Block transfer mode (MRA.MD[1:0] bits = 10b)
The CRAH register retains the block size and the CRAL register functions as an 8-bit block size counter.
The transfer count is 1, 255, and 256 when the set value is 01h, FFh, and 00h, respectively.
The CRAL value is decremented (–1) at each data transfer. When it reaches 00h, the CRAH value is reloaded to the
CRAL register.
Address(es): (inaccessible directly from the CPU)
CRA
b15 b14 b13 b12 b11 b10 b9 b8 b7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0
Value after reset:
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
x: Undefined
Address(es): (inaccessible directly from the CPU)
CRAH CRAL
b15 b14 b13 b12 b11 b10 b9 b8 b7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0
Value after reset:
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
x: Undefined
Symbol Register Name Description R/W
CRAL Transfer Counter A Lower Register Set transfer count. This register functions as a transfer counter
during data transfer.
—
CRAH Transfer Counter A Upper Register Set transfer count. This register functions as a reload register
during data transfer.
—

 Loading...
Loading...