R01UH0823EJ0100 Rev.1.00 Page 951 of 1823
Jul 31, 2019
RX23W Group 32. USB 2.0 Host/Function Module (USBc)
(4) Setup of Data to be Transmitted Using Isochronous Transfer When the Function Controller is
Selected
With isochronous data transmission using the USB in the function controller, after data has been written to the buffer
memory, a data packet can be transmitted with the next frame after the frame in which an SOF packet is detected. This
function is called the isochronous transfer transmission data setup function, and it makes it possible to designate the
frame from which transmission began.
In a double buffer configuration, even after the writing of data to both buffers has been completed, transmission will be
enabled for only one buffer to which data writing was completed first. Accordingly, even if multiple IN tokens are
received, only one packet of data is transmitted from a single buffer.
When an IN token is received, if the buffer memory is in the transmission enabled state, the USB transmits data as a
normal response. If the buffer memory is not in the transmission enabled state, however, a zero-length packet is sent and
an underrun error occurs.
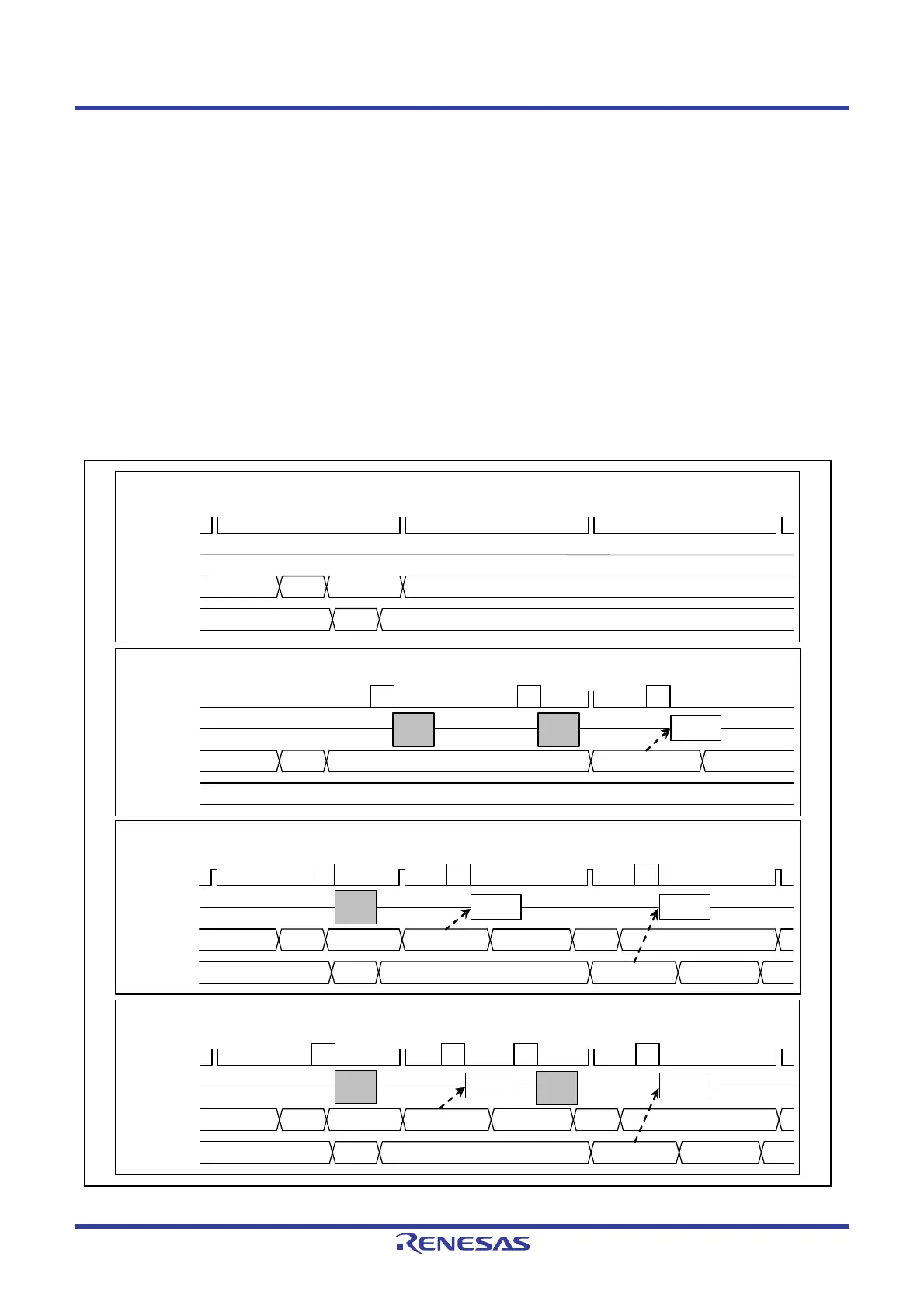
Figure 32.18 shows an example of transmission using the isochronous transfer transmission data setup function with the
USB when IITV[2:0] = 000b (every frame) has been set.
Figure 32.18 Example of Data Setup Function Operation
Zero-
length
Transfer enabled
Writing
Writing
ended
Writing Writing ended
Empty
Empty
IN
Transfer enabled
IN IN
IN
IN
IN IN
Transfer enabled
IN IN
Empty
IN
Empty
Data-A
Data-BData-A
Data-BData-A
(4) Example of IN token reception outside the interval
SOF SOF SOF SOF
Zero-
length
Zero-
length
Zero-
length
Buffer A
Buffer B
Receive token
Transmit packet
SOF SOF
SOF
SOF
(3) Reception starting example 2 (when transmit data is ready after IN token reception starts (2))
Buffer A
Buffer B
Receive token
Transmit packet
(1) Reception starting example 1 (when transmit data is ready before IN token reception starts)
Buffer A
Buffer B
Receive token
Transmit packet
Zero-
length
SOF SOF SOF SOF
(2) Reception starting example 2 (when transmit data is ready after IN token reception starts (1))
Buffer A
Buffer B
Receive token
Transmit packet
SOF
Writing Writing endedEmpty
Writing
Writing
ended
Empty Writing
Writing ended
Empty
Writing
Writing ended
Empty Transfer enabled Empty
Transfer enabledWriting
Writing
ended
Empty Writing
Writing ended
Empty
Writing
Writing ended
Empty Transfer enabled Empty

 Loading...
Loading...