Functional Description
www.ti.com
68
SWRU543–January 2019
Submit Documentation Feedback
Copyright © 2019, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Cortex
®
-M4 Processor
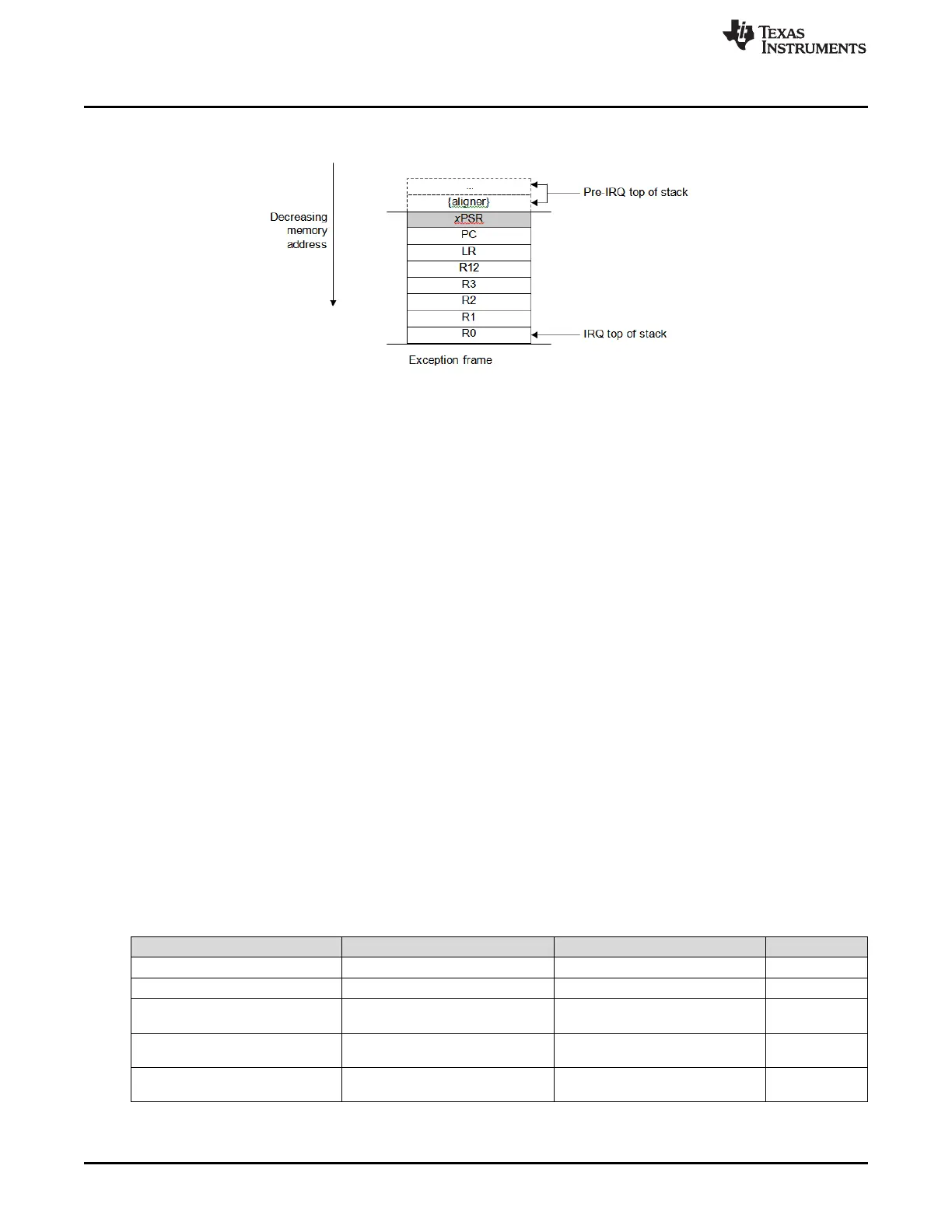
Figure 2-6. Exception Stack Frame
Immediately after stacking, the stack pointer indicates the lowest address in the stack frame.
The stack frame includes the return address, which is the address of the next instruction in the interrupted
program. This value is restored to the PC at exception return so that the interrupted program resumes.
In parallel with the stacking operation, the processor performs a vector fetch that reads the exception
handler start address from the vector table. When stacking is complete, the processor starts executing the
exception handler. At the same time, the processor writes an EXC_RETURN value to the LR, indicating
which stack pointer corresponds to the stack frame and which operation mode the processor was in
before the entry occurred.
If no higher-priority exception occurs during exception entry, the processor starts executing the exception
handler and automatically changes the status of the corresponding pending interrupt to active.
If another higher-priority exception occurs during exception entry, known as late arrival, the processor
starts executing the exception handler for this exception and does not change the pending status of the
earlier exception
2.2.5 Fault Handling
Faults are a subset of the exceptions (see Section 2.2.4). The following conditions generate a fault:
• A bus error on an instruction fetch, vector table load, or a data access
• An internally detected error, such as an undefined instruction or an attempt to change state with a BX
instruction
• Attempting to execute an instruction from a memory region marked as nonexecutable (XN)
2.2.5.1 Fault Types
Table 2-8 lists the types of fault, the handler used for the fault, the corresponding fault status register, and
the name of the register bit that indicates the fault has occurred.
(1)
Occurs on an access to an XN region.
Table 2-8. Faults
Fault Handler Fault Status Register Bit Name
Bus error on a vector read Hard fault Hard Fault Status (HFAULTSTAT) VECT
Fault escalated to a hard fault Hard fault Hard Fault Status (HFAULTSTAT) FORCED
Default memory mismatch on
instruction access
Memory management fault Memory Management Fault Status
(MFAULTSTAT)
IERR
(1)
Default memory mismatch on data
access
Memory management fault Memory Management Fault Status
(MFAULTSTAT)
DERR
Default memory mismatch on
exception stacking
Memory management fault Memory Management Fault Status
(MFAULTSTAT)
MSTKE
 Loading...
Loading...