Memory Protection Unit (MPU)
MPC5606S Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 7
Freescale Semiconductor 897
As shown in Figure 24-10, the output of the protection violation logic is the error signal.
The access evaluation macro then uses the hit_b and error signals to form two outputs. The combined
(hit_b | error) signal signals that the current access is not allowed, and (~hit_b & error) is used as the input
to MPU_EDRn (error detail register) in the event of an error.
24.3.2 Putting It All Together and AHB Error Terminations
For each AHB slave port being monitored, the MPU performs a reduction-AND of all the individual (hit_b
| error) terms from each access evaluation macro. This expression then terminates the bus cycle with an
error and reports a protection error for three conditions:
1. If the access does not hit in any region descriptor, a protection error is reported.
2. If the access hits in a single region descriptor and that region signals a protection violation, then a
protection error is reported.
3. If the access hits in multiple (overlapping) regions and all regions signal protection violations, then
a protection error is reported.
The third condition reflects that priority is given to permission granting over access denying for
overlapping regions as this approach provides more flexibility to system software in region descriptor
assignments. For an example of the use of overlapping region descriptors, see
Section 24.5, Application
information.
In event of a protection error, the MPU requires two distinct actions:
1. intercepts the error during the AHB address phase (first cycle out of two) and cancels the
transaction before it is seen by the slave device.
2. performs the required logic functions to force the standard 2-cycle AHB error response to properly
terminate the bus transaction and then provides the right values to the crossbar switch to commit
the AHB transaction to other portions of the platform.
If instead the access is allowed, then the MPU simply passes all “original” AHB signals to the slave device.
In this case, from functionality point of view, the MPU is fully transparent.
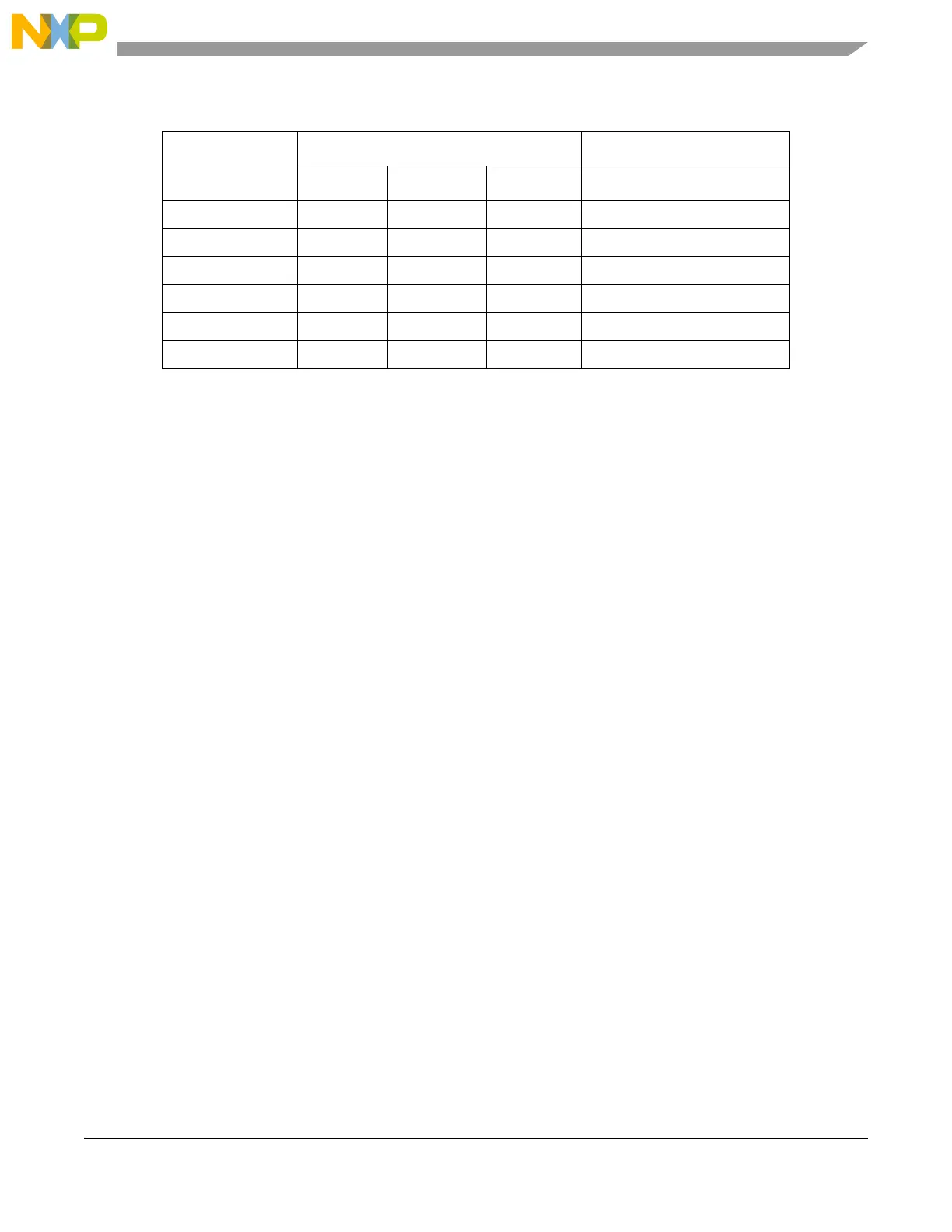
Table 24-10. Protection Violation Definition
Description
Inputs Output
eff_rgd[r] eff_rgd[w] eff_rgd[x] Protection Violation?
inst fetch read — — 0 yes, no x permission
inst fetch read — — 1 no, access is allowed
data read 0 — — yes, no r permission
data read 1 — — no, access is allowed
data write — 0 — yes, no w permission
data write — 1 — no, access is allowed
 Loading...
Loading...