Understanding How Behavior Aggregate Classifiers Prioritize Trusted Traffic
The idea behind class of service (CoS) is that packets are not treated identically by the
routers or switches on the network. In order to selectively apply service classes to specific
packets, the packets of interest must be classified in some fashion.
The simplest way to classify a packet is to use behavior aggregate (BA) classification,
also called the CoS value in this document. The DSCP, DSCP IPv6, or IP precedence bits
of the IP header convey the behavior aggregate class information. The information might
also be found in the MPLS EXP bits, IEEE 802.1ad, or IEEE 802.1p CoS bits.
NOTE: Support was added for filtering on Differentiated Services Code Point
(DSCP) and forwarding class for Routing Engine sourced packets, including
IS-IS packets encapsulated in generic routing encapsulation (GRE).
Subsequently, when upgrading from a previous version of Junos OS where
you have both a class of service (CoS) and firewall filter, and both include
DSCP or forwarding class filter actions, the criteria in the firewall filter
automatically takes precedence overthe CoS settings. The same is true when
creating new configurations; that is, where the same settings exist, the firewall
filter takes precedence over the CoS, regardless of which was created first.
BA classification is useful if the traffic comes from a trusted source and the CoS value
in the packet header is trusted. If the traffic is untrusted, multifield classifiers (see
“Overview of Assigning Service Levels to Packets Based on Multiple Packet Header Fields”
on page 891) are used to classify packets based on multiple packet fields. It is common
to use multifield classifiers to classify traffic at the ingress of a network, rewrite the packet
headers (see Rewriting Packet Headers to Ensure Forwarding Behavior), then use the more
efficient BA classification for transversing the network.
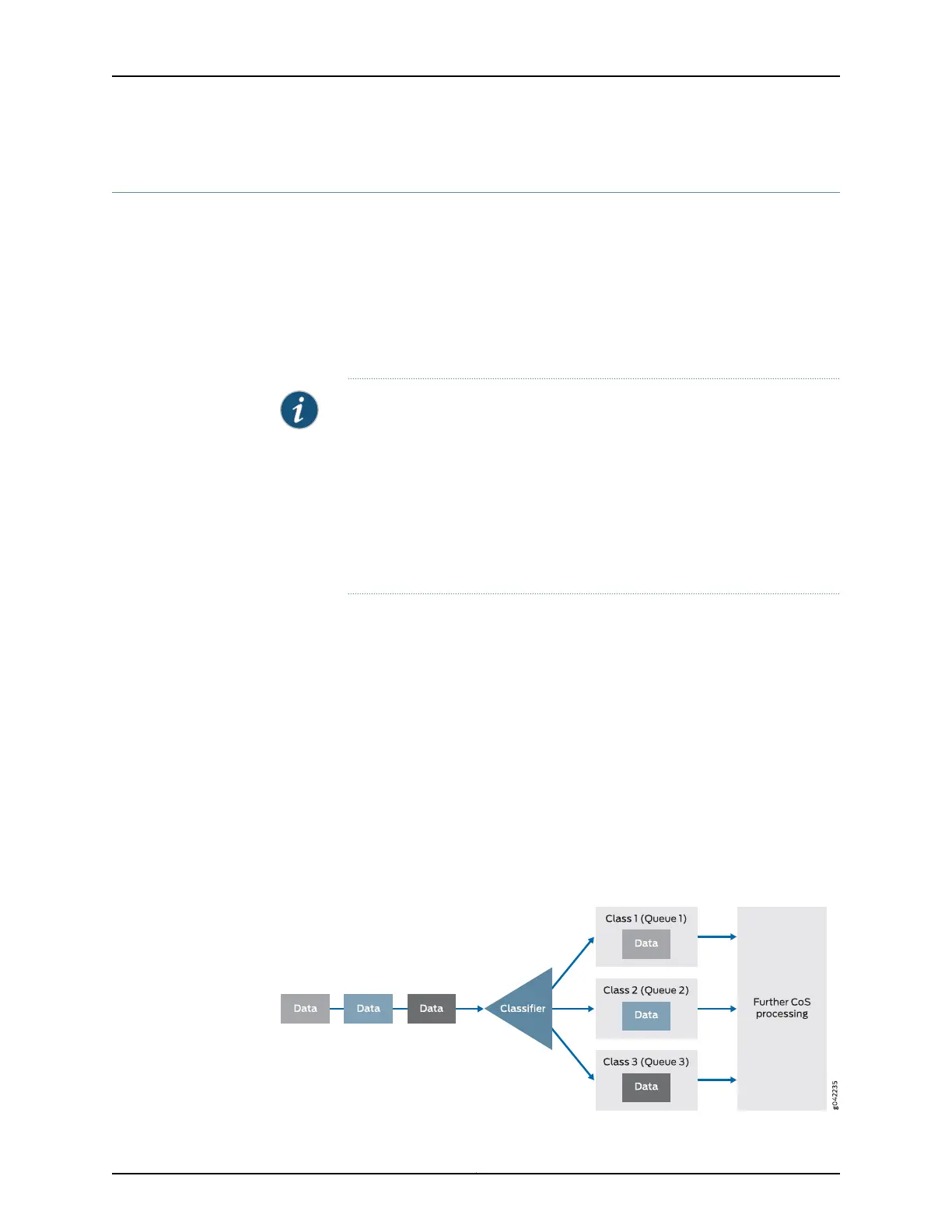
The BA classifier maps a CoS value in the packet header to a forwarding class and loss
priority. The forwarding class determines the output queue. The loss priority is used by
schedulers in conjunction with the random early discard (RED) algorithm to control
packet discard during periods of congestion.
Figure 59 on page 950 provides a high-level illustration of how a classifier works.
Figure 59: How a Classifier Works
Copyright © 2017, Juniper Networks, Inc.950
ACX Series Universal Access Router Configuration Guide

 Loading...
Loading...