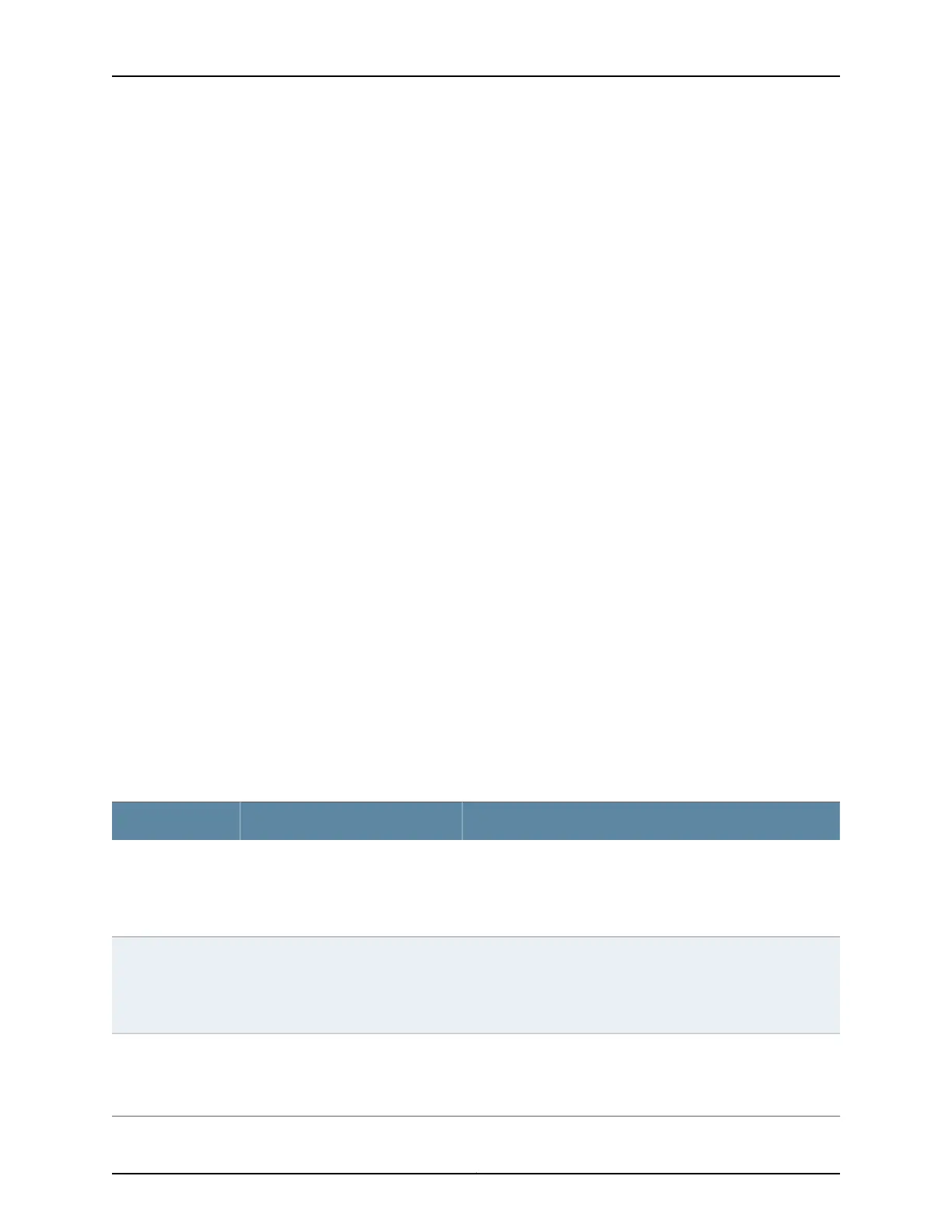For LAG bundles, the hashing algorithm determines how traffic entering a LAG bundle is
placed onto the bundle’s member links. The hashing algorithm tries to manage bandwidth
by evenly load-balancing all incoming traffic across the member links in the bundle.
The hashing algorithm makes hashing decisions based on values in various packet fields,
as well as on some internal values like source port ID and source device ID. The packet
fields used by the hashing algorithm varies by the packet’s EtherType and, in some
instances, by the configuration on the router. The hashing algorithm recognizes the
following EtherTypes:
•
IPv4
•
MPLS
Traffic that is not recognized as belonging to any of these EtherTypes is hashed based
on the Layer 2 header. IP and MPLS traffic are also hashed based on the Layer 2 header
when a user configures the hash mode as Layer 2 header.
You can configure some fields that are used by the hashing algorithm to make traffic
forwarding decisions. You cannot, however, configure how certain values within a header
are used by the hashing algorithm.
Note the following points regarding the hashing algorithm:
•
The fields selected for hashing are based on the packet type only. The fields are not
based on any other parameters, including forwarding decision (bridged or routed) or
egress LAG bundle configuration (Layer 2 or Layer 3).
•
The same fields are used for hashing unicast and multicast packets. Unicast and
multicast packets are, however, hashed differently.
Table 25 on page 157 describes the fields used for hashing by Layer 2 services. The table
explains the default behavior and the configurable fields based on the type of traffic
received on the Layer 2 service
Table 25: Hashing Behavior for Pseudowire (Layer 2 Circuit) and Bridging Services
Configurable Fields (Hash keys)Default Hash FieldsTraffic Type
Source MAC Address
Destination MAC
Source MAC and Destination MAC
NoneLayer 2
Source MAC Address
Destination MAC
Source MAC and Destination MAC
Source IP and Destination IPIP
Source MAC Address
Destination MAC
Source MAC and Destination MAC
MPLS label 1 and MPLS label 2MPLS
157Copyright © 2017, Juniper Networks, Inc.
Chapter 4: Configuring Interfaces and Chassis
 Loading...
Loading...