interface. If the VLAN tags associated with an outbound logical interface do not match
the normalizing VLAN identifier configured for the VLAN or VPLS routing instance, the
VLAN tags are rewritten as described in Table 49 on page 758.
The tables below show how VLAN tags are applied for traffic sent to and from the VLAN,
depending on how the vlan-id and vlan-tags statements are configured for the VLAN and
on how identifiers are configured for the logical interfaces in a VLAN or VPLS routing
instance. Depending on your configuration, the following rewrite operations are performed
on VLAN tags:
•
pop—Remove a VLAN tag from the top of the VLAN tag stack.
•
pop-pop—Remove both the outer and inner VLAN tags of the frame.
•
pop-swap—Remove the outer VLAN tag of the frame and replace the inner VLAN tag
of the frame.
•
swap—Replace the VLAN tag of the frame.
•
push—Add a new VLAN tag to the top of the VLAN stack.
•
push-push—Push two VLAN tags in front of the frame.
•
swap-push—Replace the VLAN tag of the frame and add a new VLAN tag to the top
of the VLAN stack.
•
swap-swap—Replace both the outer and inner VLAN tags of the frame.
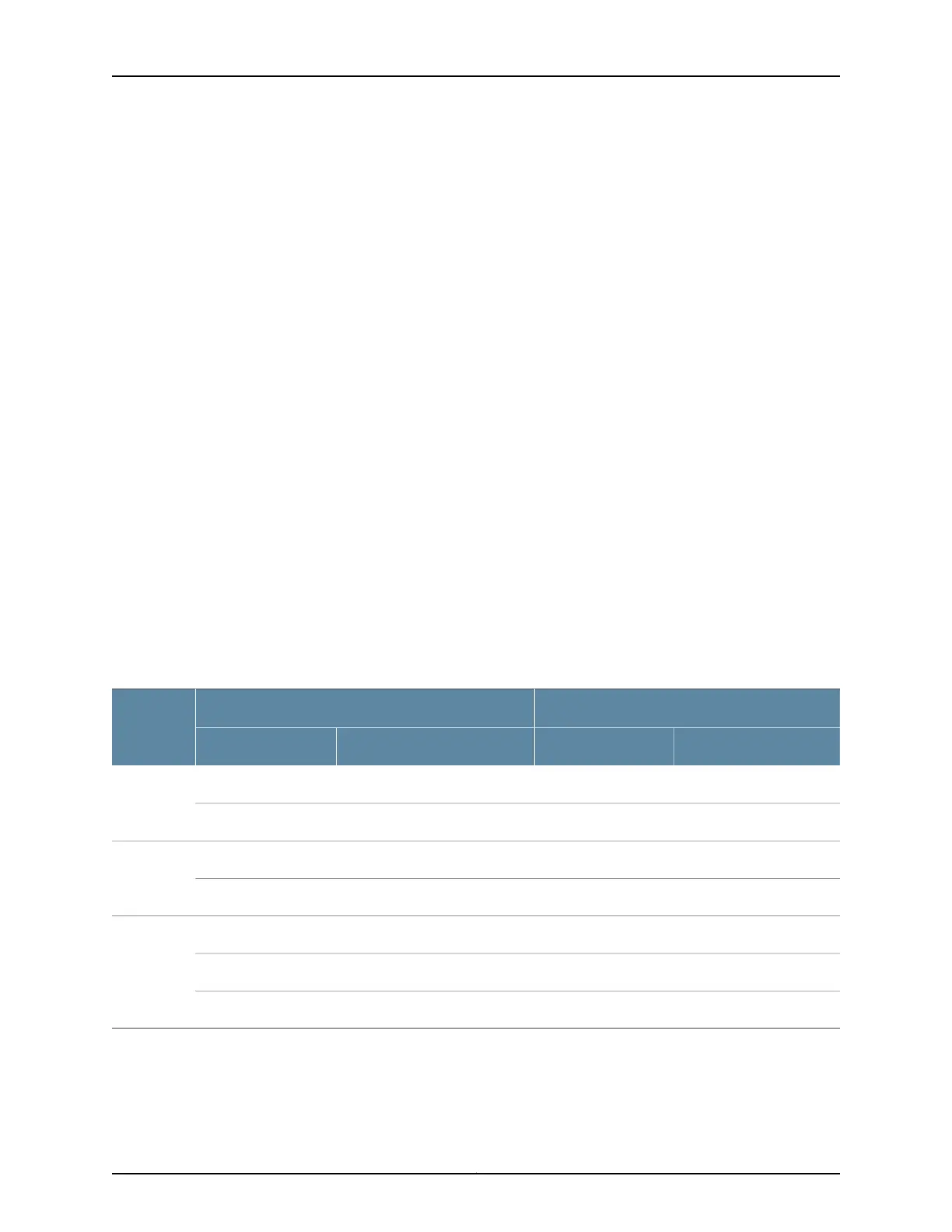
Table 103 on page 1264 shows the supported input and output VLAN map configurations.
Table 103: Supported Input and Output VLAN Map Configurations
Output-mapInput-map
Interface
Type
ParametersConfigurationParametersConfiguration
Nonepoptpid.outer-vlanpushUntagged
Nonepop-poptpid.outer-vlan/ inner-vlanpush-push
tpid.outer-vlanswaptpid.outer-vlanswapSingle
tagged
Nonepoptpid.outer-vlanpush
tpid.outer-vlanswaptpid.outer-vlanswapDual tagged
tpid.outer-vlanpushNonepop
tpid.outer-vlanswap-swaptpid.outer-vlan/inner-vlanswap-swap
Table 48 on page 758 shows specific examples of how the VLAN tags for packets sent to
the VLAN are processed and translated, depending on your configuration. “–” means
that the statement is not supported for the specified logical interface VLAN identifier.
Copyright © 2017, Juniper Networks, Inc.1264
ACX Series Universal Access Router Configuration Guide
 Loading...
Loading...