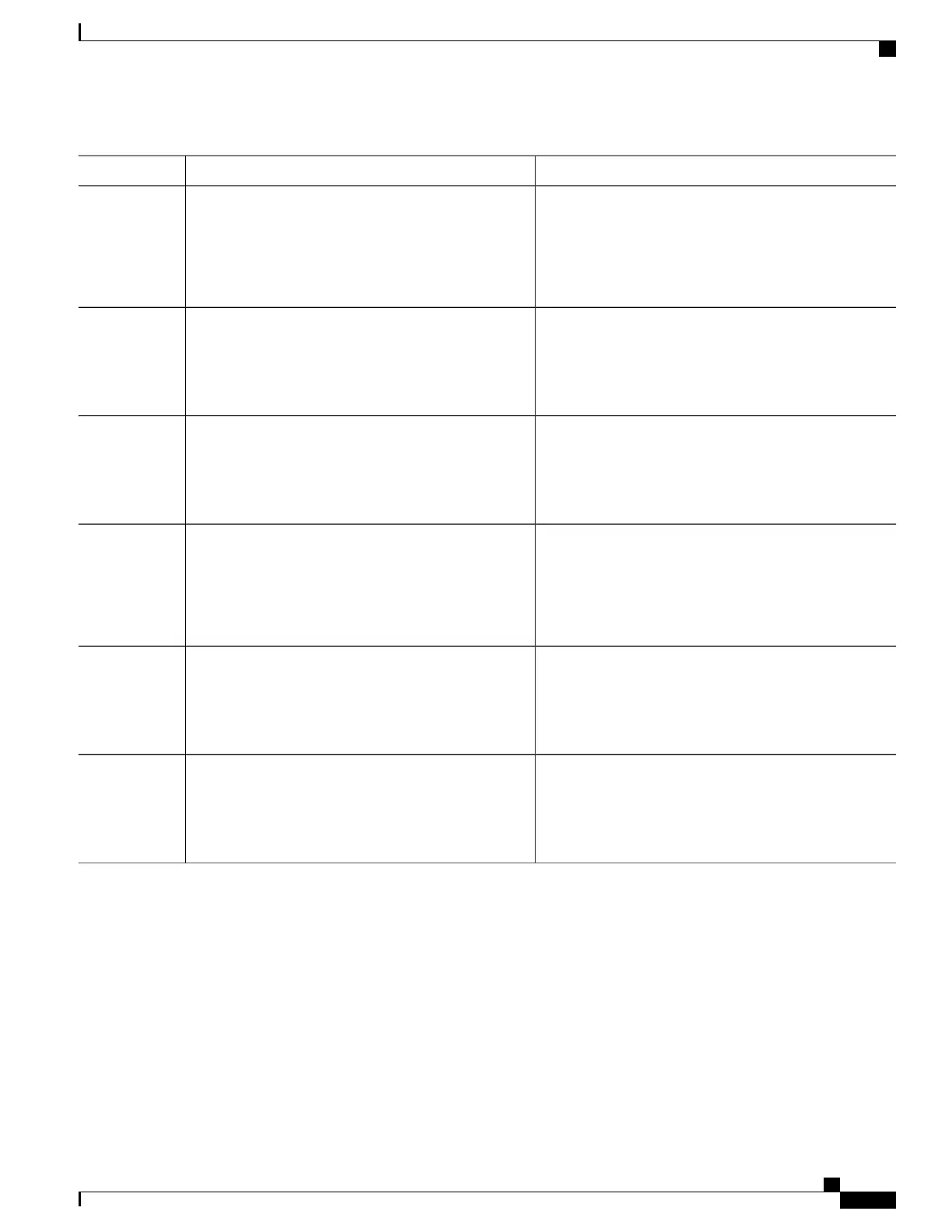
PurposeCommand or Action
Identifies a specific interface, and enter interface
configuration mode. The interface must be a physical Layer
2 interface (port ACL).
interface interface-id
Example:
Switch(config)# interface gigabitethernet1/0/2
Step 3
Controls access to the specified interface by using the
MAC access list.
mac access-group {name} {in | out }
Example:
Switch(config-if)# mac access-group mac1 in
Step 4
Port ACLs are supported in the outbound and inbound
directions .
Returns to privileged EXEC mode.end
Example:
Switch(config-if)# end
Step 5
Displays the MAC access list applied to the interface or
all Layer 2 interfaces.
show mac access-group [interface interface-id]
Example:
Switch# show mac access-group interface
Step 6
gigabitethernet1/0/2
Verifies your entries.show running-config
Example:
Switch# show running-config
Step 7
(Optional) Saves your entries in the configuration file.copy running-config startup-config
Example:
Switch# copy running-config startup-config
Step 8
After receiving a packet, the switch checks it against the inbound ACL. If the ACL permits it, the switch
continues to process the packet. If the ACL rejects the packet, the switch discards it. When you apply an
undefined ACL to an interface, the switch acts as if the ACL has not been applied and permits all packets.
Remember this behavior if you use undefined ACLs for network security.
Configuring VLAN Maps
To create a VLAN map and apply it to one or more VLANs, perform these steps:
Consolidated Platform Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS Release 15.2(4)E (Catalyst 2960-X Switches)
1251
How to Configure VLAN Access Control Lists

 Loading...
Loading...









