while waiting to be processed. In this situation, the response times would not accurately represent true network
delays. IP SLAs minimize these processing delays on the source device as well as on the target device (if the
responder is being used) to determine true round-trip times. IP SLA test packets use time stamping to minimize
the processing delays.
When the IP SLA responder is enabled, it allows the target device to take time stamps when the packet arrives
on the interface at interrupt level and again just as it is leaving, eliminating the processing time. This time
stamping is made with a granularity of sub-milliseconds (ms).
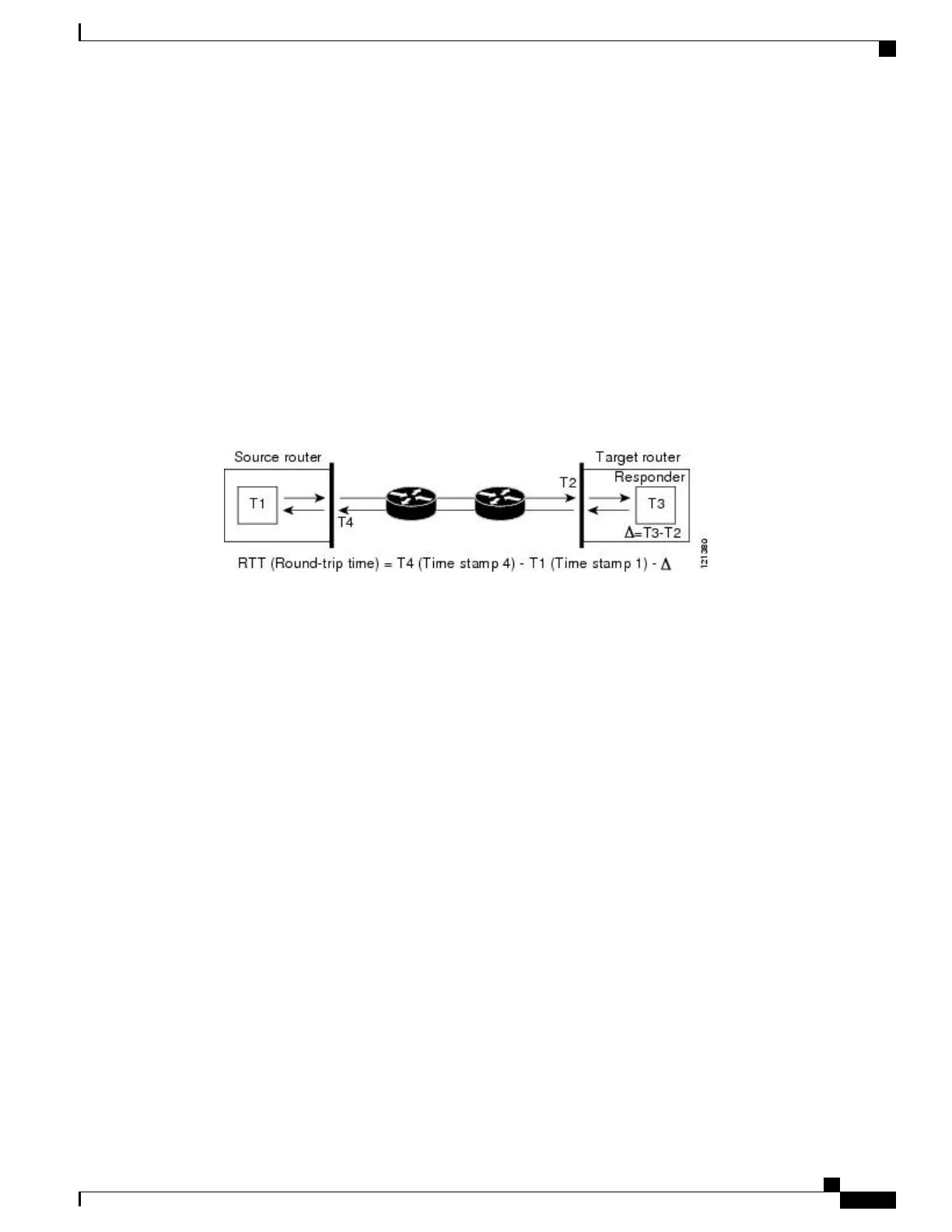
The following figure demonstrates how the responder works. Four time stamps are taken to make the calculation
for round-trip time. At the target router, with the responder functionality enabled, time stamp 2 (TS2) is
subtracted from time stamp 3 (TS3) to produce the time spent processing the test packet as represented by
delta. This delta value is then subtracted from the overall round-trip time. Notice that the same principle is
applied by IP SLAs on the source router where the incoming time stamp 4 (TS4) is also taken at the interrupt
level to allow for greater accuracy.
Figure 115: Cisco IOS IP SLA Responder Time Stamping
An additional benefit of the two time stamps at the target device is the ability to track one-way delay, jitter,
and directional packet loss. Because much network behavior is asynchronous, it is critical to have these
statistics. However, to capture one-way delay measurements, you must configure both the source router and
target router with Network Time Protocol (NTP) so that the source and target are synchronized to the same
clock source. One-way jitter measurements do not require clock synchronization.
Related Topics
Configuring the IP SLA Responder, on page 2030
Restrictions on SLAs, on page 2025
Monitoring IP SLA Operations, on page 2031
How to Configure IP SLAs Operations
This section does not include configuration information for all available operations as the configuration
information details are included in the Cisco IOS IP SLAs Configuration Guide. It does include several
operations as examples, including configuring the responder, configuring a UDP jitter operation, which requires
a responder, and configuring an ICMP echo operation, which does not require a responder. For details about
configuring other operations, see the Cisco IOS IP SLAs Configuration Guide.
Default Configuration
No IP SLAs operations are configured.
Consolidated Platform Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS Release 15.2(4)E (Catalyst 2960-X Switches)
2029
How to Configure IP SLAs Operations

 Loading...
Loading...









