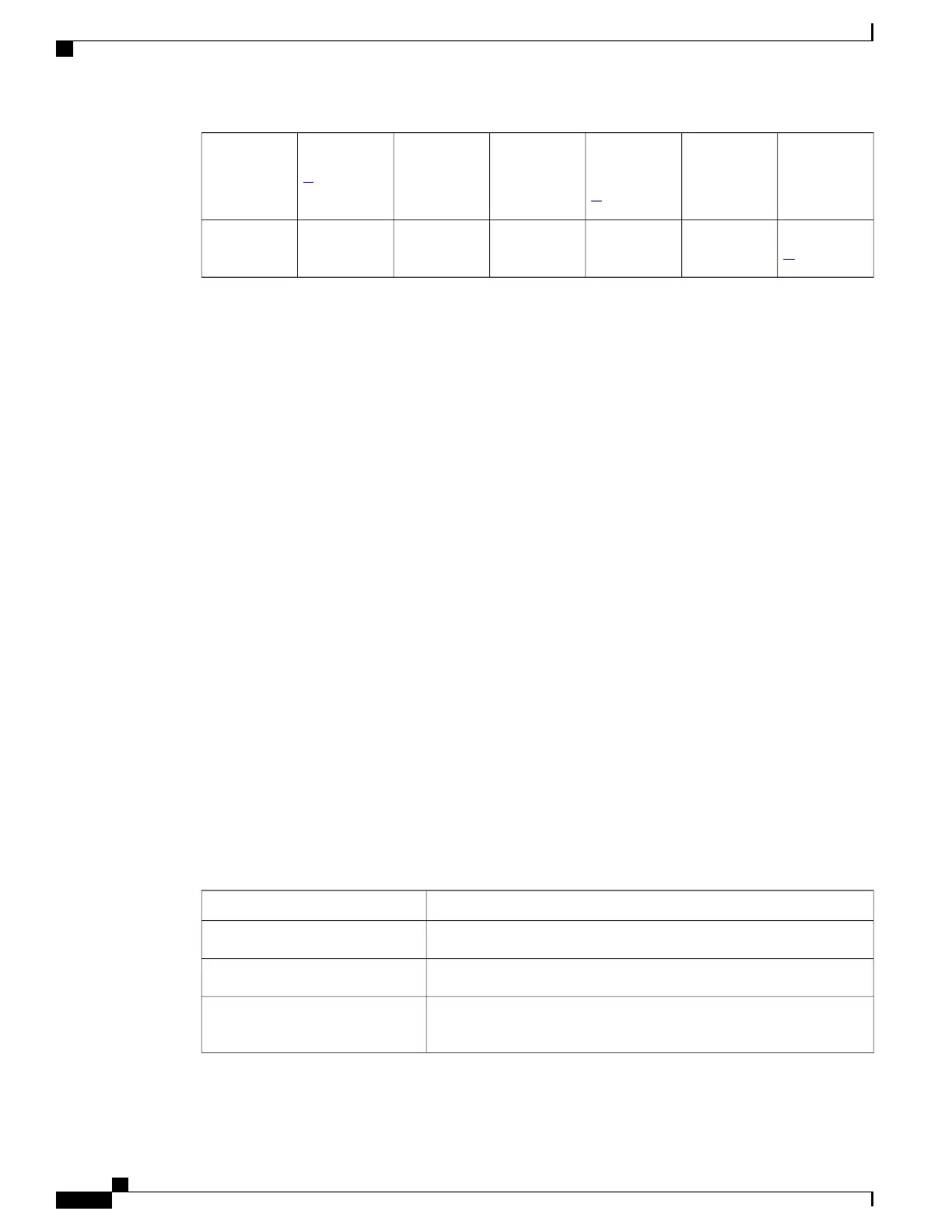
Shuts down
port
Violation
counter
increments
Displays
error
message
19
Sends syslog
message
Sends SNMP
trap
Traffic is
forwarded
18
Violation
Mode
No
20
YesNoYesNoNoshutdown
vlan
18
Packets with unknown source addresses are dropped until you remove a sufficient number of secure MAC addresses.
19
The switch returns an error message if you manually configure an address that would cause a security violation.
20
Shuts down only the VLAN on which the violation occurred.
Port Security Aging
You can use port security aging to set the aging time for all secure addresses on a port. Two types of aging
are supported per port:
• Absolute—The secure addresses on the port are deleted after the specified aging time.
• Inactivity—The secure addresses on the port are deleted only if the secure addresses are inactive for the
specified aging time.
Related Topics
Enabling and Configuring Port Security Aging, on page 1491
Port Security and Switch Stacks
When a switch joins a stack, the new switch will get the configured secure addresses. All dynamic secure
addresses are downloaded by the new stack member from the other stack members.
When a switch (either the active switch or a stack member) leaves the stack, the remaining stack members
are notified, and the secure MAC addresses configured or learned by that switch are deleted from the secure
MAC address table.
Default Port Security Configuration
Table 136: Default Port Security Configuration
Default SettingFeature
Disabled on a port.Port security
Disabled.Sticky address learning
1.Maximum number of secure MAC
addresses per port
Consolidated Platform Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS Release 15.2(4)E (Catalyst 2960-X Switches)
1484
Information About Port Security

 Loading...
Loading...











