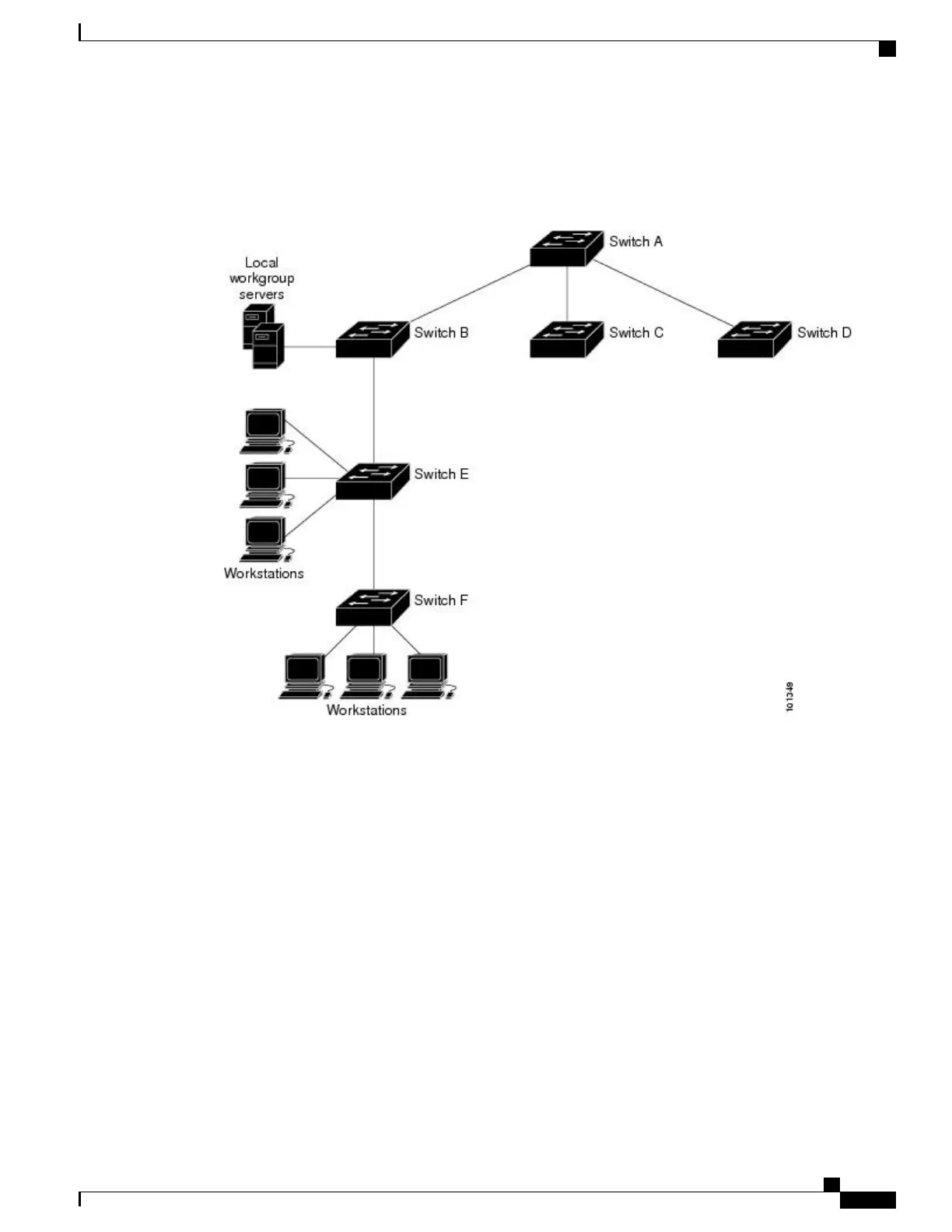
The following figure shows a typical network example using NTP. Switch A is the NTP master, with the
Switch B, C, and D configured in NTP server mode, in server association with Switch A. Switch E is configured
as an NTP peer to the upstream and downstream switches, Switch B and Switch F, respectively.
Figure 107: Typical NTP Network Configuration
If the network is isolated from the Internet, NTP allows a device to act as if it is synchronized through NTP,
when in fact it has learned the time by using other means. Other devices then synchronize to that device
through NTP.
When multiple sources of time are available, NTP is always considered to be more authoritative. NTP time
overrides the time set by any other method.
Several manufacturers include NTP software for their host systems, and a publicly available version for
systems running UNIX and its various derivatives is also available. This software allows host systems to be
time-synchronized as well.
NTP Version 4
NTP version 4 is implemented on the switch. NTPv4 is an extension of NTP version 3. NTPv4 supports both
IPv4 and IPv6 and is backward-compatible with NTPv3.
NTPv4 provides these capabilities:
•
Support for IPv6.
Consolidated Platform Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS Release 15.2(4)E (Catalyst 2960-X Switches)
1527
Information About Administering the Switch
 Loading...
Loading...











