Enhanced Direct Memory Access (eDMA) RM0046
382/936 Doc ID 16912 Rev 5
18 Enhanced Direct Memory Access (eDMA)
18.1 Introduction
This chapter describes the enhanced Direct Memory Access (eDMA) Controller, a second-
generation module capable of performing complex data transfers with minimal intervention
from a host processor.
18.2 Overview
The enhanced direct memory access (eDMA) controller hardware microarchitecture
includes a DMA engine that performs source and destination address calculations, and the
actual data movement operations, along with SRAM-based local memory containing the
transfer control descriptors (TCD) for the channels.
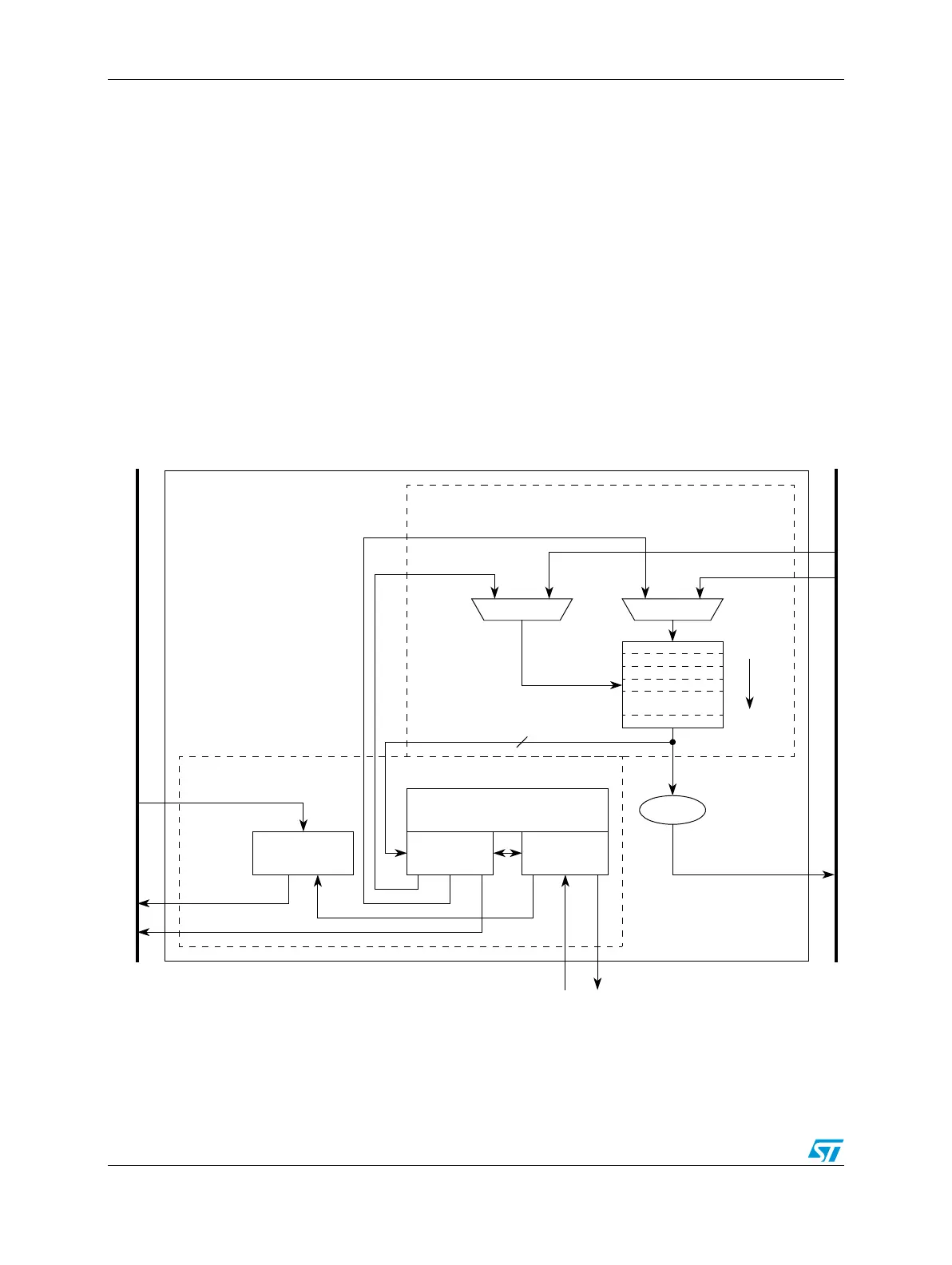
Figure 176 is a block diagram of the eDMA module.
Figure 176. eDMA block diagram
Slave Interface
eDMA
eDMA done
System Bus
Data path
Control
Address
Program model/
Slave write data
Slave write address
Bus write data
Slave read data
Bus address
eDMA Engine
TCD0
TCDn –1*
eDMA peripheral
Bus read data
channel arbitration
request
path
SRAM
Transfer Control Descriptor
(TCD)
SRAM
*n = 16 channels

 Loading...
Loading...