RM0046 Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC)
Doc ID 16912 Rev 5 803/936
32.6 Use cases and limitations
Two main use cases shall be considered:
● Calculation of the CRC of the configuration registers during the process safety time
● Calculation of the CRC on the incoming/outgoing frames for the communication
protocols (not protected with CRC by definition of the protocol itself) used as a safety-
relevant peripheral.
The signature of the configuration registers is computed in a correct way only if these
registers do not contain any status bit. Assuming that the DMA engine has N channels
(greater or equal to the number of contexts) configurable for the following type of data
transfer: mem2mem, periph2mem, mem2periph, the following sequence, as given in
Figure 477, shall be applied to manage the transmission data flow:
● DMA/CRC module configuration (context x, channel x) by CPU
● Payload transfer from the MEM to the CRC module (CRC_INP register) to calculate the
CRC signature (phase1) by DMA (mem2mem data transfer, channel x)
● CRC signature copy from the CRC module (CRC_OUTP register) to the MEM (phase
2) by CPU
● Data block (payload + CRC) transfer from the MEM to the PERIPH module (e.g., SPI
Tx fifo) (phase 3) by DMA (mem2periph data transfer, channel x)
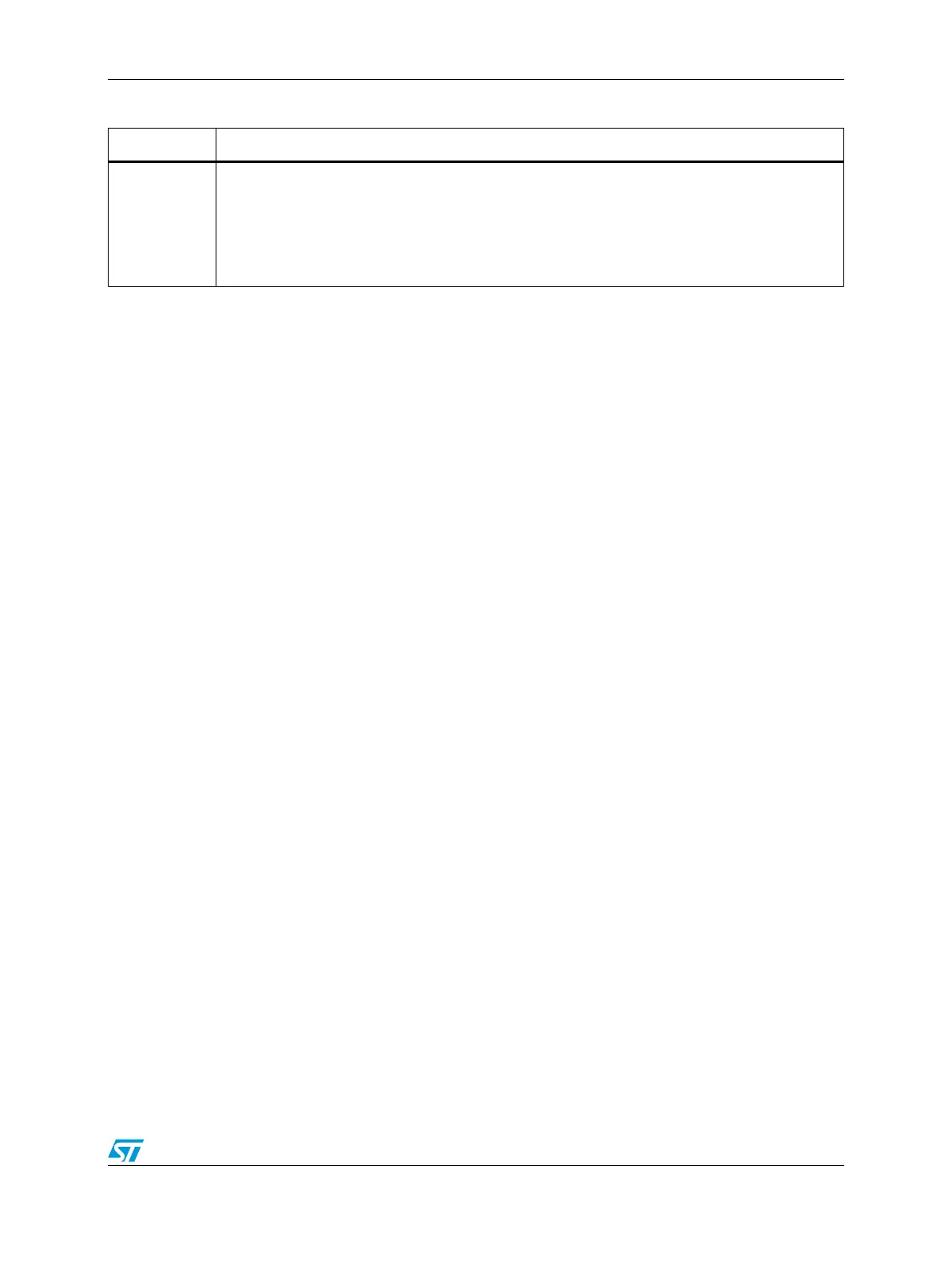
Table 433. CRC_OUTP field descriptions
Field Description
0:31
OUTP: Final CRC signature
The OUTP register includes the final signature corresponding to the CRC_CSTAT register value
eventually swapped and inverted.
In case of CRC-CCITT polynomial only the16 LSB bits are significant. The 16 MSB bits are tied at
0b during the computation.
This register can be read by the software.

 Loading...
Loading...