Reset Generation Module (MC_RGM) RM0046
202/936 Doc ID 16912 Rev 5
8.4 Functional Description
8.4.1 Reset State Machine
The main role of MC_RGM is the generation of the reset sequence which ensures that the
correct parts of the device are reset based on the reset source event. This is summarized in
Table 6 5.
Note: JTAG logic has its own independent reset control and is not controlled by the MC_RGM in
any way.
The reset sequence is comprised of five phases managed by a state machine, which
ensures that all phases are correctly processed through waiting for a minimum duration and
until all processes that need to occur during that phase have been completed before
proceeding to the next phase.
The state machine used to produce the reset sequence is shown in Figure 76.
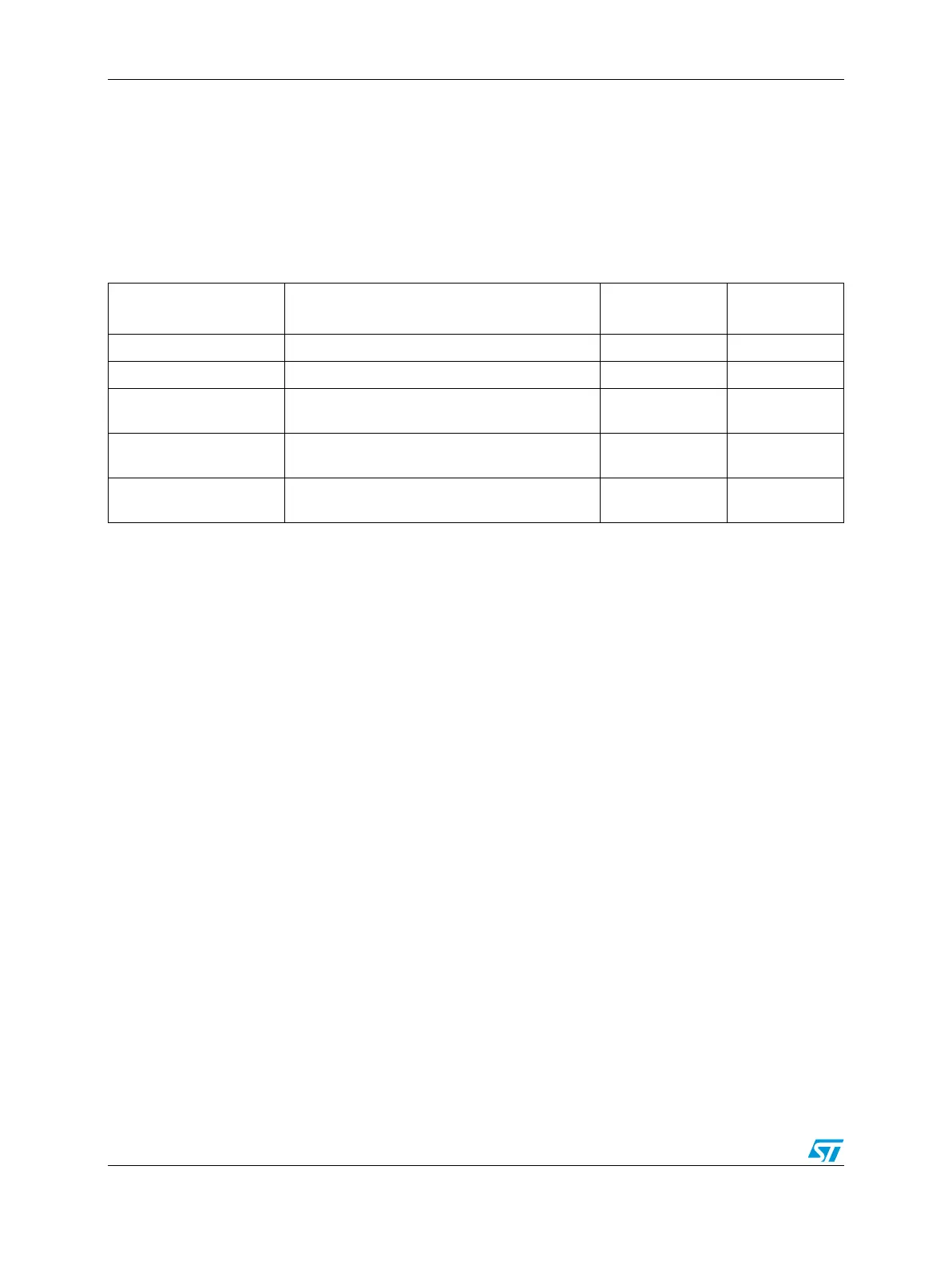
Table 65. MC_RGM Reset Implications
Source What Gets Reset
External Reset
Assertion
(1)
Boot Mode
Capture
power-on reset all yes yes
‘destructive’ resets all except some clock/reset management yes yes
external reset
all except some clock/reset management and
debug
programmable
(2)
yes
‘functional’ resets
all except some clock/reset management and
debug
programmable
(2)
programmable
(3)
shortened ‘functional’
resets
(4)
flip-flops except some clock/reset management programmable
(2)
programmable
(3)
1. ‘external reset assertion’ means that the RESET_B pin is asserted by the MC_RGM until the end of reset PHASE3
2. the assertion of the external reset is controlled via the RGM_FBRE register
3. the boot mode is captured if the external reset is asserted
4. the short sequence is enabled via the RGM_FESS register

 Loading...
Loading...