Interrupt Controller (INTC) RM0046
228/936 Doc ID 16912 Rev 5
9.6.1 Interrupt request sources
The INTC has two types of interrupt requests, peripheral and software configurable. These
interrupt requests can assert on any clock cycle.
Peripheral interrupt requests
An interrupt event in a peripheral’s hardware sets a flag bit that resides in the peripheral.
The interrupt request from the peripheral is driven by that flag bit.
The time from when the peripheral starts to drive its peripheral interrupt request to the INTC
to the time that the INTC starts to drive the interrupt request to the processor is three clocks.
External interrupts are handled by the SIU (see Section 11.6.4, “External interrupts).
Software configurable interrupt requests
An interrupt request is triggered by software by writing a ‘1’ to a SETx bit in
INTC_SSCIR0_3–INTC_SSCIR4_7. This write sets the corresponding flag bit, CLRx,
resulting in the interrupt request. The interrupt request is cleared by writing a ‘1’ to the CLRx
bit.
The time from the write to the SETx bit to the time that the INTC starts to drive the interrupt
request to the processor is four clocks.
Unique vector for each interrupt request source
Each peripheral and software configurable interrupt request is assigned a hardwired unique
9-bit vector. Software configurable interrupts 0–7 are assigned vectors 0–7 respectively.
The peripheral interrupt requests are assigned vectors 8 to as high as needed to include all
the peripheral interrupt requests. The peripheral interrupt request input ports at the
boundary of the INTC block are assigned specific hardwired vectors within the INTC (see
Table 6 7).
9.6.2 Priority management
The asserted interrupt requests are compared to each other based on their PRIx values set
in INTC Priority Select Registers (INTC_PSR0_3–INTC_PSR220_221). The result is
compared to PRI in the associated INTC_CPR. The results of those comparisons manage
the priority of the ISR executed by the associated processor. The associated LIFO also
assists in managing that priority.
Current priority and preemption
The priority arbitrator, selector, encoder, and comparator subblocks shown in Figure 77
compare the priority of the asserted interrupt requests to the current priority. If the priority of
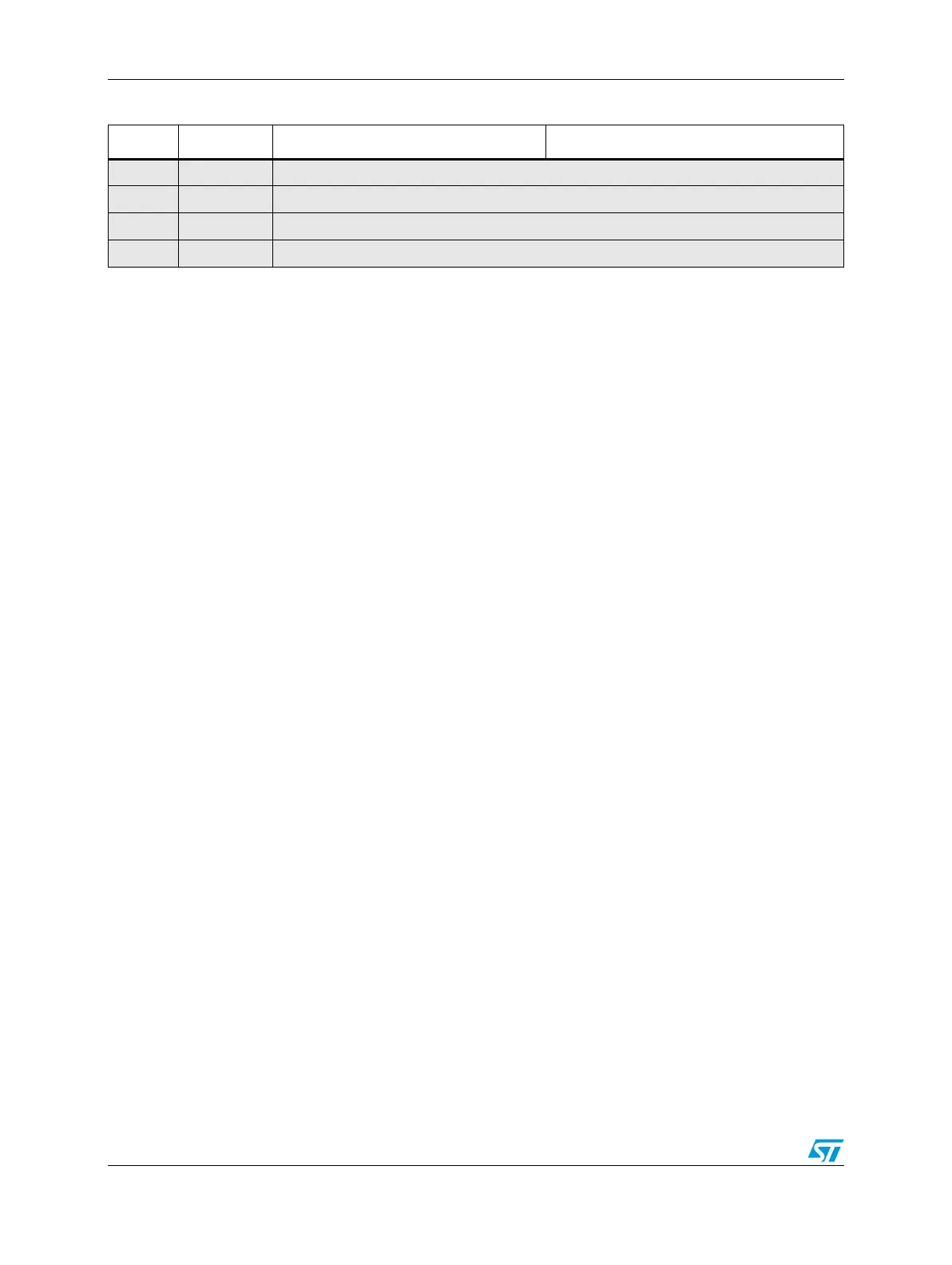
218 0x0B68 Reserved
219 0x0B6C Reserved
220 0x0B70 Reserved
221 0x0B74 Reserved
Table 75. Interrupt vector table (continued)
IRQ # Offset Interrupt Module
 Loading...
Loading...