RM0046 Internal Static RAM (SRAM)
Doc ID 16912 Rev 5 309/936
Internal SRAM write operations are performed on the following byte boundaries:
● 1 byte (0:7 bits)
● 2 bytes (0:15 bits)
● 4 bytes or 1 word (0:31 bits)
If the entire 32 data bits are written to SRAM, no read operation is performed and the ECC is
calculated across the 32-bit data bus. The 8-bit ECC is appended to the data segment and
written to SRAM.
If the write operation is less than the entire 32-bit data width (1 or 2-byte segment), the
following occurs:
1. The ECC mechanism checks the entire 32-bit data bus for errors, detecting and either
correcting or flagging errors.
2. The write data bytes (1 or 2-byte segment) are merged with the corrected 32 bits on the
data bus.
3. The ECC is then calculated on the resulting 32 bits formed in the previous step.
4. The 7-bit ECC result is appended to the 32 bits from the data bus, and the 39-bit value
is then written to SRAM.
16.5.1 Access timing
The system bus is a two-stage pipelined bus that makes the timing of any access dependent
on the access during the previous clock. Table 1 3 6 lists the various combinations of read
and write operations to SRAM and the number of wait states used for the each operation.
The table columns contain the following information:
● Current operation—Lists the type of SRAM operation currently executing
● Previous operation—Lists the valid types of SRAM operations that can precede the
current SRAM operation (valid operation during the preceding clock)
● Wait states—Lists the number of wait states (bus clocks) the operation requires, which
depends on the combination of the current and previous operation
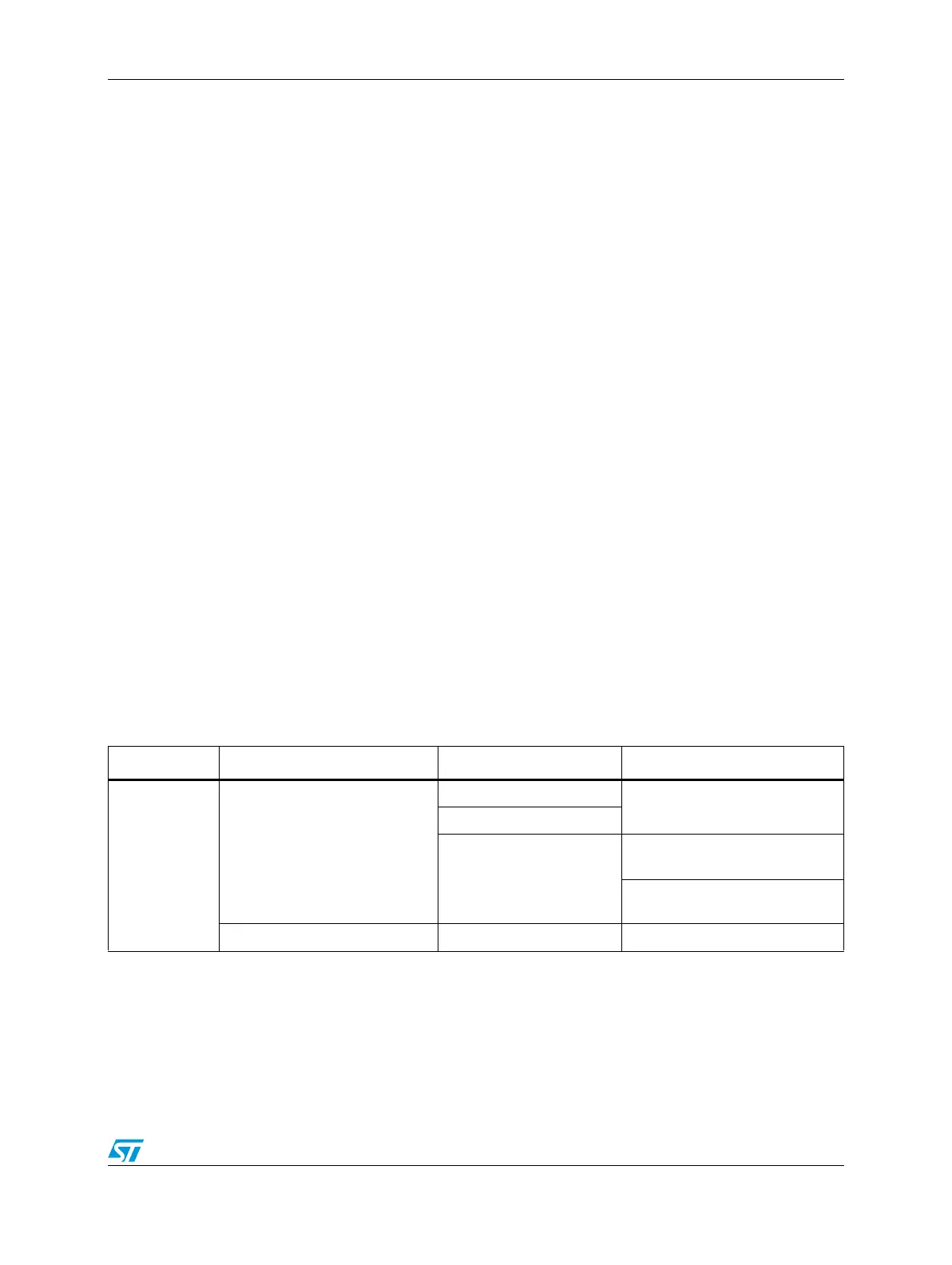
Table 136. Number of wait states required for SRAM operations
Operation type Current operation Previous operation Number of wait states required
Read
Read
Idle
1
Pipelined read
8 , 16 or 32-bit write
0
(read from the same address)
1
(read from a different address)
Pipelined read Read 0

 Loading...
Loading...