Enhanced Direct Memory Access (eDMA) RM0046
408/936 Doc ID 16912 Rev 5
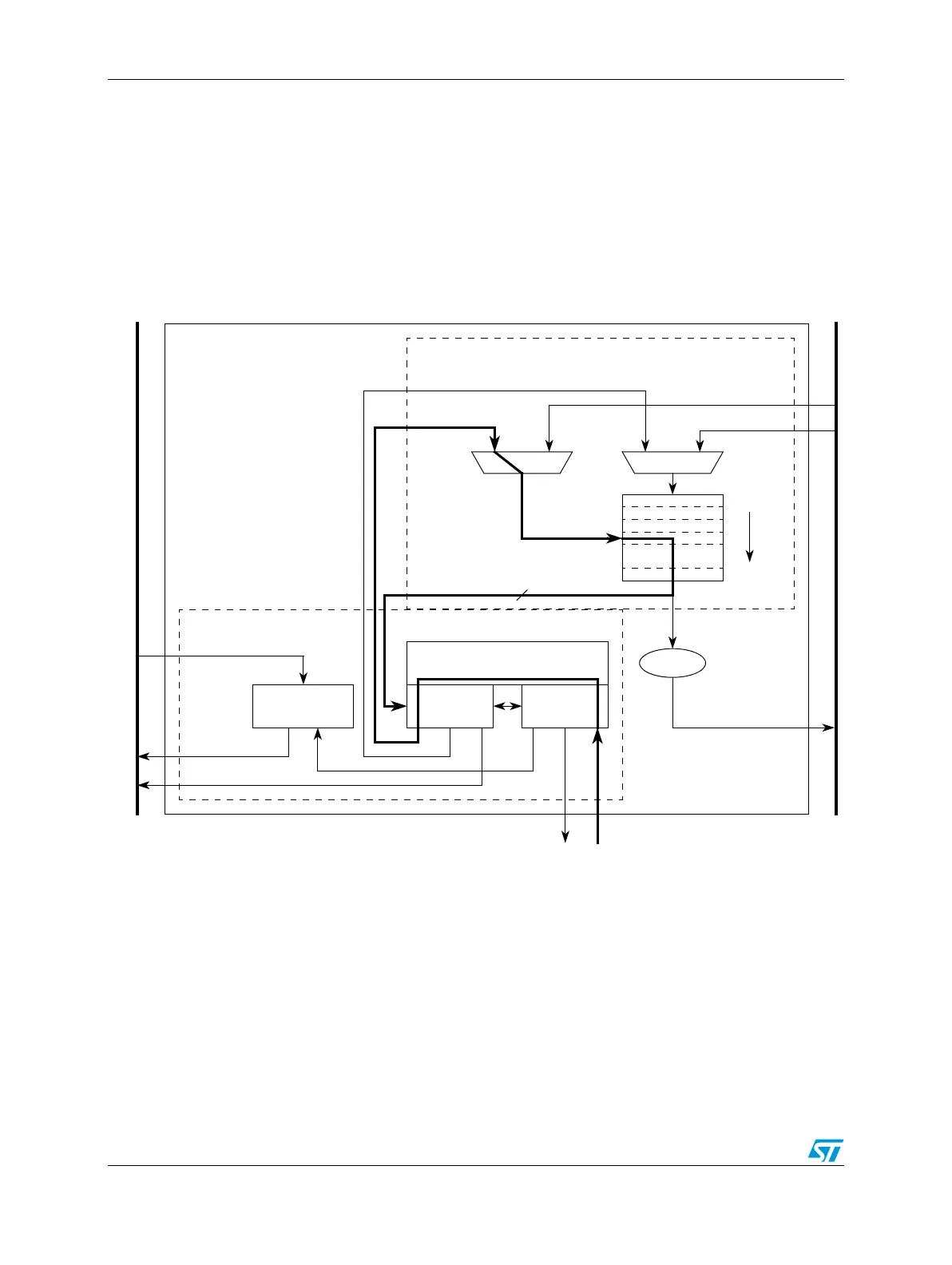
basic flow as an eDMA peripheral request. The eDMA peripheral request input signal is
registered internally and then routed through the eDMA engine, first through the control
module, then into the program model/channel arbitration module. In the next cycle, the
channel arbitration is performed, either using the fixed-priority or round-robin algorithm.
After the arbitration is complete, the activated channel number is sent through the address
path and converted into the required address to access the TCD local memory. Next, the
TCD memory is accessed and the required descriptor read from the local memory and
loaded into the eDMA engine address path channel{x,y} registers. The TCD memory is
organized 64-bits in width to minimize the time needed to fetch the activated channel’s
descriptor and load it into the eDMA engine address path channel{x,y} registers.
Figure 194. eDMA operation, part 1
In the second part of the basic data flow as shown in Figure 195, the modules associated
with the data transfer (address path, data path and control) sequence through the required
source reads and destination writes to perform the actual data movement. The source reads
are initiated and the fetched data is temporarily stored in the data path module until it is
gated onto the system bus during the destination write. This source read/destination write
processing continues until the inner minor byte count has been transferred. The eDMA
Done Handshake signal is asserted at the end of the minor byte count transfer.
Slave Interface
eDMA
eDMA Peripheral Request
System Bus
Data Path
Control
Address
Program Model/
Slave Write Data
Slave Write Address
Bus Write Data
Slave Read Data
Bus Address
eDMA Engine
TCD0
TCDn –1*
eDMA Interrupt Request
Bus Read Data
Channel Arbitration
eDMA Done Handshake
Path
SRAM
Transfer Control Descriptor
(TCD)
SRAM
*n = 16 channels
 Loading...
Loading...